Common approach to diversity in higher education reflects preferences of white Americans
2021-04-12
PRINCETON, N.J.--Increasing diversity remains a key priority at universities, especially in the wake of mass demonstrations in support of racial equality in 2020 following the death of George Floyd. Many universities are guided by the motivation that diversity enhances student learning, a rationale supported by the U.S. Supreme Court.
This approach, however, is a view preferred by white and not Black Americans, and it also aligns with better relative outcomes for white Americans, according to a paper published by Princeton University researchers in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Across eight studies including 1,200 participants, the researchers looked at two different approaches to diversity: an "instrumental rationale," which asserts that including ...
Study reveals cancer immunotherapy patients at most risk of life-threatening side effects
2021-04-12
BOSTON - Many patients with cancer receive immune checkpoint inhibitors that strengthen their immune response against tumor cells. While the medications can be life-saving, they can also cause potentially life-threatening side effects in internal organs. This double-edged sword makes it challenging for clinicians to decide who should be considered candidates for treatment. A new analysis led by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) indicates which patients are at elevated risk of side effects severe enough to require hospitalization. The findings are published in the END ...
Study reveals crucial details on skin-related side effects of cancer immune therapies
2021-04-12
BOSTON - Immune checkpoint inhibitors, which boost the immune system's response against tumor cells, have transformed treatment for many advanced cancers, but short-term clinical trials and small observational studies have linked the medications with various side effects, most commonly involving the skin. A more comprehensive, population-level analysis now provides a thorough look at the extent of these side effects and provides insights on which patients may be more likely to experience them. The research was led by investigators at Massachusetts General ...
Researchers identify surface protein as a new osteosarcoma therapeutic target for antibody-drug conjugates
2021-04-12
Abstract #LB008
HOUSTON -- A preclinical study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center shows an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) targeting surface protein MT1-MMP can act as a guided missile in eradicating osteosarcoma tumor cells without damaging normal tissues. This technology, using precision therapy targeting of cell-surface proteins through a Bicycle toxin conjugate (BTC), shows encouraging results for the treatment of osteosarcoma.
Findings from the study were presented today by Yifei Wang, M.D., a postdoctoral fellow of Pediatrics Research, at the virtual ...
Differences in B cell responses to coronaviruses and other pathogens in children and adults
2021-04-12
Blood taken from a small group of children before the COVID-19 pandemic contains memory B cells that bind SARS-CoV-2 and weakly cross-react with other coronaviruses, a new study finds, while adult blood and tissue showed few such cells. "Further study of the role of cross-reactive memory B cell populations... will be important for ongoing improvement of vaccines to SARS-CoV-2, its viral variants, and other pathogens," the authors say. As the COVID-19 pandemic has continued, children have often exhibited faster viral clearance and lower viral antigen loads than adults; whether B cell repertoires against SARS-CoV-2 (and other pathogens) differ between children and ...
Bottom-up is the way forward for nitrogen reduction at institutions
2021-04-12
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Nitrogen is an element basic for life -- plants need it, animals need it, it's in our DNA -- but when there's too much nitrogen in the environment, things can go haywire. On Cape Cod, excess nitrogen in estuaries and salt marshes can lead to algal blooms, fish kills, and degradation of the environment.
In a study published in Environmental Research Letters, scientists at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) Ecosystems Center examine ways to reduce the nitrogen footprint of smaller institutions, like the MBL, by focusing on a bottom-up approach.
"This bottom-up approach is all about balancing the needs of various stakeholders to come up with the best, ...
Road salts and other human sources are threatening world's freshwater supplies
2021-04-12
When winter storms threaten to make travel dangerous, people often turn to salt, spreading it liberally over highways, streets and sidewalks to melt snow and ice. Road salt is an important tool for safety, because many thousands of people die or are injured every year due to weather related accidents. But a new study led by Sujay Kaushal of the University of Maryland warns that introducing salt into the environment--whether it's for de-icing roads, fertilizing farmland or other purposes--releases toxic chemical cocktails that create a serious and growing global threat to our freshwater supply and human health.
Previous studies by Kaushal and his team showed that added salts in the environment can interact with soils and infrastructure to release a cocktail of metals, ...
Researchers engineer probiotic yeast to produce beta-carotene
2021-04-12
Researchers have genetically engineered a probiotic yeast to produce beta-carotene in the guts of laboratory mice. The advance demonstrates the utility of work the researchers have done to detail how a suite of genetic engineering tools can be used to modify the yeast.
"There are clear advantages to being able to engineer probiotics so that they produce the desired molecules right where they are needed," says Nathan Crook, corresponding author of the study and an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at North Carolina State University. "You're not just delivering drugs or nutrients; you are effectively manufacturing the drugs or nutrients on site."
The study focused ...
Spanking may affect the brain development of a child
2021-04-12
Spanking may affect a child's brain development in similar ways to more severe forms of violence, according to a new study led by Harvard researchers.
The research, published recently in the journal Child Development, builds on existing studies that show heightened activity in certain regions of the brains of children who experience abuse in response to threat cues.
The group found that children who had been spanked had a greater neural response in multiple regions of the prefrontal cortex (PFC), including in regions that are part of the salience network. These areas of the brain respond to cues in the environment that tend ...
UConn researchers find bubbles speed up energy transfer
2021-04-12
Energy flows through a system of atoms or molecules by a series of processes such as transfers, emissions, or decay. You can visualize some of these details like passing a ball (the energy) to someone else (another particle), except the pass happens quicker than the blink of an eye, so fast that the details about the exchange are not well understood. Imagine the same exchange happening in a busy room, with others bumping into you and generally complicating and slowing the pass. Then, imagine how much faster the exchange would be if everyone stepped back and created a safe bubble for the pass to happen unhindered.
An international collaboration of scientists, including UConn Professor of Physics Nora Berrah and post-doctoral researcher ...
Antidepressant use in pregnancy tied to affective disorders in offspring; no causal link
2021-04-12
New York, NY - Major depressive disorder is highly prevalent, with one in five people experiencing an episode at some point in their life, and is almost twice as common in women than in men. Antidepressants are usually given as a first-line treatment, including during pregnancy, either to prevent the recurrence of depression, or as acute treatment in newly depressed patients. Antidepressant use during pregnancy is widespread and since antidepressants cross the placenta and the blood-brain barrier, concern exists about potential long-term effects of intrauterine antidepressant exposure in the unborn child.
Using the Danish National Registers to follow more than 42,000 singleton babies born ...
Binge-eating is not caused by stress-induced impulsivity
2021-04-12
Stress alters brain activity in self-inhibition areas yet doesn't trigger binge-eating, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
People who binge-eat, a hallmark symptom of several eating disorders, can feel out of control and unable to stop, and often binge after stressful events. This led scientists to theorize stress impairs the brain regions responsible for inhibitory control -- the ability to stop what you are about to do or currently doing -- and triggers binge-eating.
Westwater et al. tested this theory by using fMRI to measure the brain activity of women with anorexia, bulimia, or without ...
Stress does not lead to loss of self-control in eating disorders
2021-04-12
A unique residential study has concluded that, contrary to perceived wisdom, people with eating disorders do not lose self-control - leading to binge-eating - in response to stress. The findings of the Cambridge-led research are published today in the Journal of Neuroscience.
People who experience bulimia nervosa and a subset of those affected by anorexia nervosa share certain key symptoms, namely recurrent binge-eating and compensatory behaviours, such as vomiting. The two disorders are largely differentiated by body mass index (BMI): adults affected by anorexia nervosa tend to have BMI of less than 18.5 kg/m2. More than 1.6 million people in ...
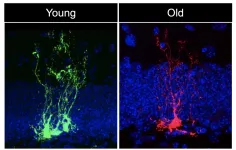
USC Stem Cell study reveals neural stem cells age rapidly
2021-04-12
In a new study published in Cell Stem Cell, a team led by USC Stem Cell scientist Michael Bonaguidi, PhD, demonstrates that neural stem cells - the stem cells of the nervous system - age rapidly.
"There is chronological aging, and there is biological aging, and they are not the same thing," said Bonaguidi, an Assistant Professor of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, Gerontology and Biomedical Engineering at the Keck School of Medicine of USC. "We're interested in the biological aging of neural stem cells, which are particularly vulnerable to the ravages of time. This has implications for the normal cognitive decline that ...
Following atoms in real time could lead to better materials design
2021-04-12
Researchers have used a technique similar to MRI to follow the movement of individual atoms in real time as they cluster together to form two-dimensional materials, which are a single atomic layer thick.
The results, reported in the journal Physical Review Letters, could be used to design new types of materials and quantum technology devices. The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, captured the movement of the atoms at speeds that are eight orders of magnitude too fast for conventional microscopes.
Two-dimensional materials, such as graphene, ...
People want to improve mental health by exercising, but stress and anxiety get in the way
2021-04-12
New research from McMaster University suggests the pandemic has created a paradox where mental health has become both a motivator for and a barrier to physical activity.
People want to be active to improve their mental health but find it difficult to exercise due to stress and anxiety, say the researchers who surveyed more than 1,600 subjects in an effort to understand how and why mental health, physical activity and sedentary behavior have changed throughout the course of the pandemic.
The results are outlined in the journal PLOS ONE.
"Maintaining a regular exercise program is difficult at the best of times and the conditions surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic ...
More than the sum of mutations
2021-04-12
A new algorithm can predict which genes cause cancer, even if their DNA sequence is not changed. A team of researchers in Berlin combined a wide variety of data, analyzed it with "Artificial Intelligence" and identified numerous cancer genes. This opens up new perspectives for targeted cancer therapy in personalized medicine and for the development of biomarkers.
In cancer, cells get out of control. They proliferate and push their way into tissues, destroying organs and thereby impairing essential vital functions. This unrestricted growth is usually induced by an accumulation of DNA changes in cancer ...
Living foams
2021-04-12
In the earliest stage of life, animals undergo some of their most spectacular physical transformations. Once merely blobs of dividing cells, they begin to rearrange themselves into their more characteristic forms, be they fish, birds or humans. Understanding how cells act together to build tissues has been a fundamental problem in physics and biology.
Now, UC Santa Barbara professor Otger Campàs, who also holds the Mellichamp Chair in Systems Biology and Bioengineering, and Sangwoo Kim, a postdoctoral fellow in professor Campàs lab, have approached this question, with surprising findings.
"When you have many cells physically interacting with each other, how does the system behave collectively? What is the physical state of the ensemble?" said ...
Research brief: How pharmacists contribute meaningfully in primary health care
2021-04-12
Evidence is growing that health care delivered by teams is superior to services delivered by a single practitioner. Published in the Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine -- University of Minnesota, University of North Carolina, American Board of Family Medicine and the American Academy of Family Physicians researchers compared key elements from the practice of a pharmacist providing comprehensive medication management to the foundational components defined for primary care.
Based on a common health care team framework -- the Four C's of Primary Care (first contact, continuity, comprehensiveness, and coordination) -- this team ...
COVID-19 pandemic may have increased mental health issues within families
2021-04-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- When the COVID-19 pandemic hit in early 2020, many families found themselves suddenly isolated together at home. A year later, new research has linked this period with a variety of large, detrimental effects on individuals' and families' well-being and functioning.
The study -- led by Penn State researchers -- found that in the first months of the pandemic, parents reported that their children were experiencing much higher levels of "internalizing" problems like depression and anxiety, and "externalizing" problems such as disruptive and aggressive behavior, than ...
Bioactive implant coatings resistant to most bacterial strains are obtained in Russia
2021-04-12
Young scientists from NUST MISIS have presented multilayer antibacterial coatings with a prolonged effect and a universal spectrum of action. The coating is based on modified titanium oxide and several antiseptic components. The coatings can be used in modern implantology as a protective layer for the prevention of concomitant complications - inflammation or implant rejection. The results of the work have been published in the international scientific journal Applied Surface Science.
Antibacterial coatings are currently being actively researched, as the search for alternatives to traditional antibiotics is growing. They can be applied to implants, thereby preventing inflammation caused by nosocomial infections.
Nevertheless, the creation of antibacterial, but at the same time biocompatible ...
SARS-CoV-2 vaccination rates among US emergency department health care personnel
2021-04-12
DES PLAINES, IL - At the beginning of prioritized health care personnel (HPC) immunization, there was a high rate of COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and receipt, with physicians and advance practice providers having the highest overall proportion. These are the findings of a surveillance project on COVID-19 vaccination rates among emergency department staff at United States academic medical centers, which will be published in the April issue of the Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM) journal, a peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
The project report, published in a ...
THC and CBD content on labels of medicinal cannabis products may not be accurate
2021-04-12
BOSTON - Medical cannabis products are not always what they seem, according to a new study led by researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH).
In fact, the contents of these products can vary considerably from distributors' claims, according to the study, published in JAMA Network Open. This is particularly important when THC, the metabolite responsible for the "high" cannabis provides, is present in medical cannabis products labeled to be CBD only.
As more states legalize cannabis sales, demand has increased. However, there is little consistency in product regulation or labeling, unlike the strict regulation of medicines purchased through a pharmacy. As a result, labeling is often not accurately informing patients of the content of the ...
Study finds Americans eat food of mostly poor nutritional quality - except at school
2021-04-12
Whether eating out or buying food from the grocery store, Americans of all ages are, for the most part, eating poorly everywhere--except at school. The information comes from a new dietary trends study, which also reveals persistent or worsening disparities in meal quality from restaurants, grocery stores, and other sources--but not school--by race, ethnicity, and income.
Published today in JAMA Network Open and led by researchers at the Gerald J. and Dorothy R. Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University, the study analyzed all meals (including snacks and beverages) consumed by Americans over 16 years.
By 2018, ...
Linking HIV screening with COVID-19 testing at an urban emergency department
2021-04-12
What The Study Did: The results of incorporating HIV screening into COVID-19 testing at an emergency department in Chicago are reported in this study.
Authors: David Pitrak, M.D., of the University of Chicago Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.0839)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link ...
[1] ... [2427]
[2428]
[2429]
[2430]
[2431]
[2432]
[2433]
[2434]
2435
[2436]
[2437]
[2438]
[2439]
[2440]
[2441]
[2442]
[2443]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.