No batteries? No sweat! Wearable biofuel cells now produce electricity from lactate
2021-04-13
It cannot be denied that, over the past few decades, the miniaturization of electronic devices has taken huge strides. Today, after pocket-size smartphones that could put old desktop computers to shame and a plethora of options for wireless connectivity, there is a particular type of device whose development has been steadily advancing: wearable biosensors. These tiny devices are generally meant to be worn directly on the skin in order to measure specific biosignals and, by sending measurements wirelessly to smartphones or computers, keep track of the user's health.
Although materials scientists have developed many types ...
Researchers streamline molecular assembly line to design, test drug compounds
2021-04-13
Researchers from North Carolina State University have found a way to fine-tune the molecular assembly line that creates antibiotics via engineered biosynthesis. The work could allow scientists to improve existing antibiotics as well as design new drug candidates quickly and efficiently.
Bacteria - such as E. coli - harness biosynthesis to create molecules that are difficult to make artificially.
"We already use bacteria to make a number of drugs for us," says Edward Kalkreuter, former graduate student at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the ...
Psychedelic experience may not be required for psilocybin's antidepressant-like benefits
2021-04-13
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers have shown that psilocybin--the active chemical in "magic mushrooms"-- still works its antidepressant-like actions, at least in mice, even when the psychedelic experience is blocked. The new findings suggest that psychedelic drugs work in multiple ways in the brain and it may be possible to deliver the fast-acting antidepressant therapeutic benefit without requiring daylong guided therapy sessions. A version of the drug without, or with less of, the psychedelic effects could loosen restrictions on who could receive the therapy, and lower costs, making the benefits of psilocybin more available to more people in need.
In all clinical ...
Novel theory addresses centuries-old physics problem
2021-04-13
The "three-body problem," the term coined for predicting the motion of three gravitating bodies in space, is essential for understanding a variety of astrophysical processes as well as a large class of mechanical problems, and has occupied some of the world's best physicists, astronomers and mathematicians for over three centuries. Their attempts have led to the discovery of several important fields of science; yet its solution remained a mystery.
At the end of the 17th century, Sir Isaac Newton succeeded in explaining the motion of the planets around the sun through ...
JNCCN Study: Important potential role for routine brain imaging in advanced kidney cancer
2021-04-13
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [April 13, 2021] -- The April 2021 issue of JNCCN--Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network publishes new research from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) and Gustave Roussy Institute, which suggests that baseline brain imaging should be considered in most patients with metastatic kidney cancer. The researchers studied 1,689 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) who had been considered for clinical trial participation at either of the two institutions between 2001 and 2019 and had undergone brain imaging in this context, without clinical suspicion for brain involvement. The researchers discovered 4% had asymptomatic brain metastases in this setting. This group was found to have a low median 1-year ...
More exposure to political TV ads heightens anxiety
2021-04-13
ITHACA, N.Y. - We've all seen them: political ads on television that promise doom gloom if Candidate X is elected, and how all your problems will be solved if you choose Candidate Y. And Candidate Y, of course, approves this message.
Beyond attempting to move a large swath of the population to vote one way or another, the seemingly constant bombardment of negativity in the name of our democratic process is anxiety-inducing, researchers have found.
"Many of my friends and family members wind up quite stressed out, for lack of a better word, during each election season," said Jeff Niederdeppe, professor in the Department of Communication in the College of ...
Webcam designed like a human eye: researchers question ubiquitous technology
2021-04-13
With 'Eyecam' they now present the prototype of a webcam that not only looks like a human eye, but imitates its movements realistically. "The goal of our project is not to develop a 'better' design for cameras, but to spark a discussion. We want to draw attention to the fact that we are surrounded by sensing devices every day. That raises the question of how that affects us," says Marc Teyssier. In 2020, the French scientist completed his doctorate on the topic of anthropomorphic design in Paris. Now he is a postdoctoral researcher in the Human-Computer Interaction Lab at Saarland University in Germany.
The research team at Saarland Informatics Campus has developed ...
Closer to human -- Mouse model more accurately reproduces fatty liver disease
2021-04-13
Human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a little-understood condition that significantly increases the risk of inflammation, fibrosis and liver cancer and ultimately requires liver transplant.
"NAFLD has been difficult to study mainly because we had no good animal model," said corresponding author Dr. Karl-Dimiter Bissig, who was at Baylor during the development of this project and is now at Duke University.
The disease has both genetic and nutritional components, which have been hard to understand in human studies, and murine models ...
Study cements age and location of hotly debated skull from early human Homo erectus
2021-04-13
A new study verifies the age and origin of one of the oldest specimens of Homo erectus--a very successful early human who roamed the world for nearly 2 million years. In doing so, the researchers also found two new specimens at the site--likely the earliest pieces of the Homo erectus skeleton yet discovered. Details are published today in the journal Nature Communications.
"Homo erectus is the first hominin that we know about that has a body plan more like our own and seemed to be on its way to being more human-like," said Ashley Hammond, an assistant curator in the American Museum of Natural History's Division of Anthropology and the lead author of the new study. "It had longer lower limbs than upper limbs, a torso ...
Elusive particle may point to undiscovered physics
2021-04-13
ITHACA, N.Y. - The muon is a tiny particle, but it has the giant potential to upend our understanding of the subatomic world and reveal an undiscovered type of fundamental physics.
That possibility is looking more and more likely, according to the initial results of an international collaboration - hosted by the U.S. Department of Energy's Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory - that involved key contributions by a Cornell team led by Lawrence Gibbons, professor of physics in the College of Arts and Sciences.
The collaboration, which brought together 200 scientists from 35 institutions in seven countries, set out to confirm the findings of a 1998 experiment that startled physicists by indicating that muons' magnetic ...
Why are there relatively few aftershocks for certain cascadia earthquakes?
2021-04-13
In the Cascadia subduction zone, medium and large-sized "intraslab" earthquakes, which take place at greater than crustal depths within the subducting plate, will likely produce only a few detectable aftershocks, according to a new study.
The findings could have implications for forecasting aftershock seismic hazard in the Pacific Northwest, say Joan Gomberg of the U.S. Geological Survey and Paul Bodin of the University of Washington in Seattle, in their paper published in the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America.
Researchers now calculate aftershock forecasts in the region based in part on data from subduction zones around the world. ...
Amoeba biology reveals potential treatment target for lung disease
2021-04-13
In a series of experiments that began with amoebas -- single-celled organisms that extend podlike appendages to move around -- Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say they have identified a genetic pathway that could be activated to help sweep out mucus from the lungs of people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease a widespread lung ailment.
"Physician-scientists and fundamental biologists worked together to understand a problem at the root of a major human illness, and the problem, as often happens, relates to the core biology of cells," says Doug Robinson, Ph.D., professor of cell ...
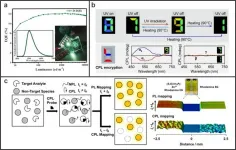
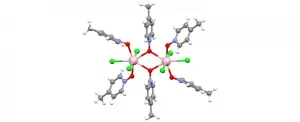
Circularly polarized luminescence from organic micro-/nano-structures
2021-04-13
Circularly polarized light exhibits promising applications in future displays and photonic technologies. Traditionally, circularly polarized light is converted from unpolarized light by the linear polarizer and the quarter-wave plate. During this indirectly physical process, at least 50% of energy will be lost. Circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) from chiral luminophores provides an ideal approach to directly generate circularly polarized light, in which the energy loss induced by polarized filter can be reduced. Among various chiral luminophores, organic micro-/nano-structures have attracted increasing attention owing to the high quantum efficiency ...
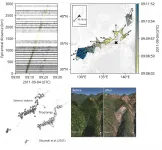
Tremors triggered by typhoon talas tell tales of tumbling terrain
2021-04-13
Tsukuba, Japan - Tropical cyclones like typhoons may invoke imagery of violent winds and storm surges flooding coastal areas, but with the heavy rainfall these storms may bring, another major hazard they can cause is landslides--sometimes a whole series of landslides across an affected area over a short time. Detecting these landslides is often difficult during the hazardous weather conditions that trigger them. New methods to rapidly detect and respond to these events can help mitigate their harm, as well as better understand the physical processes themselves.
In a new study published in Geophysical Journal International, a research team led ...
Modeling past and future glacial floods in northern Greenland
2021-04-13
Hokkaido University researchers have clarified different causes of past glacial river floods in the far north of Greenland, and what it means for the region's residents as the climate changes.
The river flowing from the Qaanaaq Glacier in northwest Greenland flooded in 2015 and 2016, washing out the only road connecting the small village of Qaanaaq and its 600 residents to the local airport. What caused the floods was unclear at the time. Now, by combining physical field measurements and meteorological data into a numerical model, researchers at Japan's Hokkaido ...
"Shedding light" on the role of undesired impurities in gallium nitride semiconductors
2021-04-13
The semiconductor industry and pretty much all of electronics today are dominated by silicon. In transistors, computer chips, and solar cells, silicon has been a standard component for decades. But all this may change soon, with gallium nitride (GaN) emerging as a powerful, even superior, alternative. While not very heard of, GaN semiconductors have been in the electronics market since 1990s and are often employed in power electronic devices due to their relatively larger bandgap than silicon--an aspect that makes it a better candidate for high-voltage and high-temperature applications. Moreover, current travels quicker through GaN, which ensures fewer switching losses during switching applications.
Not everything about GaN is perfect, however. While impurities are usually desirable ...
NTU Singapore study investigates link between COVID-19 and risk of blood clot formation
2021-04-13
People who have recovered from COVID-19, especially those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, may be at risk of developing blood clots due to a lingering and overactive immune response, according to a study led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU) scientists.
The team of researchers, led by NTU Assistant Professor Christine Cheung, investigated the possible link between COVID-19 and an increased risk of blood clot formation, shedding new light on "long-haul COVID" - the name given to the medium- and long-term health consequences of COVID-19.
The findings may help to explain why some people who have recovered from COVID-19 exhibit symptoms of blood clotting complications after their initial recovery. In some cases, they are at increased risk of heart attack, ...
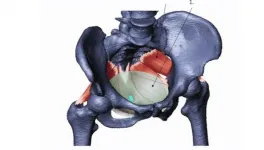
Childbirth versus pelvic floor stability
2021-04-13
Evolutionary anthropologists from the University of Vienna and colleagues now present evidence for a different explanation, published in PNAS. A larger bony pelvic canal is disadvantageous for the pelvic floor's ability to support the fetus and the inner organs and predisposes to incontinence.
The human pelvis is simultaneously subject to obstetric selection, favoring a more spacious birth canal, and an opposing selective force that favors a smaller pelvic canal. Previous work of scientists from the University of Vienna has already led to a relatively good understanding of this evolutionary "trade-off" and how it results in the high rates of obstructed labor in modern humans. ...
Snow chaos in Europe caused by melting sea-ice in the Arctic
2021-04-13
They are diligently stoking thousands of bonfires on the ground close to their crops, but the French winemakers are fighting a losing battle. An above-average warm spell at the end of March has been followed by days of extreme frost, destroying the vines with losses amounting to 90 percent above average. The image of the struggle may well be the most depressingly beautiful illustration of the complexities and unpredictability of global climate warming. It is also an agricultural disaster from Bordeaux to Champagne.
It is the loss of the Arctic sea-ice due to climate warming that has, somewhat paradoxically, been implicated with severe cold and snowy mid-latitude winters.
"Climate change doesn't always manifest in the most ...
Simple genetic modification aims to stop mosquitoes spreading malaria
2021-04-13
Altering a mosquito's gut genes to make them spread antimalarial genes to the next generation of their species shows promise as an approach to curb malaria, suggests a preliminary study published today in eLife.
The study is the latest in a series of steps toward using CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology to make changes in mosquito genes that could reduce their ability to spread malaria. If further studies support this approach, it could provide a new way to reduce illnesses and deaths caused by malaria.
Growing mosquito resistance to pesticides, as well as malaria parasite resistance ...
Consumers are willing to pay for ecosystem services
2021-04-13
Many consumers are willing to pay for improved environmental quality and thus non-market values of impacts of food production on e.g. water quality, C sequestration, biodiversity, pollution, erosion or GHG emissions may even be comparable to the market value of agricultural production. Diverfarming project elucidated how consumers value agroecosystem services enabled by diversification and provided consumer perspectives for developing future agricultural and food policies to better support cropping diversification.
The researchers quantified consumers' willingness to pay for the benefits of increased farm and regional scale diversity of cultivation practices and crop rotations. Three valuation scenarios were presented to a ...
Almond production remains stable in the long term, despite deficit irrigation
2021-04-13
Spain boasts the largest cultivated area of almond trees in the world, with more than 700,000 ha (MAPA, 2018), but ranks third in terms of production. How can this be? Actually it's easy to explain: most of the country's cultivated area of almond trees is comprised of traditional rainfed orchards and located in marginal areas featuring a low density of trees per hectare.
Over the last decade, however, the nut's surging prices havegiven rise to intensive almond tree plantations characterised bya high density of trees per hectare and the employment offertilisation and irrigation, yielding endless rows of white when the trees are in bloom. Knowing what the future of these plantations will be like in a ...
Practicing 'mindfulness' in summer camp benefits campers and counselors alike
2021-04-13
With summer around the corner, a project shows how implementing an evidence-based mindfulness program in a summer camp setting decreases emotional distress in school age children and empowers campers and counselors alike - enhancing camper-counselor relationships. Mindfulness - a state of consciousness that fosters awareness - has the potential to help regulate emotions and behaviors.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University's Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing implemented an eight-week program guided by the Mindful Schools© curricula in a large urban summer day camp program (ages 3 to seventh grade). Mindfulness-based practices are intentional exercises ...
A molecule that responds to light
2021-04-13
Light can be used to operate quantum information processing systems, e.g. quantum computers, quickly and efficiently. Researchers at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and Chimie ParisTech/CNRS have now significantly advanced the development of molecule-based materials suitable for use as light-addressable fundamental quantum units. As they report in the journal Nature Communications, they have demonstrated for the first time the possibility of addressing nuclear spin levels of a molecular complex of europium(III) rare-earth ions with light. (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22383-x)
Whether in drug development, communication, or for climate forecasts: Processing information quickly and efficiently is crucial in many areas. It is currently done using digital computers, ...
Smell you later: Exposure to smells in early infancy can modulate adult behavior
2021-04-13
Imprinting is a popularly known phenomenon, wherein certain animals and birds become fixated on sights and smells they see immediately after being born. In ducklings, this can be the first moving object, usually the mother duck. In migrating fish like salmon and trout, it is the smells they knew as neonates that guides them back to their home river as adults. How does this happen?
Exposure to environmental input during a critical period early in life is important for forming sensory maps and neural circuits in the brain. In mammals, early exposure to environmental inputs, as in the case of imprinting, is known to affect perception and social behavior later in life. Visual imprinting has ...
[1] ... [2424]
[2425]
[2426]
[2427]
[2428]
[2429]
[2430]
[2431]
2432
[2433]
[2434]
[2435]
[2436]
[2437]
[2438]
[2439]
[2440]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.