Oregon scientists create mechanism to precisely control soundwaves in metamaterials
2021-04-16
EUGENE, Ore. -- April 16, 2021 -- University of Oregon physicists have developed a new method to manipulate sound -- stop it, reverse it, store it and even use it later -- in synthetic composite structures known as metamaterials.
The discovery was made using theoretical and computational analysis of the mechanical vibrations of thin elastic plates, which serve as the building blocks for the proposed design. The physicists, Pragalv Karki and Jayson Paulose, also developed a simpler minimal model consisting of springs and masses demonstrating the same signal manipulation ability.
"There have been a lot of mechanisms that can guide or block the transmission of sound waves through a metamaterial, but our design is the first to dynamically stop and reverse a sound pulse," said Karki, ...
Coronavirus does not infect the brain but still inflicts damage
2021-04-16
NEW YORK, NY (April 16, 2021)--SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, likely does not directly infect the brain but can still inflict significant neurological damage, according to a new study from neuropathologists, neurologists, and neuroradiologists at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
"There's been considerable debate about whether this virus infects the brain, but we were unable to find any signs of virus inside brain cells of more than 40 COVID-19 patients," says James E. Goldman, MD, PhD, professor of pathology & cell biology (in psychiatry), who led the ...
CNIO researchers explain the toxicity of USP7 inhibitors, under development for cancer treatment
2021-04-16
Understanding the components that control cell division is fundamental to understanding how life works and how alterations in this delicate process can cause diseases such as cancer. It was precisely the discoveries of "key regulators of the cell cycle" and their implications for processes such as cancer, that won the British scientists R. Timothy Hunt and Paul M. Nurse and the American scientist Leland H. Hartwell the 2001 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. A study led by Óscar Fernández-Capetillo, Head of the Genomic Instability Group at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) and published this week in The EMBO Journal uncovers a new cell cycle control element, the USP7 protein. It acts as a brake to prevent cells ...
Study sheds light on stellar origin of 60Fe
2021-04-16
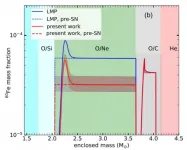
Researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and their collaborators have recently made great progress in the study of the stellar beta-decay rate of 59Fe, which constitutes an important step towards understanding 60Fe nucleosynthesis in massive stars. The results were published in Physical Review Letters on April 12.
Radioactive nuclide 60Fe plays an essential role in nuclear astrophysical studies. It is synthesized in massive stars by successive neutron captures on a stable nucleus of 58Fe and, during the late stages of stellar evolution, ejected into space via a core-collapse supernova.
The characteristic gamma lines associated with the decay of 60Fe have been detected by space gamma-ray detectors. By comparing the 60Fe ...
A rich marine algal ecosystem 600 million years earlier than previously thought
2021-04-16
The first photosynthetic oxygen-producing organisms on Earth were cyanobacteria. Their evolution dramatically changed the Earth allowing oxygen to accumulate into the atmosphere for the first time and further allowing the evolution of oxygen-utilizing organisms including eukaryotes. Eukaryotes include animals, but also algae, a broad group of photosynthetic oxygen-producing organisms that now dominate photosynthesis in the modern oceans. When, however, did algae begin to occupy marine ecosystems and compete with cyanobacteria as important phototrophic organisms?
In a new study Zhang et al use the molecular remains of ancient algae (so-called biomarkers) to show that algae occupied an important ...
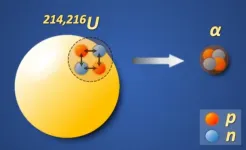
Scientists report remarkable enhancement of α-particle clustering in uranium isotopes
2021-04-16
It is always exciting to find new isotopes with extreme neutron/proton numbers in nuclear physics research. In the region of heavy nuclei, α-decay is one of the pervasive decay modes and plays an essential role in searching for new isotopes. However, even after about a century of studying α-decay, scientists still cannot perfectly describe how the α-particle is formed at the surface of the nucleus before its emission.
In the α-decay process, the α-particle can be regarded not only as two protons plus two neutrons, but also as two proton-neutron pairs. Although previous studies have proved the importance of the pairing forces between the identical nucleons, it remains unclear whether ...
Older adults most likely to make the effort to help others
2021-04-16
Older adults are more willing to make an effort to help others than younger adults, according to new research from the University of Birmingham.
The study, led by researchers in the University's School of Psychology, is the first to show how effortful 'prosocial' behaviour - intended to benefit others - changes as people get older. In particular, it focused on people's willingness to exert physical effort, rather than to give money or time, since attitudes to both these are known to change with age. The research results are published in Psychological Science.
In the study, the research team tested a group of 95 adults aged between 18 and 36, and a group of 92 adults aged 55-85. Each participant made 150 choices about whether or not to grip a handheld ...
Sweat sensor could alert doctors, patients to looming COVID cytokine storm (video)
2021-04-16
WASHINGTON, April 16, 2021 -- Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, doctors recognized that patients who developed a "cytokine storm" -- a surge of pro-inflammatory immune proteins -- were often the sickest and at highest risk of dying. But a cytokine storm can also occur in other illnesses, such as influenza. Today, scientists report preliminary results on a sweat sensor that acts as an early warning system for an impending cytokine storm, which could help doctors more effectively treat patients.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2021 is being held online April 5-30. Live sessions will be hosted April 5-16, ...
New tech builds ultralow-loss integrated photonic circuits
2021-04-16
Encoding information into light, and transmitting it through optical fibers lies at the core of optical communications. With an incredibly low loss of 0.2 dB/km, optical fibers made from silica have laid the foundations of today's global telecommunication networks and our information society.
Such ultralow optical loss is equally essential for integrated photonics, which enable the synthesis, processing and detection of optical signals using on-chip waveguides. Today, a number of innovative technologies are based on integrated photonics, including semiconductor ...
New nanoscale device for spin technology
2021-04-16
Researchers at Aalto University have developed a new device for spintronics. The results have been published in the journal Nature Communications, and mark a step towards the goal of using spintronics to make computer chips and devices for data processing and communication technology that are small and powerful.
Traditional electronics uses electrical charge to carry out computations that power most of our day-to-day technology. However, engineers are unable to make electronics do calculations faster, as moving charge creates heat, and we're at the ...
Vitamin D deficiency may impair muscle function
2021-04-16
Vitamin D deficiency may impair muscle function due to a reduction in energy production in the muscles, according to a mouse study published in the Journal of Endocrinology. Vitamin D deficient mice were found to have impaired muscle mitochondrial function, which may have implications for muscle function, performance and recovery. This may suggest that preventing vitamin D deficiency in older adults could help maintain better muscle strength and function and reduce age related muscle deterioration, but further studies are needed to confirm this.
Vitamin D is a hormone well known to be important for maintaining bone health and preventing ...
Research shows to disrupt online extremism freewill is key
2021-04-16
Douglas Wilbur '14, a visiting Ph.D. scholar in the Department of Communication at UTSA, has published a study that shows how researchers can craft message campaigns to protect individuals from adopting extremist views.
According to his research, when people are explicitly told that they are free to accept or reject propagandistic claims, the likelihood of choosing a moderate view increases. This was a result of a survey of attitudes that tested counter-propaganda strategies, which stressed a person's autonomy, and then measured sentiments after exposure.
The study was ...
Heart health of shift workers linked to body clock
2021-04-16
Sophia Antipolis - 16 April 2021: Working hours that deviate from an individual's natural body clock are associated with greater cardiovascular risk, according to research presented at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
"Our study found that for each hour the work schedule was out of sync with an employee's body clock, the risk of heart disease got worse," said study author Dr. Sara Gamboa Madeira of the University of Lisbon, Portugal.
At least 20% of European employees work atypical hours or shifts,2 and growing scientific evidence associates these with deleterious cardiovascular outcomes.3 A number of explanations ...
A new treatment for rare muscular disease
2021-04-16
Rare diseases are sometimes the most difficult to treat because of a lack of research and fewer participants to study.
An example would be those who have Pompe disease, a genetic condition when a body can't make a protein that breaks down a complex sugar, called glycogen, for energy. Too much glycogen builds up and damages muscles and organs. The disease causes muscle weakness and trouble breathing and can affect the heart and muscles.
In the case of Pompe disease, however, University of Cincinnati researchers have found a newer, more effective treatment for the rare condition that could become the new standard of care.
Hani Kushlaf, MD, an associate professor in both the Department of Neurology and Rehabilitation Medicine and the ...
Triangular-shaped spikes key to coronavirus transmission, finds new study
2021-04-16
COVID-19 needs no introduction. Last year, the disease, which is caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2, reached every continent across the globe. By the end of March 2021, there had been an estimated 128 million cases recorded with almost three million of these being fatal. As scientists' race to develop vaccines and politicians coordinate their distribution, fundamental research on what makes this virus so successful is also being carried out.
Within the Mathematics, Mechanics, and Materials Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST), postdoctoral researcher, Dr. Vikash Chaurasia, and Professor Eliot Fried have been using energy minimization techniques to look at charged proteins on biological particles. Previously they researched ...
Key policy considerations for reducing public consumption of vice products
2021-04-16
Researchers from University of British Columbia, Emory University, and New York University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that investigates the relationship between branding and counter-marketing in the cigarette industry.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Investigating the Effects of Excise Taxes, Public Usage Restrictions, and Anti-Smoking Ads across Cigarette Brands" and is authored by Yanwen Wang, Michael Lewis, and Vishal Singh.
While the goal of marketing is usually to boost purchase rates and strengthen relationships between consumers and brands, counter-marketing is an increasingly common strategy for reducing the consumption of "vice" goods such as cigarettes. Counter-marketing activities may ...
The Lancet Respiratory Medicine: Past COVID-19 infection does not fully protect young people from reinfection
2021-04-16
A past COVID-19 infection does not completely protect against reinfection in young people, according to an observational study of more than 3,000 healthy members of the US Marines Corps most of whom were aged 18-20 years, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine journal.
The authors say that despite previous infection and the presence of antibodies, vaccination is still necessary to boost immune responses, prevent reinfection, reduce transmission, and that young people should take up the vaccine wherever possible.
In the study, between May and November 2020, around 10% (19 out of 189) of participants who were previously infected with SARS-CoV-2 (seropositive) became reinfected, compared with new infections in 50% (1,079 out of 2,247) ...
Ten reasons why the coronavirus is airborne
2021-04-16
There is consistent, strong evidence that the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes COVID-19, is predominantly transmitted through the air, according to a new assessment published today in the medical journal Lancet. Therefore, public health measures that fail to treat the virus as predominantly airborne leave people unprotected and allow the virus to spread, according to six experts from the UK, USA and Canada, including Jose-Luis Jimenez, chemist at the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) and University of Colorado Boulder.
"The evidence supporting airborne transmission is overwhelming, and evidence supporting large droplet transmission is almost ...
Protein linked to ALS/Ataxia could play key role in other neurodegenerative disorders
2021-04-15
Neurological disorders are the number one cause of disability in the world, leading to seven million deaths each year. Yet few treatments exist for these diseases, which progressively diminish a person's ability to move and think.
Now, a new study suggests that some of these neurological disorders share a common underlying thread. Staufen1, a protein that accumulates in the brains of patients with certain neurological conditions, is linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or Lou Gehrig's disease, along with other neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's disease, according to University of Utah Health scientists.
The findings connect Staufen1 ...
Water crisis took toll on Flint adults' physical, mental health
2021-04-15
ITHACA, N.Y. - Since state austerity policies initiated a potable water crisis seven years ago in Flint, Michigan, public health monitoring has focused on potential developmental deficits associated with lead exposure in adolescents or fetuses exposed in utero.
New research from Cornell and the University of Michigan offers the first comprehensive evidence that the city's adult residents suffered a range of adverse physical and mental health symptoms potentially linked to the crisis in the years during and following it, with Black residents affected disproportionately.
In a survey of more than 300 residents, 10% reported having been diagnosed by a clinician with elevated ...
Child vaccination rates declined during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-04-15
PASADENA, Calif. -- The numbers of recommended vaccine doses, including measles vaccine, administered to children decreased dramatically after the declaration of a national state of emergency on March 13, 2020, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a Kaiser Permanente study published in Pediatrics. While the decrease was lower and recovered in children under 2 years of age, it was more severe and persistent in older children.
"When vaccination rates decline, we worry about an increase in vaccine-preventable diseases that can be harmful to children," said the study's lead author, Bradley Ackerson, MD, a Kaiser Permanente South Bay Medical Center pediatric infectious disease specialist and an investigator with the Kaiser Permanente Southern ...
A method to assess COVID-19 transmission risks in indoor settings
2021-04-15
Two MIT professors have proposed a new approach to estimating the risks of exposure to Covid-19 under different indoor settings. The guideline they developed suggests a limit for exposure time, based on the number of people, the size of the space, the kinds of activity, whether masks are worn, and the ventilation and filtration rates. Their model offers a detailed, physics-based guideline for policymakers, businesses, schools, and individuals trying to gauge their own risks.
The guideline, appearing this week in the journal PNAS, was developed by Martin .Z. Bazant, professor of chemical engineering and applied mathematics, and John W. M. Bush, professor of applied mathematics. They stress that one key feature of their model, which has received less attention in existing public-health policies, ...
How the humble woodchip is cleaning up water worldwide
2021-04-15
URBANA, Ill. - Australian pineapple, Danish trout, and Midwestern U.S. corn farmers are not often lumped together under the same agricultural umbrella. But they and many others who raise crops and animals face a common problem: excess nitrogen in drainage water. Whether it flows out to the Great Barrier Reef or the Gulf of Mexico, the nutrient contributes to harmful algal blooms that starve fish and other organisms of oxygen.
But there's a simple solution that significantly reduces the amount of nitrogen in drainage water, regardless of the production system or location: denitrifying bioreactors.
"Nitrogen pollution from farms is relevant around the world, ...
Study reveals how some antibodies can broadly neutralize ebolaviruses
2021-04-15
LA JOLLA, CA--Some survivors of ebolavirus outbreaks make antibodies that can broadly neutralize these viruses--and now, scientists at Scripps Research have illuminated how these antibodies can disable the viruses so effectively. The insights may be helpful for developing effective therapies.
Ebolavirus is a family of often-deadly viruses that includes Ebola virus and many lesser-known viruses such as Bundibugyo virus, Sudan virus and Reston virus.
Structural biologists at Scripps Research used electron microscopy techniques to visualize a set of antibodies that target a key site on these viruses called the "glycan cap." Their research showed ...
Novel muscular dystrophy gene connects to a key biological pathway
2021-04-15
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (04/15/2021) -- New research from the University of Minnesota Medical School found mutations in a novel gene that may help identify patients with a specific form of muscular dystrophy.
The laboratory of Peter B. Kang, MD, the new director of the Paul & Sheila Wellstone Muscular Dystrophy Center at the U of M Medical School, studies the genetics and disease mechanisms of muscular dystrophy. It uses cutting-edge genomic methods to discover disease-causing mutations in patients who cannot find answers via clinical genetic test facilities.
The Kang laboratory ...
[1] ... [2432]
[2433]
[2434]
[2435]
[2436]
[2437]
[2438]
[2439]
2440
[2441]
[2442]
[2443]
[2444]
[2445]
[2446]
[2447]
[2448]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.