Stanford researchers and others illuminate mystery of sea turtles' epic migrations
2021-04-08
"Not all those who wander are lost ... "
--J.R.R. Tolkien
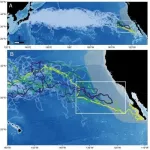
Known as "the lost years," it is a little-understood journey that unfolds over thousands of miles and as much as two decades or more. Now, a Stanford-led study illuminates secrets of the North Pacific loggerhead turtles' epic migration between their birthplace on the beaches of Japan and reemergence years later in foraging grounds off the coast of Baja California. The study, published April 8 in Frontiers in Marine Science, provides evidence for intermittent passages of warm water that allow sea turtles to cross otherwise inhospitably cold ocean barriers. The findings could help inform the design of conservation measures to protect sea turtles and other migratory sea creatures amid climatic ...
Mars didn't dry up in one go
2021-04-08
The Perseverance rover has just landed on Mars. Meanwhile, its precursor Curiosity continues to explore the base of Mount Sharp (officially Aeolis Mons), a mountain several kilometres high at the centre of the Gale crater. Using the telescope on the ChemCam instrument to make detailed observations of the steep terrain of Mount Sharp at a distance, a French-US team headed by William Rapin, CNRS researcher at the Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie (CNRS/Université Toulouse III/CNES) (1), has discovered that the Martian climate recorded there alternated between dry and wetter periods, before drying up completely about 3 billion years ago. Spacecraft in orbit ...
Heart failure and stroke rising in men under 40
2021-04-08
Heart failure and stroke are unusual diagnoses among younger people. But they are now clearly on the rise in men below the age of 40, according to a University of Gothenburg study. The scientists have found links to obesity and low fitness in the upper teens.
The present study, published in Journal of Internal Medicine, includes data on 1,258,432 men who, at an average age of 18.3 years, enlisted for military service in Sweden between 1971 and 1995.
Particulars of the men's weight, height and physical fitness on enlistment were merged with data in the National Board of Health and Welfare's National Patient Register and Cause of Death Register for the period 1991-2016. From when they enlisted, the men were thus monitored over a period exceeding 20 years.
The proportion ...
Lockdown for genome parasites
2021-04-08
Researchers at GMI - Gregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences - uncover an ingenious mechanism by which Arabidopsis safeguards the integrity of its genome. The paper is published in the journal Nature Cell Biology.
Is it possible for one single gene product to silence undesirable genetic elements? Can such a strong effect be seen in the regulation of Transposable Elements (TEs), or genome parasites? If yes, how does this gene product singlehandedly keep transposons in check? New research from Frédéric Berger's group at GMI provides answers to these questions and dissects a mechanism of gene silencing that has long remained shrouded in mystery.
Genome parasites
Although jumping transposons promote ...
Fostered flamingos just as friendly
2021-04-08
Flamingo chicks raised by foster parents from another flamingo species develop normally, scientists say.
Six Chilean flamingo chicks were reared by Andean flamingos - a species of similar size and behaviour - at WWT Slimbridge Wetland Centre in the summer of 2018.
University of Exeter scientists studied the chicks' behaviour after they re-joined the Chilean flamingo flock early in 2019.
The results showed fostering had no negative effects, with fostered flamingos still forming stable social ties - making "friends" and behaving like parent-reared birds.
"Slimbridge's Andean flamingos hadn't nested for about 20 years," said Dr Paul Rose, of the University of Exeter.
"But in the ...
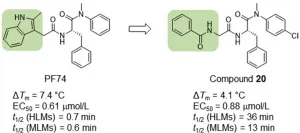
Novel PF74-like small molecules targeting the HIV-1 capsid protein
2021-04-08
Novel PF74-like small molecules targeting the HIV-1 capsid protein: Balance of potency and metabolic stability
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.07.016
Of all known small molecules targeting human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) capsid protein (CA), PF74 represents by far the best characterized chemotype, due to its ability to confer antiviral phenotypes in both early and late phases of viral replication. However, the prohibitively low metabolic stability renders PF74 a poor antiviral lead. The authors report on their medicinal chemistry efforts ...
New study explains Mycobacterium tuberculosis high resistance to drugs and immunity
2021-04-08
A consortium of researchers from Russia, Belarus, Japan, Germany and France led by a Skoltech scientist have uncovered the way in which Mycobacterium tuberculosis survives in iron-deficient conditions by utilizing rubredoxin B, a protein from a rubredoxin family that play an important role in adaptation to changing environmental conditions. The new study is part of an effort to study the role of M. tuberculosis enzymes in developing resistance to the human immune system and medication. The paper was published in the journal Bioorganic Chemistry.
According to the World Health Organization, every year 10 million people fall ill with tuberculosis and about 1.5 million die from it, making it the world's top infectious killer. ...
One in four children want better pain treatment
2021-04-08
A great need for better pain treatment
After an appendectomy, a quarter (24.8%) of all children wanted a stronger pain treatment in the first 24 hours after their operation. Among children who had a tonsillectomy, this was one-fifth (20.2%). Analysis of the data showed that this desire was primarily associated with sleep impairments and with movement pain. The lead author of the study, Prof. Ulrike M. Stamer, explained: "We are dealing with a large number of affected patients. Appendectomies and tonsillectomies are the most common operations performed on children overall. Just under a quarter of these cases strongly signal a desire for
improvement".
A comprehensive, multicentre study
This study is based on the international pain registry "PAIN OUT infant", which was established ...
Moffitt investigators identify STING gene methylation allows melanoma to evade the immune system
2021-04-08
TAMPA, Fla. (April 8, 2021) -- A dysfunctional immune system significantly contributes to the development of cancer. Several therapeutic strategies to activate the immune system to target cancer cells have been approved to treat different types of cancer, including melanoma. However, some patients do not show beneficial clinical responses to these novel and very promising immunotherapies. In a new article published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers demonstrate how an important defect in STING gene expression in melanoma cells contributes to their evasion from immune cell detection and destruction.
Several different mechanisms have been discovered ...
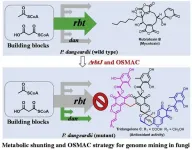
Endophytic fungi as promising producers of bioactive small molecules
2021-04-08
Genome mining combined metabolic shunting and OSMAC strategy of an endophytic fungus leads to the production of diverse natural products
Endophytic fungi are promising producers of bioactive small molecules. Bioinformatic analysis of the genome of an endophytic fungus Penicillium dangeardii revealed 43 biosynthetic gene clusters, exhibited its strong ability to produce numbers of secondary metabolites. However, this strain mainly produce rubratoxins alone with high yield in varied culture conditions, suggested most gene clusters are silent. Efforts for mining the cryptic gene clusters in P. dangeardii, including epigenetic regulation and one-strain-many-compounds (OSMAC) approach were failed probably due to the high yield of rubratoxins. A metabolic ...
Archaeologists uncover earliest evidence of domesticated dogs in Arabian Peninsula
2021-04-08
A team of archaeologists in north-west the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has uncovered the earliest evidence of dog domestication by the region's ancient inhabitants.
The discovery came from one of the projects in the large-scale archaeological surveys and excavations of the region commissioned by the Royal Commission for AlUla (RCU).
The researchers found the dog's bones in a burial site that is one of the earliest monumental tombs identified in the Arabian Peninsula, roughly contemporary with such tombs already dated further north in the Levant.
Evidence ...
The fastest one wins
2021-04-08
Indole, and structures derived from it, are a component of many natural substances, such as the amino acid tryptophan. A new catalytic reaction produces cyclopenta[b]indoles--frameworks made of three rings that are joined at the edges--very selectively and with the desired spatial structure. As a research team reports in the journal Angewandte Chemie, the rates of the different steps of the reaction play a critical role.
Indole derivates are widely distributed in nature; they are part of serotonin and melatonin, as well as many alkaloids--some of which are used as drugs, for example, as treatments for Parkinson's disease. Indole is an aromatic six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring along one edge. The five-membered ring has a double bond and ...
'Bug brain soup' expands menu for scientists studying animal brains
2021-04-08
Using a surprisingly simple technique, researchers in the University of Arizona Department of Neuroscience have succeeded in approximating how many brain cells make up the brains of several species of bees, ants and wasps. The work revealed that certain species of bees have a higher density of brain cells than even some species of birds, whereas ants turned out to have fewer brain cells than originally expected.
Published in the scientific journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, the study marks the first time the new cell counting method has been applied to invertebrate animals and provides a robust and reproducible protocol for other research groups studying the brains of ...
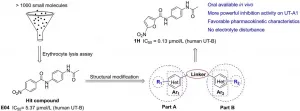
Novel diarylamides as orally active diuretics targeting urea transporters
2021-04-08
Discovery of novel diarylamides as orally active diuretics targeting urea transporters
Urea transporters (UT) play a vital role in the mechanism of urine concentration and are recognized as novel targets for the development of salt-sparing diuretics. Thus, UT inhibitors are promising for development as novel diuretics. In this study the authors discovered a novel UT inhibitor with a diarylamide scaffold by high-throughput screening. Optimization of the inhibitor led to the identification of a promising preclinical candidate, N-[4-(acetylamino)phenyl]-5-nitrofuran-2-carboxamide ...
Complete chromosome 8 sequence reveals novel genes and disease risks
2021-04-08
The full assembly of human chromosome 8 is reported this week in Nature. While on the outside this chromosome looks typical, being neither short nor long or distinctive, its DNA content and arrangement are of interest in primate and human evolution, in several immune and developmental disorders, and in chromosome sequencing structure and function generally.
This linear assembly is a first for a human autosome - a chromosome not involved in sex determination. The entire sequence of chromosome 8 is 146,259,671 bases. The completed assembly fills in the gap of more than 3 million bases missing from the current reference genome.
The Nature paper is titled "The structure, function and evolution of a complete chromosome 8."
One of several intriguing characteristics ...
Energy transmission by gold nanoparticles coupled to DNA structures
2021-04-08
Using DNA structures as scaffolds, Tim Liedl, a scientist of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich, has shown that precisely positioned gold nanoparticles can serve as efficient energy transmitters.
Since the inception of the field in 2006, laboratories around the world have been exploring the use of 'DNA origami' for the assembly of complex nanostructures. The method is based on DNA strands with defined sequences that interact via localized base pairing. "With the aid of short strands with appropriate sequences, we can connect specific regions of long DNA molecules together, rather like forming three-dimensional structures by folding a flat sheet of paper in certain ...
Living fossils: Microbe discovered in evolutionary stasis for millions of years
2021-04-08
It's like something out of science fiction. Research led by Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences has revealed that a group of microbes, which feed off chemical reactions triggered by radioactivity, have been at an evolutionary standstill for millions of years. The discovery could have significant implications for biotechnology applications and scientific understanding of microbial evolution.
"This discovery shows that we must be careful when making assumptions about the speed of evolution and how we interpret the tree of life," said Eric Becraft, the lead author on the paper. "It is possible that some organisms go into an evolutionary ...
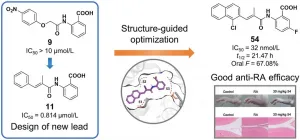
Acrylamide derivatives for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
2021-04-08
Design, synthesis, molecular modeling, and biological evaluation of acrylamide derivatives as potent inhibitors of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) is a viable target for the development of therapeutics to treat cancer and immunological diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriasis and multiple sclerosis (MS).
The authors designed and synthesized a series of acrylamide-based novel DHODH inhibitors as potential RA treatment agents. 2-Acrylamidobenzoic acid analog 11 was identified as the lead compound for structure-activity ...
Where Siberian orchids thrive: New hotspot of orchids discovered near Novosibirsk
2021-04-08
Orchids of the Boreal zone are rare species. Most of the 28,000 species of the Orchid family actually live in the tropics. In the Boreal zone, ground orchids can hardly tolerate competition from other plants -- mainly forbs or grasses. So they are often pushed into ecotones -- border areas between meadows and forests, or between forests and swamps.
Furthermore, there has been a decline in wild orchids all over North America and Eurasia, caused in part by human-induced destruction of their habitats, the transformation of ecosystems, and the harvesting of flowers from the wild.
In the Novosibirsk region, ...
Research gives new insight into formation of the human embryo
2021-04-08
Pioneering research led by experts from the University of Exeter's Living Systems Institute has provided new insight into formation of the human embryo.
The team of researchers discovered an unique regenerative property of cells in the early human embryo.
The first tissue to form in the embryo of mammals is the trophectoderm, which goes on to connect with the uterus and make the placenta. Previous research in mice found that trophectoderm is only made once.
In the new study, however, the research team found that human early embryos are able to regenerate trophectoderm. They also showed that human embryonic stem cells grown in the laboratory can similarly ...
More than 5,000 tons of extraterrestrial dust fall to Earth each year
2021-04-08
Every year, our planet encounters dust from comets and asteroids. These interplanetary dust particles pass through our atmosphere and give rise to shooting stars. Some of them reach the ground in the form of micrometeorites. An international program conducted for nearly 20 years by scientists from the CNRS, the Université Paris-Saclay and the National museum of natural history with the support of the French polar institute, has determined that 5,200 tons per year of these micrometeorites reach the ground. The study will be available in the journal Earth & Planetary Science Letters from April 15.
Micrometeorites have always fallen on our planet. These interplanetary dust particles from comets or asteroids are particles of a few tenths to hundredths of a millimetre that have passed ...
Research shows cytonemes distribute Wnt proteins in vertebrate tissue
2021-04-08
Scientists have made a pivotal breakthrough in understanding the way in which cells communicate with each other.
A team of international researchers, including experts from the University of Exeter's Living Systems Institute, has identified how signalling pathways of Wnt proteins - which orchestrate and control many cell developmental processes - operate on both molecular and cellular levels.
Various mechanisms exist for cells to communicate with each other, and many are essential for development. This information exchange between cells is often based on signalling proteins that activate specific intracellular signalling cascades to control cell behaviour at a distance.
Wnt proteins are produced by a relatively small group ...
Health impacts of holocaust linger long after survival
2021-04-08
The damaging effects of life under Nazi rule have long been known with many victims having experienced periods of protracted emotional and physical torture, malnutrition and mass exposure to disease. But recent research from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem show that even for those who survived, their health and mortality continued to be directly impacted long after the end of the Holocaust.
The study, led by Drs. Iaroslav Youssim and Hagit Hochner from the School of Public Health at the Faculty of Medicine and published in the American Journal of Epidemiology, investigated mortality rates from ...
How to tame a restless genome
2021-04-08
Short pieces of DNA--jumping genes--can bounce from one place to another in our genomes. When too many DNA fragments move around, cancer, infertility, and other problems can arise. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor & HHMI Investigator Leemor Joshua-Tor and a research investigator in her lab, Jonathan Ipsaro, study how cells safeguard the genome's integrity and immobilize these restless bits of DNA. They found that one of the jumping genes' most needed resources may also be their greatest vulnerability.
The mammalian genome is full of genetic elements that have the potential to move from place to place. One type is an LTR retrotransposon (LTR). In normal cells, these elements don't ...
Religion follows patterns of politicization during COVID-19
2021-04-08
ITHACA, N.Y. - Research shows people turn to religion in times of fear and uncertainty - and March 2020 was one of those times.
To find the impact of religion during the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, Landon Schnabel, the Robert and Ann Rosenthal Assistant Professor of Sociology in the College of Arts and Sciences, analyzed responses from 11,537 Americans surveyed March 19-24, 2020, shortly after the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a global health pandemic.
Religion protected mental health of members of several ...
[1] ... [2437]
[2438]
[2439]
[2440]
[2441]
[2442]
[2443]
[2444]
2445
[2446]
[2447]
[2448]
[2449]
[2450]
[2451]
[2452]
[2453]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.