New formulation of existing medicines prove highly effective against drug-resistant fungus
2021-04-07
CLEVELAND--A team of researchers from Case Western Reserve University has discovered a formulation of existing medicines that can significantly reduce the presence of the fungus Candida auris (C. auris) on skin, controlling its spread and potentially keeping it from forming infections that have a high mortality rate.
By using a proprietary formulation of topical medications terbinafine or clotrimazole, researchers prevented the growth and spread of the fungus on the skin of a host; the findings appear in the most recent issue of the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.
"It's a very ...
South Korea data helps create framework to identify COVID-19 vulnerable areas worldwide
2021-04-07
Though the U.S. and South Korea recorded their first official COVID-19 case on the same day, January 20, 2020, there were notable differences in how each country would ultimately address what has become the world's most severe pandemic since 1918.
Yoonjung Lee, Pharm.D., Ph.D., a pharmacy preceptor and pharmaceutical sciences researcher at the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) Jerry H. Hodge School of Pharmacy, said she was surprised at how South Korea effectively managed the pandemic without the business shutdowns and lockdowns that occurred in China, the U.S. and many European countries.
"I am amazed at how the Korean government had prompt and effective public health interventions to not only address COVID-19, but also to address COVID-19-vulnerable ...
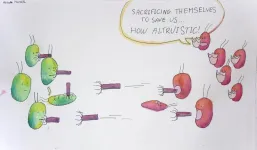
The incredible bacterial 'homing missiles' that scientists want to harness
2021-04-07
Imagine there are arrows that are lethal when fired on your enemies yet harmless if they fall on your friends. It's easy to see how these would be an amazing advantage in warfare, if they were real. However, something just like these arrows does indeed exist, and they are used in warfare ... just on a different scale.
These weapons are called tailocins, and the reality is almost stranger than fiction.
"Tailocins are extremely strong protein nanomachines made by bacteria," explained Vivek Mutalik, a research scientist at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) who studies tailocins and phages, the bacteria-infecting viruses that tailocins appear to be remnants of. "They ...
AI-powered symptom checkers can help healthcare systems deal with the COVID-19 burden
2021-04-07
AI-powered symptom checkers can potentially reduce the number of people going to in-person clinics during the pandemic, but first, researchers say, people need to know they exist.
COVID symptom checkers are digital self-assessment tools that use AI to help users identify their level of COVID-19 risk and assess whether they need to seek urgent care based on their reported symptoms. These tools also aim to provide reassurance to people who are experiencing symptoms that are not COVID-19 related.
Most platforms, like Babylon and Isabel, are public-facing tools, but the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) has one of the first COVID-19 symptom checkers that is fully integrated with the users' medical ...
The Lancet Psychiatry: Largest study to date suggests link between COVID-19 infection and subsequent mental health and neurological conditions
2021-04-07
Study using electronic health records of 236,379 COVID-19 patients mostly from the USA estimates that one in three COVID-19 survivors (34%) were diagnosed with a neurological or psychiatric condition within six months of infection.
Anxiety (17%) and mood disorders (14%) were the most common. Neurological diagnoses such as stroke and dementia were rarer, but not uncommon in those who had been seriously ill during COVID-19 infection. For example, of those who had been admitted to intensive care, 7% had a stroke and almost 2% were diagnosed with dementia.
These diagnoses were more common in COVID-19 patients than in flu or respiratory tract infection patients ...
Study examines antibody response to COVID-19 vaccination in patients with kidney failure
2021-04-07
Highlight
Most patients with kidney failure who were undergoing hemodialysis developed a positive antibody response after being vaccinated for COVID-19, but their response was lower than that of individuals without kidney disease.
Washington, DC (April 6, 2021) -- In a recent study, most patients with kidney failure who were undergoing hemodialysis developed a substantial antibody response following the vaccination with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine against COVID-19, but it was significantly lower than that of individuals without kidney disease. The findings will appear in an upcoming ...
Key brain molecule may play role in many brain disorders
2021-04-06
CHAPEL HILL, NC - A team led by scientists at the UNC School of Medicine identified a molecule called microRNA-29 as a powerful controller of brain maturation in mammals. Deleting microRNA-29 in mice caused problems very similar to those seen in autism, epilepsy, and other neurodevelopmental conditions.
The results, published in Cell Reports, illuminate an important process in the normal maturation of the brain and point to the possibility that disrupting this process could contribute to multiple human brain diseases.
"We think abnormalities in microRNA-29 activity are likely to be a common theme in neurodevelopmental ...
Secure type: consumers say compact logos signal product safety
2021-04-06
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (4/6/2021) -- Compact logos can encourage favorable brand evaluations by signaling product safety, according to a new study by researchers at Boston College's Carroll School of Management and Indian Institute of Management Udaipur, who reviewed the opinions of 17,000 consumers and conducted additional experiments with a variety of logos.
The findings reveal that typography -- specifically tracking, or the spacing between letters in a word -- can influence consumers' interpretations of brand logos. Further, the interpretation is influenced by cultural factors, the researchers reported ...
Fossil discovery deepens snakefly mystery
2021-04-06
Fossil discoveries often help answer long-standing questions about how our modern world came to be. However, sometimes they only deepen the mystery--as a recent discovery of four new species of ancient insects in British Columbia and Washington state is proving.
The fossil species, recently discovered by paleontologists Bruce Archibald of Simon Fraser University and Vladimir Makarkin of the Russian Academy of Sciences, are from a group of insects known as snakeflies, now shown to have lived in the region some 50 million years ago. The findings, published in Zootaxa, raise more questions about the evolutionary history of the distinctly elongated insects and why they live where they do today.
Snakeflies are slender, predatory insects that are native to the Northern Hemisphere ...
A quick morning reflection could make you a better leader -- even if you're not the boss
2021-04-06
Starting your day by thinking about what kind of leader you want to be can make you more effective at work, a new study finds.
"It's as simple as taking a few moments in the morning while you're drinking your coffee to reflect on who you want to be as a leader," said Remy Jennings, a doctoral student in the University of Florida's Warrington College of Business, who authored the study in the journal Personnel Psychology with UF management professor Klodiana Lanaj.
When study participants took that step, they were more likely to report helping co-workers and providing ...
Opioid prescribing for analgesia after common otolaryngology operations
2021-04-06
April 6, 2021, Alexandria, VA - The American Academy of Otolaryngology?Head and Neck Surgery Foundation published the Clinical Practice Guideline: Opioid Prescribing for Analgesia After Common Otolaryngology Operations today in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. This specialty-specific guideline provides evidence-based recommendations on postoperative management for pain in common otolaryngologic procedures, with a focus on opioids.
"As otolaryngologist-head and neck surgeons, we can help reduce the risk of opioid use disorder among our patients and their families," said Samantha Anne, MD, MS, Chair of the Guideline Development Group (GDG). "This clinical practice guideline ...
Study finds risk of leukemia higher than expected in children with Down syndrome
2021-04-06
A new large-scale study led by UC Davis Health and UC San Francisco researchers assessed the risks of leukemia in children with Down syndrome. It pointed to stronger than expected associations between Down syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia (AML), one type of blood cancer.
Down syndrome is one of the most common genetic conditions in the U.S. and Canada. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 6,000 babies with Down syndrome are born in the United States each year. That's approximately one in every 700 babies born in the U.S. and one in 750 newborns ...
Researchers find a connection between Trump's tweets and the exchange rate of the rouble
2021-04-06
Tweets about Russia by Donald Trump during his presidency caused short but noticeable depreciations of the rouble. Meanwhile, the introduction of new sanctions, upon which the president did not comment, had no such effect. This was the finding of a group of researchers, which included Elena Fedorova, Professor of the Faculty of Economic Sciences of HSE University. The group published their findings in in the Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization.
With the growing influence of social media, officials, politicians, and entrepreneurs increasingly express their positions on various issues directly (for example, using Facebook or Twitter), and their messages serve as an independent source of financial and business ...
Research identifies gender bias in estimation of patients' pain
2021-04-06
"On a scale of one to 10, how much pain are you in?"
In a recent study published by the Journal of Pain, co-authored by Elizabeth Losin, assistant professor of psychology and director of the Social and Cultural Neuroscience lab at the University of Miami, researchers found that a patient's pain responses may be perceived differently by others based on their gender.
According to "Gender biases in estimation of others' pain," when male and female patients expressed the same amount of pain, observers viewed female patients' pain as less intense and more likely to benefit from psychotherapy versus medication as compared to men's pain, exposing a significant patient gender bias that could lead to disparities in treatments.
The study consisted of ...
Carpal tunnel syndrome is not just an office workers' condition
2021-04-06
DETROIT - Researchers at Henry Ford Health System have found that workers in construction and other manufacturing jobs are more susceptible for developing carpal tunnel syndrome than those who work in office jobs.
In a retrospective study published in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, researchers report that manual labor jobs that require lifting, gripping and forceful wrist motion contribute to higher rates of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Injuries related to carpal tunnel have steadily declined from 1.3 million in 2003 to 900,380 in 2018, according to the most recent figures compiled by the U.S. Department ...
Structural biology opens new perspectives for treating psychiatric disorders
2021-04-06
Glycine regulates neuronal activity in the brain
Glycine is the smallest amino acid - one of the building blocks of proteins. It acts also as a neurotransmitter in the brain, enabling neurons to communicate with each other and modulating neuronal activity. Many researchers have focused on increasing glycine levels in synapses to find an effective treatment for schizophrenia. This could be done using inhibitors targeting Glycine Transporter 1 (GlyT1), a protein that sits in neuronal cell membranes and is responsible for the uptake of glycine into neurons. However, the development of such drugs has been hampered ...
Gained in translation: Subgenome fractionation determines hybrid vigor in maize
2021-04-06
The adage goes, "Two is better than one." Well, that might be true for endeavors involving human heads, but when it comes to ears, hybrid maize tends to have a superior advantage over the parental stocks in most cases. This phenomenon, called hybrid vigor or "heterosis," has been used by agriculturalists across ages to create higher-yielding, more resistant varieties of maize all over the world.
But what are the factors contributing to the increased hybrid vigor of maize? Several different genetic models have been proposed to explain heterosis in varied ...
No pain, no gain in exercise for peripheral artery disease
2021-04-06
Pain will lessen over time
Results include longer distance and walking time
8.5 million people in U.S., 250 million worldwide, have PAD
CHICAGO --- No pain means no gain when it comes to reaping exercise benefits for people with peripheral artery disease (PAD), reports a new Northwestern Medicine study.
In people with peripheral artery disease, walking for exercise at an intensity that induces ischemic leg pain (caused by restricted blood flow) improves walking performance -- distance and length of time walking -- the study found. Walking at a slow pace that does not induce ischemic leg symptoms is no more effective than no exercise at all, the study showed.
This randomized trial is the first to show that a home-based walking exercise program ...
Gut microbiome plays role in autism
2021-04-06
Washington, D.C. - April 6, 2021 - A new study has demonstrated that autism spectrum disorder is related to changes in the gut microbiome. The findings are published this week in mSystems, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Longitudinally, we were able to see that within an individual, changes in the microbiome were associated with changes in behavior," said principal study investigator Catherine Lozupone, PhD, a microbiologist in the Department of Medicine, University of Colorado, Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado. "If we are going to understand the link between the gut microbiome and autism, we need more collaborative efforts across different regions and ...
A novel form of cellular logistics
2021-04-06
Biophysicists from Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have shown that a phenomenon known as diffusiophoresis, which can lead to a directed particle transport, can occur in biological systems.
In order to perform their biological functions, cells must ensure that their logistical schedules are implemented smoothly, such that the necessary molecular cargoes are delivered to their intended destinations on time. Most of the known transport mechanisms in cells are based on specific interactions between the cargo to be transported and the energy-consuming motor ...
Screening for skin disease on your laptop
2021-04-06
The founding chair of the Biomedical Engineering Department at the University of Houston is reporting a new deep neural network architecture that provides early diagnosis of systemic sclerosis (SSc), a rare autoimmune disease marked by hardened or fibrous skin and internal organs. The proposed network, implemented using a standard laptop computer (2.5 GHz Intel Core i7), can immediately differentiate between images of healthy skin and skin with systemic sclerosis.
"Our preliminary study, intended to show the efficacy of the proposed network architecture, holds promise in the characterization of SSc," reports Metin Akay, John S. Dunn Endowed Chair Professor of biomedical engineering. ...
Alien raindrops surprisingly like rain on Earth
2021-04-06
WASHINGTON--Raindrops on other planets and moons are close to the size of raindrops on Earth despite having different chemical compositions and falling through vastly different atmospheres, a new study finds. The results suggest raindrops falling from clouds are surprisingly similar across a wide range of planetary conditions, which could help scientists better understand the climates and precipitation cycles of other worlds, according to the researchers.
Raindrops on Earth are made of water, but other worlds in our solar system have precipitation made of more unusual stuff. On Venus, ...
New perspective to understand and treat a rare calcification disease
2021-04-06
As part of an international collaboration, researchers from ELTE Eötvös Loránd University developed a new animal model to study a rare genetic disease that can lead to blindness at the age of 40-50. The new model could open up new perspectives in our understanding of this metabolic disease and will also help to identify new potential drug candidates, according to the recent study published in Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) is a rare genetic disease with symptoms that usually manifest in adolescence or in early adulthood. The symptoms are caused by the appearance of hydroxyapatite crystal deposits in the subcutaneous connective tissue and retina ...
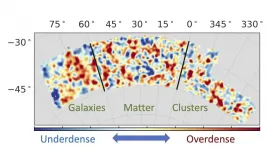
Dark Energy Survey physicists open new window into dark energy
2021-04-06
The universe is expanding at an ever-increasing rate, and while no one is sure why, researchers with the Dark Energy Survey (DES) at least had a strategy for figuring it out: They would combine measurements of the distribution of matter, galaxies and galaxy clusters to better understand what's going on.
Reaching that goal turned out to be pretty tricky, but now a team led by researchers at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Stanford University and the University of Arizona have come up with a solution. Their analysis, published April 6 in Physical Review ...
For breastfeeding moms, COVID-19 vaccinations may also protect babies
2021-04-06
Nursing mothers who receive a COVID-19 vaccine may pass protective antibodies to their babies through breast milk for at least 80 days following vaccination, suggests new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
"Our study showed a huge boost in antibodies against the COVID-19 virus in breast milk starting two weeks after the first shot, and this response was sustained for the course of our study, which was almost three months long," said first author Jeannie Kelly, MD, assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology. "The antibodies levels were still high at the end of our study, so the protection likely extends even longer."
Based ...
[1] ... [2445]
[2446]
[2447]
[2448]
[2449]
[2450]
[2451]
[2452]
2453
[2454]
[2455]
[2456]
[2457]
[2458]
[2459]
[2460]
[2461]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.