Brain damage caused by plasticisers
2021-04-12
The plasticisers contained in many everyday objects can impair important brain functions in humans. Biologists from the University of Bayreuth warn of this danger in an article in Communications Biology. Their study shows that even small amounts of the plasticisers bisphenol A and bisphenol S disrupt the transmission of signals between nerve cells in the brains of fish. The researchers consider it very likely that similar interference can also occur in the brains of adult humans. They therefore call for the rapid development of alternative plasticisers that do ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has been linked with six unhealthy eating behaviors
2021-04-12
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (04/12/2021) -- A new probe into the lingering impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic revealed correlations to six unhealthy eating behaviors, according to a study by the University of Minnesota Medical School and School of Public Health. Researchers say the most concerning finding indicates a slight increase or the re-emergence of eating disorders, which kill roughly 10,200 people every year -- about one person every 52 minutes.
U of M Medical School's Melissa Simone, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, collaborated with School of Public Health ...
Pain receptors linked to the generation of energy-burning brown fat cells
2021-04-12
BOSTON - (April 12, 2021) - A new source of energy expending brown fat cells has been uncovered by researchers at the Joslin Diabetes Center, which they say points towards potential new therapeutic options for obesity. According to the new report, published today by Nature Metabolism, the key lies in the expression of a receptor called Trpv1 (temperature-sensitive ion channel transient receptor potential cation subfamily V member 1) -- a protein known to sense noxious stimuli, including pain and temperature.
Specifically, the authors point to smooth muscle cells expressing the Trpv1 receptor and identify them as a novel source of energy-burning brown fat cells (adipocytes). This should translate into increased overall energy ...
Technique allows mapping of epigenetic information in single cells at scale
2021-04-12
Histones are tiny proteins that bind to DNA and hold information that can help turn on or off individual genes. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet have developed a technique that makes it possible to examine how different versions of histones bind to the genome in tens of thousands of individual cells at the same time. The technique was applied to the mouse brain and can be used to study epigenetics at a single-cell level in other complex tissues. The study is published in the journal Nature Biotechnology.
"This technique will be an important tool for examining what makes cells different from each other at the epigenetic level," says Marek ...
Poop core records 4,300 years of bat diet and environment
2021-04-12
WASHINGTON--Deep in a Jamaican cave is a treasure trove of bat poop, deposited in sequential layers by generations of bats over 4,300 years.
Analogous to records of the past found in layers of lake mud and Antarctic ice, the guano pile is roughly the height of a tall man (2 meters), largely undisturbed, and holds information about changes in climate and how the bats' food sources shifted over the millennia, according to a new study.
"We study natural archives and reconstruct natural histories, mostly from lake sediments. This is the first time scientists have interpreted past bat ...
Exercise benefit in breast cancer linked to improved immune responses
2021-04-12
BOSTON - Exercise training may slow tumor growth and improve outcomes for females with breast cancer - especially those treated with immunotherapy drugs - by stimulating naturally occurring immune mechanisms, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Harvard Medical School (HMS) have found.
Tumors in mouse models of human breast cancer grew more slowly in mice put through their paces in a structured aerobic exercise program than in sedentary mice, and the tumors in exercised mice exhibited an increased anti-tumor immune response.
"The most exciting finding was that exercise training brought into tumors immune cells capable of killing cancer cells known as cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CD8+ ...
"Look before you leap:" Cardiologists warn about the risks of vaping
2021-04-12
Philadelphia, April 12, 2021 - Electronic cigarette (EC) use, or vaping, has both gained incredible popularity and generated tremendous controversy, but although they may be less harmful than tobacco cigarettes (TCs), they have major potential risks that may be underestimated by health authorities, the public, and medical professionals. Two cardiovascular specialists review the latest scientific studies on the cardiovascular effects of cigarette smoking versus ECs in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier. They conclude that young non-smokers should be discouraged from vaping, flavors targeted towards adolescents should be banned, and laws and regulations ...
A multidimensional view of the coronavirus
2021-04-12
What exactly happens when the corona virus SARS-CoV-2 infects a cell? In an article published in Nature, a team from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry paints a comprehensive picture of the viral infection process. For the first time, the interaction between the coronavirus and a cell is documented at five distinct proteomics levels during viral infection. This knowledge will help to gain a better understanding of the virus and find potential starting points for therapies.
When a virus enters a cell, viral and cellular protein molecules begin to interact. Both the replication of the virus and the reaction of ...
Living in a majority-black neighborhood linked to severe maternal morbidity
2021-04-12
PHILADELPHIA - Residents in majority-Black neighborhoods experience higher rates of severe pregnancy-related health problems than those living in predominantly-white areas, according to a new study of pregnancies at a Philadelphia-based health system, which was led by researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The findings, published today in Obstetrics and Gynecology, suggest that neighborhood-level public health interventions may be necessary in order to lower the rates of severe maternal morbidity -- such as a heart attack, heart failure, eclampsia, or hysterectomy -- and mortality ...
Large US study suggests survival benefit for severely ill COVID-19 patients treated with ECMO
2021-04-12
April 12, 2021 - For critically ill COVID-19 patients treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), the risk of death remains high - but is much lower than suggested by initial studies, according to a report published today by Annals of Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The findings support the use of ECMO as "salvage therapy" for COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or respiratory failure who do not improve with conventional mechanical ventilatory support, according to the new research by Ninh T. Nguyen, MD, Chair of the Department of Surgery, University ...
Study shows young early-onset colorectal cancer patients have increased survival
2021-04-12
New research by Yale Cancer Center shows patients with early-onset colorectal cancer, age 50 and younger, have a better survival rate than patients diagnosed with the disease later in life. The study was presented virtually today at the American Association of Cancer Research (AACR) annual meeting.
"Although small, we were surprised by our findings," said En Cheng, MD, MSPH, lead author of the study from Yale Cancer Center. "Past studies have shown younger colorectal patients, those under 50, were reported to experience worse survival compared with patients diagnosed at older ages. We hope this result can be inspiring for these ...
Yale Cancer Center study shows novel immunotherapy approach to fight melanoma
2021-04-12
In a new study led by Yale Cancer Center, researchers have advanced a tumor-targeting and cell penetrating antibody that can deliver payloads to stimulate an immune response to help treat melanoma. The study was presented today at the American Association of Cancer Research (AACR) virtual annual meeting.
"Most approaches rely on direct injection into tumors of ribonucleic acids (RNAs) or other molecules to boost the immune response, but this is not practical in the clinic, especially for patients with advanced cancer," said Peter M. Glazer, MD, PhD, Chair of the Department of Therapeutic Radiology ...
Better treatment for aggressive prostate cancer
2021-04-12
New research from CU Cancer Center member Scott Cramer, PhD, and his colleagues could help in the treatment of men with certain aggressive types of prostate cancer.
Published this week in the journal Molecular Cancer Research, Cramer's study specifically looks at how the loss of two specific prostate tumor-suppressing genes -- MAP3K7 and CHD1 --increases androgen receptor signaling and makes the patient more resistant to the anti-androgen therapy that is typically administered to reduce testosterone levels in prostate cancer patients.
"Doctors don't normally stratify patients based on this subtype and say, 'We're going to have to treat these people differently,' but we think this should be considered before treating ...
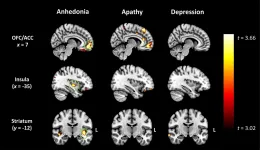
Profound loss of pleasure related to early-onset dementia
2021-04-12
KEY POINTS:
- Loss of pleasure has been revealed as a key feature in early-onset dementia (FTD), in contrast to Alzheimer's disease.
- Scans showed grey matter deterioration in the so-called pleasure system of the brain.
- These regions were distinct from those implicated in depression or apathy - suggesting a possible treatment target.
People with early-onset dementia are often mistaken for having depression and now Australian research has discovered the cause: a profound loss of ability to experience pleasure - for example a delicious meal or beautiful sunset - related to degeneration of 'hedonic hotspots' in the brain where pleasure mechanisms are concentrated.
The University of Sydney-led ...
Pandemic-inspired discoveries: New insect species from Kosovo named after the Coronavirus
2021-04-12
While the new Coronavirus will, hopefully, be effectively controlled sooner rather than later, its latest namesake is here to stay - a small caddisfly endemic to a national park in Kosovo that is new to science.
Potamophylax coronavirus was collected near a stream in the Bjeshkët e Nemuna National Park in Kosovo by a team of scientists, led by Professor Halil Ibrahimi of the University of Prishtina. After molecular and morphological analyses, it was described as a caddisfly species, new to science in the open-access, peer-reviewed Biodiversity Data Journal.
Ironically, the study of this new insect was impacted by the same pandemic that inspired its scientific name. Although it was collected a few years ago, the new species was only described during the global pandemic, ...
New research reveals why some of us are hungry all the time
2021-04-12
New research shows that people who experience big dips in blood sugar levels, several hours after eating, end up feeling hungrier and consuming hundreds more calories during the day than others.
A study published today in Nature Metabolism, from PREDICT, the largest ongoing nutritional research program in the world that looks at responses to food in real life settings, the research team from King's College London and health science company ZOE (including scientists from Harvard Medical School, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Massachusetts General Hospital, the University of Nottingham, Leeds University, and Lund University ...
Can we end the cage age?
2021-04-12
Between 2018 and 2020, 1,4 million EU citizens signed the petition 'End the Cage Age', with the aim of ending cage housing for farm animals in Europe. In response to this citizens initiative, the European Parliament requested a study by Utrecht University researchers on the possibilities to end cage housing. On 13 April, the scientists will present their report 'End the Cage Age - Looking for Alternatives' to the European Parliament.
In the report, behavioural biologists, animal scientists, veterinarians and ethicists from Utrecht University's Faculty of Veterinary Medicine analysed the available scientific literature on alternatives to cage housing. "Our focus was on laying hens and pigs" says Bas Rodenburg, Professor of Animal Welfare at Utrecht University. "Because these ...
Women 'risk' grey hair to feel authentic
2021-04-12
Many women "risk" allowing natural grey hair to show in order to feel authentic, a new study shows.
Researchers from the University of Exeter surveyed women who chose not to dye their grey hair, and found a "conflict" between looking natural and being seen as competent.
Participants in the study - mostly from English-speaking countries - belonged to online groups whose members allow their natural grey hair to show, and the researchers noted "solidarity and sisterhood" among these women.
"We are all constrained by society's norms and expectations when it comes to appearance, but expectations are more rigorous for women - especially older women," said lead author Vanessa Cecil, of the University of Exeter.
"The 'old woman' is an undesirable character in Western societies, being seen ...
The indestructible light beam
2021-04-12
Why is sugar not transparent? Because light that penetrates a piece of sugar is scattered, altered and deflected in a highly complicated way. However, as a research team from TU Wien (Vienna) and Utrecht University (Netherlands) has now been able to show, there is a class of very special light waves for which this does not apply: for any specific disordered medium--such as the sugar cube you may just have put in your coffee--tailor-made light beams can be constructed that are practically not changed by this medium, but only attenuated. The light beam penetrates the medium, and a light pattern arrives on the other ...
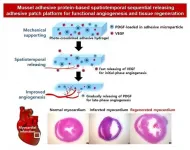
Blood vessel formation in damaged tissues with mussel adhesive protein
2021-04-12
Blood vessels deliver nutrients and oxygen to each organ in our body. They are difficult to completely restore to their original conditions once damaged by myocardial infarction or severe ischemic diseases. This is because various angiogenic growth factors must be applied sequentially in order to restore the vascular structure. Recently, a research team at POSTECH has bioengineered a novel adhesive patch platform that can efficiently deliver blood vessel-forming growth factors spatiotemporally using mussel adhesive protein (MAP), a bio-adhesive material that is made from mussels harmless to humans.
A POSTECH research team led by Professor Hyung Joon ...
Bigger brains gave squirrels the capacity to move up in the world
2021-04-12
Squirrels and other tree-dwelling rodents evolved to have bigger brains than their burrowing cousins, a study suggests.
This greater brain power has given them key abilities needed to thrive in woodland habitats, including better vision and motor skills, and improved head and eye movements, researchers say.
Scientists have shed light on how the brains of rodents - a diverse group that accounts for more than 40 per cent of all mammals - have changed since they evolved around 50 million years ago.
Few studies looking into factors affecting brain size in mammals have taken account ...
Study identifies specific antioxidants that may reduce oncogenic HPV infection in women
2021-04-12
New Orleans, LA - A study led by Hui-Yi Lin, Ph.D., Professor of Biostatistics, and a team of researchers at LSU Health New Orleans Schools of Public Health and Medicine has found that adequate levels of five antioxidants may reduce infection with the strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV) associated with cervical cancer development. Findings are published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
Although previous studies have suggested that the onset of HPV-related cancer development may be activated by oxidative stress, the association had not been clearly understood. This study evaluated associations between 15 antioxidants and vaginal HPV infection status -- no, low-risk, and oncogenic/high-risk HPV (HR-HPV) -- in 11,070 women aged 18-59 who participated ...
UPF presents its Planetary Wellbeing initiative to the world in a scientific article
2021-04-12
In 2018, Pompeu Fabra University launched its Planetary Wellbeing initiative, a long-term institutional strategy spurred by the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) and based on the Planetary Health project promoted by the Rockefeller Foundation and The Lancet.
Fifteen academics and public officials, led by the three directors of the initiative, Josep Maria Antó, scientific director of ISGlobal; Josep Lluís Martí, UPF vice-rector for innovation projects, and Jaume Casals, UPF rector, are the authors of an academic article published in the journal ...
Mapping the paradigm shift of China's cancer burden for designing prevention strategies
2021-04-12
Cancer is one of the top causes of death worldwide. The cancer burden is related not only to genetic predisposition, but also to environmental pollution and socioeconomic factors such as lifestyle. Consequently, the burden of this disease is not uniform across all countries. In fact, the public health of China, a country known for the rapid change in its development status in the last few decades, has undergone a paradigm shift with respect to cancer incidence and mortality.
To better understand the cancer burden of the country, a team of researchers from Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College reviewed the data of GLOBOCAN 2020, an online database of cancer incidence and mortality compiled by the International Agency for Research ...
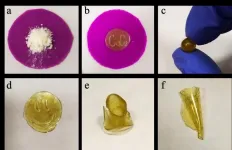
Chemists at St. Petersburg University create renewable plant-based polymers
2021-04-12
Researchers at the Laboratory of Cluster Catalysis at St Petersburg University have synthesised polymers from biomass. What makes them different is that they can be easily recycled.
Today, our life is simply unthinkable without polymers. Plastics, fibres, films, paint and lacquer coating - they are all polymers. We use them both in our everyday life and in industry. Yet the goods made from polymers, e.g. bottles, bags, or disposable tableware, are used just once or for a short period of time before they are thrown away. Due to the chemical compounds that they may release during recycling, they pose a real threat to our environment.
There ...
[1] ... [2446]
[2447]
[2448]
[2449]
[2450]
[2451]
[2452]
[2453]
2454
[2455]
[2456]
[2457]
[2458]
[2459]
[2460]
[2461]
[2462]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.