Health policy researchers propose filling health care coverage gap to help 'near poor'
2021-04-05
PITTSBURGH, April 5, 2021 - "Near-poor" Americans--people just above the federal poverty level but still well below the average U.S. income--who rely on Medicare for health insurance face high medical bills and may forgo essential health care, according to new research led by health policy scientists at the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health. This is due to a coverage "cliff" in Medicaid, which supplements Medicare for people with incomes below poverty but excludes individuals above the federal poverty threshold, including the near-poor.
In a report published today in the April issue of the journal Health Affairs, the authors describe the effects of this cliff and propose solutions to fix it, with the aim of lessening barriers to care among near-poor people ...
Medication access for opioid use disorder lower among those involved with criminal justice
2021-04-05
PHILADELPHIA-- Approximately 6.5 million people are under correctional supervision in the United States on any given day. Justice-involved individuals (people currently or recently in prison or jail, on probation or parole, or arrested) experience higher rates of substance use disorders than the general population. In fact, among people with opioid use disorder (OUD), more than half have reported contact with the criminal justice system.
Numerous clinical studies have shown that medications for OUD -- specifically, methadone or buprenorphine -- lead to superior outcomes for retention in treatment, reduced illicit opioid use, and decreased opioid-related overdose rates and serious acute care compared with treatments that ...
Urgent care centers deter some emergency department visits, but costs remain high
2021-04-05
PHILADELPHIA-- While the emergency department (ED) functions as an integral part of the United States healthcare safety net by handling all medical complaints regardless of insurance status, ED visits are expensive, and many are for lower-acuity conditions that may be amenable to care in other settings. Previous research has suggested that greater availability of urgent care centers - freestanding facilities with extended hours that staff emergency physicians, primary care physicians, or nurse practitioners, and focus on a broad range of lower acuity complaints, like rash, muscle strain, bronchitis, and urinary tract infection - helps decrease ED visits, but whether the centers reduce or increase net spending for patients ...
Virtual "urgent care" may lead to higher rates of downstream follow-up care
2021-04-05
Even before the pandemic made telehealth a hot topic, people with minor urgent health needs had started to turn to companies that offer on-demand video chats with physicians that they don't normally see.
Insurers and employers even started buying access to this direct-to-consumer form of virtual care, hoping it might reduce in-person care, including emergency department visits.
But a new University of Michigan study casts some doubt on whether that will actually happen.
Published in the April issue of Health Affairs, the study finds that patients who had an on-demand ...
Nearly half of those convicted of sharing explicit images of partners online show remorse
2021-04-05
In a new study, researchers found nearly half of those who share explicit images of others without permission feel remorse after the fact and 24% try to deflect blame onto victims. Amy Hasinoff, a researcher at the University of Colorado Denver, joined Danish researcher Sidsel K. Harder, to take a deeper dive into the issue of sexual abuse and image sharing.
Hasinoff and Harder looked at how people who shared explicit images online spoke to police officers about the harmful acts they committed. While looking over cases where the image-sharer was caught and convicted, ...
End-of-life care remains aggressive for people with ovarian cancer
2021-04-05
People with ovarian cancer frequently receive aggressive end-of-life care despite industry guidelines that emphasize quality of life for those with advanced disease, according to a recent study.
In fact, by 2016, ICU stays and emergency department visits in the last month of life had become more common for people with ovarian cancer than they were in 2007, the earliest year from which researchers analyzed data.
The proportion of non-Hispanic Black people who turned to the emergency department for care was even higher -- double that of non-Hispanic whites. Black people were also nearly twice as likely to undergo intensive treatment, including ...
Raindrops also keep fallin' on exoplanets
2021-04-05
One day, humankind may step foot on another habitable planet. That planet may look very different from Earth, but one thing will feel familiar -- the rain.
In a recent paper, Harvard researchers found that raindrops are remarkably similar across different planetary environments, even planets as drastically different as Earth and Jupiter. Understanding the behavior of raindrops on other planets is key to not only revealing the ancient climate on planets like Mars but identifying potentially habitable planets outside our solar system.
"The lifecycle of clouds is really important when we think about planet habitability," said Kaitlyn Loftus, a graduate student in the Department ...
For some Black students, discrimination outweighed integration's benefits
2021-04-05
DURHAM, N.C. -- Integrating the American classroom has long been a goal of many who seek to eradicate racial discrimination. But a new paper from four economists, including Duke University's William A. "Sandy" Darity Jr., suggests that Black students do not always benefit from attending racially balanced schools.
Instead, Black adults who attended racially balanced high schools in the mid-20th century completed significantly less schooling than those who attended either predominantly black or predominantly white schools, the authors found.
"Standard wisdom has it that school desegregation paves the way to racial ...
A sun reflector for earth?
2021-04-05
NEW YORK, APRIL 5, 2021 -- Nine of the hottest years in human history have occurred in the last decade. Without a major shift in this climate trajectory, the future of life on Earth is in question. Should humans, whose fossil-fueled society is driving climate change, use technology to put the brakes on global warming?
Every month since September 2019 the Climate Intervention Biology Working Group, a team of internationally recognized experts in climate science and ecology, has gathered remotely to bring science to bear on that question and the consequences of geoengineering a cooler ...
Ranking virus spillover risk
2021-04-05
SARS-CoV-2 showed the world with devastating clarity the threat undetected viruses can pose to global public health. SpillOver, a new web application developed by scientists at the University of California, Davis, and contributed to by experts from all over the world, ranks the risk of wildlife-to-human spillover for newly-discovered viruses.
SpillOver is the first open-source risk assessment tool that evaluates wildlife viruses to estimate their zoonotic spillover and pandemic potential. It effectively creates a watchlist of newly-discovered viruses to help policymakers and health scientists prioritize them for further characterization, surveillance, and risk-reducing interventions.
The tool is linked to a study published in the journal PNAS, in which ...
Researchers identify genes behind uterine leiomyosarcoma
2021-04-05
New Haven, Conn. -- In a new study, Yale Cancer Center researchers have defined the genetic landscape of uterine leiomyosarcomas (uLMS). Furthermore, using fully sequenced patient-derived xenografts, the team has preclinically validated new treatment modalities, which may point to new treatments for uterine cancer. Study results were published online in an early edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS).
Uterine cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy and uterine leiomyosarcomas (uLMS) are highly lethal sarcomas arising from the myometrium, the smooth muscle layer of the uterus. They represent ...
Overfishing of Atlantic cod likely did not cause genetic changes
2021-04-05
Overfishing likely did not cause the Atlantic cod, an iconic species, to evolve genetically and mature earlier, according to a study led by Rutgers University and the University of Oslo - the first of its kind - with major implications for ocean conservation.
"Evolution has been used in part as an excuse for why cod and other species have not recovered from overfishing," said first author END ...
Sex differences in brain in response to midlife stress linked to fetal stress exposures
2021-04-05
BOSTON - Men and women whose mothers experienced stressful events during pregnancy regulate stress differently in the brain 45 years later, results of a long-term study demonstrate.
In a unique sample of 40 men and 40 women followed from the womb into their mid-forties, the brain imaging study showed that exposure during fetal development to inflammation-promoting natural substances called cytokines, produced by mothers under negative stress, results in sex-associated differences in how the adult brain responds to negative stressful situations more than 45 years after ...
Biodiversity's healthy byproduct -- nutrient-rich seafood
2021-04-05
High levels of biodiversity in aquatic settings offers a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids crucial for human health, a range of nutrients that are lacking in ecosystems where the number of species have been reduced by overfishing, pollution, or climate change, researchers report April 5 in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"What we found is that biodiversity is crucial to human health," said Yale's Joey Bernhardt, a G. Evelyn Hutchinson Postdoctoral Fellow in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and co-author of the paper.
While humans can achieve their protein requirements even with seafood from less-diverse systems, ...
A diversity of wildlife is good for our health
2021-04-05
A growing body of evidence suggests that biodiversity loss increases our exposure to both new and established zoonotic pathogens. Restoring and protecting nature is essential to preventing future pandemics. So reports a new Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) paper that synthesizes current understanding about how biodiversity affects human health and provides recommendations for future research to guide management.
Lead author Felicia Keesing is a professor at Bard College and a Visiting Scientist at Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies. She explains, "There's a persistent myth ...
To intervene or not to intervene? That is the future climate question
2021-04-05
EAST LANSING, Mich. - Nine of the hottest years in human history have occurred in the past decade. Without a major shift in this climate trajectory, the future of life on Earth is in question, which poses a new question: Should humans, whose fossil fueled society is driving climate change, use technology to put the brakes on global warming?
Michigan State University community ecologist Phoebe Zarnetske is co-lead of the Climate Intervention Biology Working Group, a team of internationally recognized experts in climate science and ecology that is bringing science to bear on the question and consequences of geoengineering a cooler Earth.
The group's ...
For 80% of Americans with resolved drug problem, significant personal achievements
2021-04-05
BOSTON - Addiction is associated with social exclusion, loss of access to resources, and general disengagement from civic life. Now, a study recently published in the journal Psychology of Addictive Behaviors and led by David Eddie, PhD, of the Massachusetts General Hospital's Recovery Research Institute has found that the majority of Americans who have resolved an alcohol or other drug problem report achievements related to self-improvement, family engagement, and civic and economic participation since resolving their addiction. Additionally, it appears these achievements accumulate with time in addiction recovery.
Incorporating data from the Recovery Research Institute's landmark 2017 National Recovery Study, which indicated ...
Surprising disconnect between physical characteristics and genetic ancestry in certain
2021-04-05
A new study by Stanford University biologists finds an explanation for the idea that physical characteristics such as skin pigmentation are "only skin deep." Using genetic modeling, the team has found that when two populations with distinct traits combine over generations, traits of individuals within the resulting "admixed" population come to reveal very little about individuals' ancestry. Their findings were published March 27 in a special edition of the American Journal of Physical Anthropology on race and racism.
"When two founding groups first come together, a visible physical trait that differed between those founders initially carries information about the genetic ancestry of admixed individuals," says Jaehee Kim, a postdoctoral research fellow in biology at Stanford and first author ...
Understanding how cancer can relapse
2021-04-05
In the fight against cancers, activating mutations in the RAS family of genes stand in the way of finding viable treatment options. Now, scientists at the University of Missouri and Yale University have discovered that one of these mutations -- oncogenic RAS or RASV12 -- is also responsible for the regrowth of cancer cells following genotoxic therapy treatment, or drugs that cause damage to a cancer cell's DNA in order to eliminate it from the body.
"Most of our knowledge of how cells respond to DNA damage is mainly derived from studies looking at the single cell level," said Yves Chabu, an assistant professor in the MU College of Arts and Science. "Therefore, we don't know much about how tumor cells respond to DNA damage in the broader ...
How climate change affects Colombia's coffee production
2021-04-05
URBANA, Ill. ¬- If your day started with a cup of coffee, there's a good chance your morning brew came from Colombia. Home to some of the finest Arabica beans, the country is the world's third largest coffee producer. Climate change poses new challenges to coffee production in Colombia, as it does to agricultural production anywhere in the world, but a new University of Illinois study shows effects vary widely depending on where the coffee beans grow.
"Colombia is a large country with a very distinct geography. The Andes Mountains cross the country from its southwest to northeast corner. Colombian coffee is currently growing in areas with different altitude levels, and climate impacts will likely be very different for low ...
Contraceptive planning is essential to optimal health for women with heart disease
2021-04-05
Pregnancy can increase the risk of morbidity and mortality in women with cardiovascular disease; however, many cardiologists are not having pre-pregnancy contraception discussions with their patients of child-bearing age. There is a need to provide evidence-based guidance for contraceptive safety and effectiveness and pregnancy planning options for this high-risk patient group, according to a paper published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC). This paper is one of a five-part JACC focus seminar series addressing a wide range of topics in the emerging cardio-obstetrics field.
Prior research has found that 68% of females have had sex at least once by the time they were 17, ...
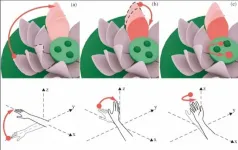
Amazing integration of technology and art: a 3D LotusMenu in your palm
2021-04-05
A recent study proposed a three-dimensional LotusMenu that can "bloom in the palm". With this menu, even if you are not Nezha, you can also control your own lotus.
The research paper is titled: "LotusMenu: A 3D Menu using Wrist and Elbow Rotation Inspired by Chinese Traditional Symbol". It's published in SCIENCE CHINA Information Sciences recently, written by Associate Professor Lu Fei's human-computer interaction research team from Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications. Based on the metaphor of the traditional lotus pattern, the researchers ...
Reclamation releases technical reports supporting the 2021 SECURE Water Act Report
2021-04-05
The Bureau of Reclamation today released final technical reports supporting the Water Reliability in the West - 2021 SECURE Water Act Report. Reclamation's 2021 West-Wide Climate and Hydrology Assessment and seven individual basin reports provide detailed information on climate change impacts and adaptation strategies to increase water supply reliability in the West. A new 2021 SECURE Report Web Portal is also available to provide a user-friendly, web-based format for delivery of information in the reports.
"Western water supply and delivery systems are affected by changing hydrologic conditions and competing demands," Deputy Commissioner Camille Calimlim Touton said. "These reports highlight Reclamation's effort to use ...
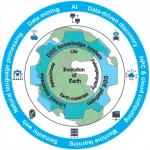
The Deep-time Digital Earth program: data-driven discovery in geosciences
2021-04-05
Humans have long explored three big scientific questions: evolution of the universe, evolution of Earth, and evolution of life. Geoscientists have embraced the mission of elucidating the evolution of Earth and life, which are preserved in the information-rich but incomplete geological record that spans more than 4.5 billion years of Earth history. Delving into Earth's deep-time history helps geoscientists decipher mechanisms and rates of Earth's evolution, unravel the rates and mechanisms of climate change, locate natural resources, and envision the future of Earth.
Two common approaches, deductive reasoning ...
Reopen and regenerate: Exosome-coated stent heals vascular injury, repairs damaged tissue
2021-04-05
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed an exosome-coated stent with a "smart-release" trigger that could both prevent reopened blood vessels from narrowing and deliver regenerative stem cell-derived therapy to blood-starved, or ischemic, tissue.
Angioplasty - a procedure that opens blocked arteries - often involves placing a metal stent to reinforce arterial walls and prevent them from collapsing once the blockage is removed. However, the stent's placement usually causes some injury to the blood vessel wall, which stimulates smooth muscle cells to proliferate and migrate to the site in an attempt to repair the injury. The result is restenosis: a re-narrowing of the blood vessel previously opened by angioplasty.
"The ...
[1] ... [2448]
[2449]
[2450]
[2451]
[2452]
[2453]
[2454]
[2455]
2456
[2457]
[2458]
[2459]
[2460]
[2461]
[2462]
[2463]
[2464]
... [8812]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.