Fewer breast cancer cases between screening rounds with 3D-mammography
2021-04-07
3D-mammography reduces the number of breast cancer cases diagnosed in the period between routine screenings, when compared with traditional mammography, according to a large study from Lund University in Sweden. The results are published in the journal Radiology.
"Our results indicate that 3D-mammography, or digital breast tomosynthesis, possibly detects cancers that would otherwise have been diagnosed later at a more advanced stage", says Kristin Johnson, doctoral student at Lund University and radiology resident at Skåne University Hospital.
A large prospective screening study conducted at Skåne ...
Researchers validate new technique for rapidly diagnosing herbicide-resistant weeds
2021-04-07
WESTMINSTER, Colorado - April 07, 2021 - As the number of weed populations resistant to multiple herbicides continues to soar, it is clear that better tools are needed to help growers rapidly diagnose resistance issues. With more timely access to information, they can take earlier, proactive steps to keep resistant weeds from spreading.
A recent article in the journal END ...
Red deer have personality and it is related to their dominance behavior
2021-04-07
An international team of researchers has studied individual differences in the behaviour of red deer. They found that several observed behaviours form a personality component, which they labelled "Confidence/Aggressiveness".
As is commonly known, individual people behave consistently different from each other and these kinds of consistent differences in behaviour are called personality. Studies on species other than humans, from insects to elephants, have found that personalities are widespread in nature.
The team consists of researchers from the Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, the University of South Bohemia, Czech Republic, the University of Vienna, Austria, and the University of Turku, Finland and is led by Bruno Esattore from the Department of ...
Anticoagulation and cerebral small vessel disease
2021-04-07
Cardiovascular diseases are usually complex and affect multiple organs simultaneously. Treatments for vascular diseases in the brain may therefore have implications for the treatment of cardiac diseases. It is therefore important to understand the respective causes and effects. This study explores the causes of intracerebral haemorrhages and links them to the risk of stroke associated with atrial fibrillation. It suggests a fundamental new assessment of the effects of blood thinning on intracerebral haemorrhages.
About 1,000 patients with intracerebral haemorrhage are treated at stroke units each year in Switzerland. Intracerebral haemorrhages are more often fatal than other forms of strokes, ...
Entropy measurements reveal exotic effect in "magic-angle" graphene
2021-04-07
Most materials go from being solids to liquids when they are heated. One rare counter-example is helium-3, which can solidify upon heating. This counterintuitive and exotic effect, known as the Pomeranchuk effect, may now have found its electronic analogue in a material known as magic-angle graphene, says a team of researchers from the Weizmann Institute of Science led by Prof. Shahal Ilani, in collaboration with Prof. Pablo Jarillo-Herrero's group at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
This result, published today in Nature, comes thanks to the first ever measurement of electronic entropy in an atomically-thin two dimensional ...
New Lyme disease test distinguishes between early and late-stage disease
2021-04-07
For those who live in an area blighted by ticks, the threat of Lyme disease can cast a shadow over the joy of spring and summer. These blood-sucking arachnids can transmit bacteria into the bloodstream of their unsuspecting host, causing the disease. Early treatment is essential, but current tests are not usually sensitive enough to detect the disease in early-stage patients. A recent study in open-access journal END ...
Scientists discover two new species of ancient, burrowing mammal ancestors
2021-04-07
A joint research team led by Dr. MAO Fangyuan and Dr. ZHANG Chi from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. MENG Jin from the American Museum of Natural History have discovered two new species of mammal-like, burrowing animals that lived about 120 million years ago in what is now northeastern China.
The new species, described in Nature on April 7, are distantly related. However, they independently evolved traits to support their digging lifestyle. They represent the first "scratch diggers" discovered in this ecosystem.
"There are many hypotheses about why animals dig into the soil and live underground," said Prof. MENG, lead author of the study. "For protection against predators, ...
Study finds late night snacks may hurt your workplace performance
2021-04-07
A recent study finds that unhealthy eating behaviors at night can make people less helpful and more withdrawn the next day at work.
"For the first time, we have shown that healthy eating immediately affects our workplace behaviors and performance," says Seonghee "Sophia" Cho, corresponding author of the study and an assistant professor of psychology at North Carolina State University. "It is relatively well established that other health-related behaviors, such as sleep and exercise, affect our work. But nobody had looked at the short-term effects of unhealthy eating."
Fundamentally, the researchers had two questions: Does unhealthy eating behavior affect you at work the next day? And, if so, why?
For the study, ...
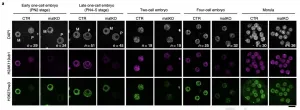
Inheriting acquired traits requires trailblazer modifications to unfertilized eggs
2021-04-07
An epigenetic study at the RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences shows that in mouse egg cells, modifications to histone H2A at lysine 119 lay the groundwork for inherited DNA functional modifications from the mother.
In books and the movies, a group of people on a special mission always sends out a scout to do reconnaissance before they proceed. Sometimes, the scouts leave signs or markers that allow the group to know where there should go. Researchers led by Azusa Inoue at the RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences in Japan have discovered a mark left behind in unfertilized egg cells that determine which DNA modifications ...
A new mouse model gave surprising findings about Folling Disease
2021-04-07
In Norway, all newborn children are tested for 25 rare genetic diseases through the Newborn Screening program, and the most common of these is phenylketonuria (abbreviated to PKU), known as Folling Disease.
Every year, between 3-7 children are born in Norway with PKU, and this diagnosis has a great impact on the rest of their lives. People with PKU must follow a very strict diet all their lives, where they must avoid almost all foods that contain proteins.
"Failure to implement the diet from birth may result in irreversible physical problems and brain damage, and optimal brain function requires life-long adherence", explains Professor ...
UMD tracks the adoption of green infrastructure, from water conservation to policy
2021-04-07
In a new paper published in the Journal of Environmental Policy & Planning, the University of Maryland teamed up with local researchers to examine green infrastructure adoption and leadership in Tucson, Arizona, an interesting case study where grassroots efforts have helped to drive policy change in a growing urban area surrounded by water-constrained desert. Green infrastructure (any installation that manages water or environmental factors, such as rain gardens, stormwater basins, or urban tree cover) is slowly transitioning from a fringe activity to an important part of the way governments and municipalities are dealing with water and the local effects of a changing climate. By examining ...
Study revises understanding of cancer metabolism
2021-04-07
Tumors consume glucose at high rates, but a team of Vanderbilt researchers has discovered that cancer cells themselves are not the culprit, upending models of cancer metabolism that have been developed and refined over the last 100 years.
Instead, non-cancer cells in a tumor -- primarily immune cells called macrophages -- have the highest glucose uptake, the group reported April 7 in the journal Nature. The findings that different cells in the tumor microenvironment use distinct nutrients according to their own metabolic programs could be exploited to develop new therapies and imaging strategies, ...
Early indicators of magma viscosity could help forecast a volcano's eruption style
2021-04-07
Washington, DC-- The 2018 eruption of Kīlauea Volcano in Hawai'i provided scientists with an unprecedented opportunity to identify new factors that could help forecast the hazard potential of future eruptions.
The properties of the magma inside a volcano affect how an eruption will play out. In particular, the viscosity of this molten rock is a major factor in influencing how hazardous an eruption could be for nearby communities.
Very viscous magmas are linked with more powerful explosions because they can block gas from escaping through vents, allowing pressure ...
Childhood cognitive problems could lead to mental health issues in later life
2021-04-07
Children experiencing cognitive problems such as low attention, poor memory or lack of inhibition may later suffer mental health issues as teenagers and young adults, a new study reveals.
Targeting specific markers in childhood for early treatment may help to minimise the risk of children developing certain psychopathological problems in adolescence and adult life, such as borderline personality disorder, depression and psychosis.
Cognitive deficits are core features of mental disorders and important in predicting long-term prognosis - the researchers' work indicates that individual patterns of such deficits predate ...
Ocular assessments of newborns gestationally exposed to maternal COVID-19 infection
2021-04-07
What The Study Did: This case series examines whether maternal SARS-CoV-2 is associated with outcomes in the eyes of their newborns.
Authors: Olívia Pereira Kiappe, M.D., M.Sc., of Universidade Federal de São Paulo in Brazil, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2021.1088)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
Association of race/ethnicity, sex, income with well-being during COVID-19
2021-04-07
What The Study Did: This observational study identifies and quantifies the association of race/ethnicity, sex and income, as well as state-specific lockdown measures, with six well-being dimensions in the United States.
Authors: Leigh C. Hamlet, B.S., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.7373)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
The muon's magnetic moment fits just fine
2021-04-07
A new estimation of the strength of the magnetic field around the muon--a sub-atomic particle similar to, but heavier than, an electron--closes the gap between theory and experimental measurements, bringing it in line with the standard model that has guided particle physics for decades.
A paper describing the research by an international team of scientists appears April 8, 2021 in the journal Nature.
Twenty years ago, in an experiment at Brookhaven National Laboratory, physicists detected what seemed to be a discrepancy between measurements of the muon's "magnetic ...
New dermatologic presentation associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection
2021-04-07
What The Study Did: Researchers report on the observation of a newly associated mucocutaneous eruption in a pediatric patient with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection
Authors: Zachary E. Holcomb, M.D., of Boston Children's Hospital, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0385)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers ...
State immigrant policies and preterm births
2021-04-07
What The Study Did: In this observational study of 3.4 million live births in 2018, criminalizing immigrant policies were associated with higher rates of preterm birth for Black women born outside the U.S., while inclusive immigrant policies were associated with lower preterm birth for all women born outside the U.S.,particularly White women born outside the U.S.
Authors: May Sudhinaraset, Ph.D., of the Jonathan and Karin Fielding School of Public Health at the University of California, Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
Projecting cancer cases, types, deaths in US to 2040
2021-04-07
What The Study Did: Researchers projected to the year 2040 what will become the most common and deadly cancers in the United States.
Authors: Lola Rahib, Ph.D., of Cancer Commons in Mountain View, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4708)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and ...
Evaluating anxiety, depression among transgender children, teens
2021-04-07
What The Study Did: Questionnaire responses were compared to examine whether transgender children and teens experience significantly higher levels of anxiety and depression than their cisgender peers.
Authors: Dominic J. Gibson, Ph.D., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4739)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, ...
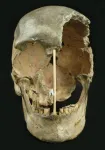
Neanderthal ancestry identifies oldest modern human genome
2021-04-07
Ancient DNA from Neandertals and early modern humans has recently shown that the groups likely interbred somewhere in the Near East after modern humans left Africa some 50,000 years ago. As a result, all people outside Africa carry around 2% to 3% Neandertal DNA. In modern human genomes, those Neandertal DNA segments became increasingly shorter over time and their length can be used to estimate when an individual lived. Archaeological data published last year furthermore suggests that modern humans were already present in southeastern Europe 47-43,000 years ago, but due to a scarcity of fairly complete human fossils and the lack of genomic DNA, there is little understanding of who these early human colonists were - or of their relationships to ancient and present-day ...
First transiting exoplanet's 'chemical fingerprint' reveals its distant birthplace
2021-04-07
Analysis by international team including University of Warwick of the first transiting exoplanet that was discovered has revealed six different chemicals in its atmosphere.
It is the first time that so many molecules have been measured, and points to an atmosphere with more carbon present than oxygen
This chemical fingerprint is typical of a planet that formed much further away from its sun than the current location, a mere 7 million km from the star
Study tests techniques that will be useful for detecting signs of potentially habitable planets when more powerful telescopes come online
Artist's impression available - see Notes to Editors
Astronomers have found ...
Paranoia therapy app SlowMo helps people 'slow down' and manage their fears
2021-04-07
A new clinical trial from King's College London's Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology, & Neuroscience, in collaboration with Oxford University, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust, Sussex University, and Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust has established an innovative therapy as an effective means of treating paranoid thoughts in people experiencing psychosis.
In research published in JAMA Psychiatry today, participants of the SlowMo therapy trial had eight face-to-face therapy sessions with support from an interactive web platform and app. The app, designed in collaboration with people experiencing psychosis and the Royal College of Art, is used outside the clinic to help individuals feel safer in daily life.
Paranoia is fuelled ...
Reversing a genetic cause of poor stress responses in mice
2021-04-07
Everyone faces stress occasionally, whether in school, at work, or during a global pandemic. However, some cannot cope as well as others. In a few cases, the cause is genetic. In humans, mutations in the OPHN1 gene cause a rare X-linked disease that includes poor stress tolerance. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Linda Van Aelst seeks to understand factors that cause specific individuals to respond poorly to stress. She and her lab studied the mouse gene Ophn1, an analog of the human gene, which plays a critical role in developing brain cell connections, memories, and stress tolerance. When Ophn1 was removed in a specific part of the ...
[1] ... [2442]
[2443]
[2444]
[2445]
[2446]
[2447]
[2448]
[2449]
2450
[2451]
[2452]
[2453]
[2454]
[2455]
[2456]
[2457]
[2458]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.