Rescuing street art from vandals' graffiti
2021-04-13
WASHINGTON, April 13, 2021 -- From Los Angeles and the Lower East Side of New York City to Paris and Penang, street art by famous and not-so-famous artists adorns highways, roads and alleys. In addition to creating social statements, works of beauty and tourist attractions, street art sometimes attracts vandals who add their unwanted graffiti, which is hard to remove without destroying the underlying painting. Now, researchers report novel, environmentally friendly techniques that quickly and safely remove over-paintings on street art.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2021 is being held online April 5-30. Live sessions will be hosted April 5-16, and on-demand and networking ...
Study links structural brain changes to behavioral problems in children who snore
2021-04-13
WHAT:
A large study of children has uncovered evidence that behavioral problems in children who snore may be associated with changes in the structure of their brain's frontal lobe. The findings support early evaluation of children with habitual snoring (snoring three or more nights a week). The research, published in Nature Communications, was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) and nine other Institutes, Centers, and Offices of the National Institutes of Health.
Large, population-based studies have established a clear link between snoring and behavioral problems, such as inattention or hyperactivity, but the exact nature ...
Ancient ammonoids' shell designs may have aided buoyancy control
2021-04-13
Ammonoids, ancestors of today's octopus, squid and cuttlefish, bobbed and jetted their way through the oceans for around 340 million years beginning long before the age of the dinosaurs. If you look at the fossil shells of ammonoids over the course of that 340 million years, you'll notice something striking--as time goes on, the wavy lines inside the shell become more and more complex, eventually becoming frilled almost like the edges of kale leaves.
Fossil of Menuites oralensis with external shell removed to reveal intricate suture patterns.
These ...
Habitual snoring linked to significant brain changes in children
2021-04-13
Children who regularly snore have structural changes in their brain that may account for the behavioral problems associated with the condition including lack of focus, hyperactivity, and learning difficulties at school. That is the finding of a new study conducted by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), which was published today in the journal Nature Communications.
The research was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) and nine other Institutes, Centers, and Offices of the National Institutes of Health.
To conduct study, the researchers examined MRI images collected from more than 10,000 children aged 9 to 10 years enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development ...
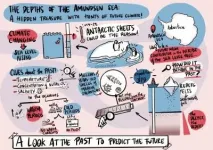
Past Global Changes Horizons - a new paleoscience magazine for teenagers and young adults
2021-04-13
Past Global Changes Horizons is a scientific review of why the study of Earth's history is important, and uses comics, pictures, and drawings that support short papers with strong messages about past sciences and how to prepare for a changing future. Articles cover different environments across the planet, from caves to oceans, and from Antarctica to the Rift valley in Africa.
Each of the 18 contributions addresses a scientific question and includes appealing and understandable figures or images, without sacrificing scientific rigor. Tips and suggestions for further research and discussion topics are also included, meaning Horizons is ...
Crop rotations with beans and peas offer more sustainable and nutritious food production
2021-04-13
Growing more legumes, like beans and lentils, is potentially a more sustainable and nutritious approach to European agriculture, shows a new study in END ...
Five research-backed steps to a pro-vaccination social media campaign
2021-04-13
PITTSBURGH, April 13, 2021 - What can vaccine proponents, clinicians and public health communicators learn from "anti-vaxxers?" A lot, according to new guidance for pro-vaccination social media events written by University of Pittsburgh health scientists.
The five-part guidelines, published today in the journal Vaccine, arose from an analysis of a grassroots pro-vaccination campaign organized last year by popular physician and social media personality Zubin Damania, M.D., colloquially known as "ZDoggMD." Unexpectedly, more than three-quarters of the tweets associated with the ...
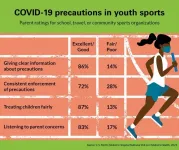
1 in 4 parents give youth sports low rankings for enforcement of COVID-19 guidelines
2021-04-13
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- For young athletes, the new normal on soccer fields and basketball courts means temperature checks before practice, wearing masks through games and a sparse in-person fan base.
But that hasn't kept children and teens from playing. Close to a fourth of parents say their child has participated in school, travel, or community sports during the fall or winter months, according to the C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health at the University of Michigan.
And while the majority of parents give their child's sports organization high marks for communication about safety protocols, one in four rate their sports ...
Doctors still reluctant to prescribe medical cannabis: McMaster
2021-04-13
Hamilton, ON (April 13, 2021) - Ontario doctors are still hesitant to prescribe medical cannabis to patients suffering long-term pain 20 years after it was first introduced, says a new study carried out at McMaster University.
Physicians surveyed said their main concerns relate to possible ill-effects and a lack of understanding regarding their effectiveness as painkillers.
Of particular concern among doctors were potentially harmful effects on cognitive development, a possible worsening of existing mental illnesses in patients and the drug's effects in older adults, which may include dizziness or drowsiness.
Meanwhile, the ...
Influence of sea surface temperature in the Indian Ocean on air quality in the Yangtze River Delta region
2021-04-13
As the foremost economic zone in China, the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) region has recently been experiencing more frequent haze events, resulting in dramatic damages to human and ecosystem health.
Anthropogenic aerosol emissions play a key role in affecting the formation of haze events. However, aside from local sources of pollution, some studies have found that external and preceding climate drivers, such as Arctic sea ice and subtropical western Pacific sea surface temperature, are also influential factors. However, most research has mainly been confined to analyzing the effects on haze pollution in the Northern Hemisphere, with few considering the Southern Hemisphere.
"We found that the December sea surface temperature ...
Frog species with 6 sex chromosomes offer new clues on evolution of complex XY systems
2021-04-13
Scientists found six sex chromosomes in the Odorrana swinhoana frog species endemic in Taiwan, giving new insights into how complex XY systems evolve.
The discovery was a surprise to the international research team led by Associate Professor Ikuo Miura of Hiroshima University's Amphibian Research Center. In 1980, the first reported instance of multiple sex chromosome systems in amphibians was found in the Taiwanese brown frog Raina narina -- a synonym for O. swinhoana -- which had a male-specific translocation between two chromosomes. Its sex chromosomes could be described as ?X1Y1X2Y2-?X1X1X2X2.
The ...
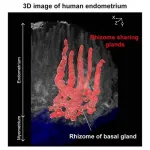
Study reveals the 3D structure of human uterine endometrium and adenomyosis tissue
2021-04-13
Niigata, Japan- New insights into the three-dimensional (3D) morphology of the human uterine endometrium could advance our understanding of the mechanisms of endometrial regeneration and fertilized egg implantation while clarifying the pathogenesis of menstrual disorders, infertility and endometrium-related diseases such as adenomyosis, endometriosis, endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial cancer.
The endometrial glands are comprised of complicated winding and branching structures, and conventional 2D imaging techniques have been unable to adequately assess their shape. This limitation has prevented elucidation of the mechanisms of endometrial regeneration during the menstrual cycle and the location of endometrial progenitor cells. Recent developments in 3D tissue-clearing imaging ...
ETRI develops a haptic film activated by LEDs
2021-04-13
A Korean research team succeeded in developing a technology generating various vibration using LED light signals. The technology allows various tactile sensations by area and reduction in size by considerably lowering the cost of light source, and these are expected to be applied to many industries including automobile and electronics.
The Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute, or ETRI for short, announced that it succeeded in developing a technology to implement various vibrations using LED. This technology was widely recognized as published on the cover of the February 10 issue of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces1), a leading ...
Researchers' work will help the pipeline industry limit the destructive power of bubbles
2021-04-13
Researchers have answered key questions to help prevent damage and improve the safety of hydraulic systems used for pipelines, water turbines and other applications.
The work, led by engineers at the University of Waterloo, investigates a phenomenon known as cavitation, or the formation and collapse of destructive gas-filled bubbles resulting from rapid pressure changes in liquids.
Cavitation is behind a well-known party trick that involves shattering the bottom of a liquid-filled bottle by striking its open top with the palm of your hand.
"The growth and collapse of cavitation bubbles are fascinating," said Zhao Pan, a professor of mechanical and mechatronics engineering who led the research. ...
E-cigarettes with a cigarette-like level of nicotine are effective in reducing smoking
2021-04-13
RICHMOND, Va. (April 12, 2021) -- E-cigarettes that deliver a cigarette-like amount of nicotine are associated with reduced smoking and reduced exposure to the major tobacco-related pulmonary carcinogen, NNAL, even with concurrent smoking, according to a new study led by researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University and Penn State College of Medicine in Hershey, Pennsylvania.
The study, which will be published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine journal, provides new and important information for smokers who may be trying to use e-cigarettes as a means to cut down on their smoking habit and lower their exposure to harmful toxicants.
"[We found] e-cigarettes with nicotine delivery like a combustible cigarette were effective in helping reduce ...
Deep Learning model developed at UHN to maximize lifespan after liver transplant
2021-04-13
Toronto (April 12, 2021) - Researchers from University Health Network have developed and validated an innovative deep learning model to predict a patient's long-term outcome after receiving a liver transplant.
First of its kind in the field of Transplantation, this model is the result from a collaboration between the Ajmera Transplant Centre and Peter Munk Cardiac Centre. The study, published in Lancet Digital Health, shows it can significantly improve long-term survival and quality of life for liver transplant recipients.
"Historically, we have seen good advances in one-year post-transplant outcomes, but survival in the longer term hasn't significantly improved in the past decades," explains Dr. Mamatha Bhat, a hepatologist with the Ajmera Transplant Centre ...
Convenience over reputation: Study looks at how older adults pick a doctor
2021-04-13
Convenience and access win out over reputation when people over 50 look for a doctor for themselves, a new study finds.
But online ratings and reviews of physicians play an important role, and should receive attention from providers and policymakers, the researchers say.
About 20% of older adults called such ratings very important to them, but 43% said they had checked such reviews in the past for physicians they were considering for themselves.
Still, factors like insurance acceptance, appointment availability, location and hours won out over reputational information, although about 40% said a recommendation from another physician was very important to them. Recommendations from family and friends ...
Ocean bacteria release carbon into the atmosphere
2021-04-12
A team led by University of Minnesota researchers has discovered that deep-sea bacteria dissolve carbon-containing rocks, releasing excess carbon into the ocean and atmosphere. The findings will allow scientists to better estimate the amount of carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, a main driver of global warming.
The study is published in END ...
Spotting cows from space
2021-04-12
Cows don't seem to have a whole lot going on most of the time. They're raised to spend their days grazing in the field, raised for the purpose of providing milk or meat, or producing more cows. So when students in UC Santa Barbara ecologist Doug McCauley's lab found themselves staring intently at satellite image upon image of bovine herds at Point Reyes National Seashore, it was funny, in a "Far Side" kind of way.
"There were about 10 undergrads involved in the project, spotting cows from space -- not your typical student research and always amusing to see in the ...
Scientists watch 2D puddles of electrons emerge in a 3D superconducting material
2021-04-12
Creating a two-dimensional material, just a few atoms thick, is often an arduous process requiring sophisticated equipment. So scientists were surprised to see 2D puddles emerge inside a three-dimensional superconductor - a material that allows electrons to travel with 100% efficiency and zero resistance - with no prompting.
Within those puddles, superconducting electrons acted as if they were confined inside an incredibly thin, sheet-like plane, a situation that requires them to somehow cross over to another dimension, where different rules of quantum physics apply.
"This is a tantalizing example of emergent behavior, which is often difficult or impossible to replicate by trying to engineer it from scratch," said Hari Manoharan, a professor at Stanford University and investigator ...
Research suggests SEC's increasing focus on terrorism may limit financial oversight
2021-04-12
When Iranian authorities started seizing Barbie dolls from Tehran toy shops in 2012, Mattel Inc. execs faced concerns not only about the dolls' attire -- miniskirts and swimsuits considered immodest in an Islamic country -- but also questions from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) about Mattel's ties to Iran.
U.S. businesses are restricted from business in Iran, which U.S. authorities have designated a state sponsor of terrorism (SST). The number of SEC inquiries about potential terrorist ties has grown substantially in recent years, and according to new research from Duke University's Fuqua School of Business, the increase could reduce the quality of the agency's financial reporting oversight.
"Comments on terrorism are getting to a critical level of importance ...
Plastic planet: Tracking pervasive microplastics across the globe
2021-04-12
Really big systems, like ocean currents and weather, work on really big scales. And so too does your plastic waste, according to new research from Janice Brahney from the Department of Watershed Sciences. The plastic straw you discarded in 1980 hasn't disappeared; it has fragmented into pieces too small to see, and is cycling through the atmosphere, infiltrating soil, ocean waters and air. Microplastics are so pervasive that they now affect how plants grow, waft through the air we breathe, and permeate distant ecosystems. They can be found in places as varied as the human bloodstream to ...
Gut epithelium muscles up against infection
2021-04-12
To maximise absorption of nutrients from the diet, the intestinal mucous membrane has a large surface area. However, this also makes it vulnerable to attack from aggressive gut microbes. A new study by Uppsala University researchers now shows that the surface layer of the mucosa, known as the epithelium, can rapidly contract when it recognises a bacterial attack. The results are published in the journal PNAS.
Every year, hundreds of millions of people worldwide suffer from bacterial gut infections of one kind or another, which are often hard to treat. Antibiotics can kill the normal flora of the intestine, ...
Scientists discover three liquid phases in aerosol particles
2021-04-12
Researchers at the University of British Columbia have discovered three liquid phases in aerosol particles, changing our understanding of air pollutants in the Earth's atmosphere.
While aerosol particles were known to contain up to two liquid phases, the discovery of an additional liquid phase may be important to providing more accurate atmospheric models and climate predictions. The study was published today in PNAS.
"We've shown that certain types of aerosol particles in the atmosphere, including ones that are likely abundant in cities, can often have three distinct liquid phases." says ...
New mechanism identified behind blindness in older adults
2021-04-12
Using laboratory-grown roundworms as well as human and mouse eye tissue, University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers have identified a new potential mechanism for age-related macular degeneration--the leading cause of blindness among older adults. The UMSOM researchers say that the findings suggest a new and distinct cause that is different from the previous model of a problematic immune system, showing that the structural organization of the eye's light-detecting cells may be affected by the disease.
The discovery offers the potential to identify new molecular targets to treat the disease. Their discovery was published on April 12 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
According to the National Eye Institute, ...
[1] ... [2426]
[2427]
[2428]
[2429]
[2430]
[2431]
[2432]
[2433]
2434
[2435]
[2436]
[2437]
[2438]
[2439]
[2440]
[2441]
[2442]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.