Using sound waves to make patterns that never repeat
2021-04-14
Mathematicians and engineers at the University of Utah have teamed up to show how ultrasound waves can organize carbon particles in water into a sort of pattern that never repeats. The results, they say, could result in materials called "quasicrystals" with custom magnetic or electrical properties.
The research is published in Physical Review Letters.
"Quasicrystals are interesting to study because they have properties that crystals do not have," says Fernando Guevara Vasquez, associate professor of mathematics. "They have been shown to be stiffer than similar periodic or disordered materials. They can also conduct electricity, ...
Mediterranean diet with lean beef may lower risk factors for heart disease
2021-04-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Eating red meat may have a bad reputation for being bad for the heart, but new research found that lean beef may have a place in healthy diets, after all.
In a randomized controlled study, researchers found that a Mediterranean diet combined with small portions of lean beef helped lower risk factors for developing heart disease, such as LDL cholesterol.
Jennifer Fleming, assistant teaching professor of nutrition at Penn State, said the study suggests that healthy diets can include a wide variety of foods, such as red meat, and still be heart friendly.
"When you create a healthy diet built on fruits, vegetables, and other plant-based foods, it leaves room for moderate amounts of other foods like lean beef," Fleming said. "There are still ...
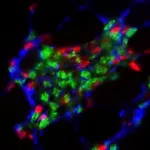
New discovery could lead to therapies for patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy
2021-04-14
Irvine, CA - April 14, 2021 - A new study, led by the University of California, Irvine (UCI), reveals how chronic inflammation promotes muscle fibrosis, which could inform the development of new therapies for patients suffering from Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), a fatal muscle disease.
Titled, "A Stromal Progenitor and ILC2 Niche Promotes Muscle Eosinophilia and Fibrosis-Associated Gene Expression," the study was published today in Cell Reports.
Chronic inflammation is a major pathological process contributing to the progression and severity of several degenerative disorders, including Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Studies directed at establishing a causal link between muscular ...
Guide for science outreach
2021-04-14
What are scientists passionate about? What do they actually do, and why does it matter? Answering questions like these is often part of public outreach efforts that, through demystifying the world of science for non-scientists, can increase appreciation for science and boost support for important research initiatives. Outreach can also make the sciences attractive and accessible to a broader diversity of people, who, in turn, can bring new ideas and perspectives.
"Science is having challenges in terms of getting the general public to support it and ...
Diabetes drug shows potential in fighting cancer
2021-04-14
BOSTON - The anti-diabetic drug phenformin may prompt stronger cancer-fighting activities than its sister compound metformin, a finding that could have major implications for current and future clinical trials investigating both agents for their anti-cancer potential, according to researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). In a review article in Trends in Cancer, the team presented evidence that immunotherapies such as immune checkpoint inhibitors (which enable T cells to attack and kill cancer cells) in combination with phenformin may also be a promising way to repurpose this diabetic drug as an anti-cancer ...
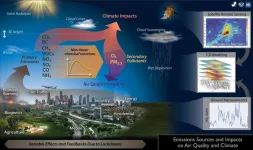
Impacts of coronavirus lockdowns: New study collects data on pollutants in the atmosphere
2021-04-14
One consequence of the coronavirus pandemic has been global restrictions on mobility. This, in turn, has had an effect on pollution levels in the atmosphere. Researchers from across the world are using this unique opportunity to take measurements, collect data, and publish studies. An international team led by Forschungszentrum Jülich's Institute of Climate and Energy Research - Troposphere has now published a comprehensive review providing an overview of results up to September 2020. The study also has its own dedicated website, where additional measurement data can be added to supplement and refine existing research results. At the same time, this collection of data allows scientifically substantiated predictions to be made about the ...
Scientists program microalgae's 'oil factory' to produce various oils
2021-04-14
By combining the 'chassis' of an oil-producing microalgae with genes from a Cuphea plant, scientists from the Single-Cell Center, Qingdao Institute of BioEnergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), can turn the algae into a microbial cell factory that can produce various oils with different properties.
The study was published in Metabolic Engineering on April 3.
Oils are composed of fatty acids, and fatty acids are composed in part of chains of carbon atoms. The length of these carbon chains can impact the physical properties of the fatty acid and thus the ...
ER visits for suicidal behavior declined during the first 8 months of pandemic, U-M study shows
2021-04-14
While people may expect suicide rates to rise during a worldwide crisis such as the COVID-19 pandemic, a University of Michigan study suggests the onset of the pandemic and state of emergency executive orders likely did not increase suicide-related behavior in the early months of the outbreak.
The report, led by U-M researchers Rachel Bergmans and Peter Larson, found that emergency room visits related to suicide attempt and self-harm decreased by 40% during the first eight months of Michigan's lockdown. Their results are published in the Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health.
The study compared emergency room reports of suicide attempt and intentional self-harm at a hospital in Michigan's Washtenaw County during the first 8 months of the ...
Plasma device designed for consumers can quickly disinfect surfaces
2021-04-14
The COVID-19 pandemic has cast a harsh light on the urgent need for quick and easy techniques to sanitize and disinfect everyday high-touch objects such as doorknobs, pens, pencils, and personal protective gear worn to keep infections from spreading. Now scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory and the New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT) have demonstrated the first flexible, hand-held, device based on low-temperature plasma -- a gas that consists of atoms, molecules, and free-floating electrons ...
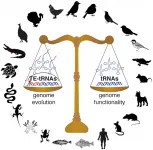
Birds take tRNA efficiency to new heights
2021-04-14
Birds have been shaped by evolution in many ways that have made them distinct from their vertebrate cousins. Over millions of years of evolution, our feathered friends have taken to the skies, accompanied by unique changes to their skeleton, musculature, respiration, and even reproductive systems. Recent genomic analyses have identified another unique aspect of the avian lineage: streamlined genomes. Although bird genomes contain roughly the same number of protein-coding genes as other vertebrates, their genomes are smaller, containing less noncoding DNA. Scientists are still exploring the potential consequences of this genome reduction on bird biology. In a new ...
Suppression of COVID-19 waves reflects time-dependent social activity, not herd immunity
2021-04-14
UPTON, NY--Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) have developed a new mathematical model for predicting how COVID-19 spreads. This model not only accounts for individuals' varying biological susceptibility to infection but also their levels of social activity, which naturally change over time. Using their model, the team showed that a temporary state of collective immunity--what they coined "transient collective immunity"--emerged during early, fast-paced stages of the epidemic. However, subsequent "waves," ...
Why do some alloys become stronger at room temperature?
2021-04-14
An alloy is typically a metal that has a few per cent of at least one other element added. Some aluminium alloys have a seemingly strange property.
"We've known that aluminium alloys can become stronger by being stored at room temperature - that's not new information," says Adrian Lervik, a physicist at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
The German metallurgist Alfred Wilm discovered this property way back in 1906. But why does it happen? So far the phenomenon has been poorly understood, but now Lervik and his colleagues from NTNU and SINTEF, the largest independent research institute in Scandinavia, have tackled that question.
Lervik recently completed his doctorate at NTNU's Department of Physics. His work explains an important part of this ...
Air pollution may affect severity and hospitalization in COVID-19 patients
2021-04-14
Patients who have preexisting respiratory conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and live in areas with high levels of air pollution have a greater chance of hospitalization if they contract COVID-19, says a University of Cincinnati researcher.
Angelico Mendy, MD, PhD, assistant professor of environmental and public health sciences, at the UC College of Medicine, looked at the health outcomes and backgrounds of 1,128 COVID-19 patients at UC Health, the UC-affiliated health care system in Greater Cincinnati.
Mendy led a team of researchers in an individual-level study which used a statistical model to evaluate the association between long-term exposure to particulate matter less or equal to 2.5 micrometers -- it refers to a mixture of tiny particles and ...
Protein found to control drivers of normal growth and cancer
2021-04-14
Researchers have found a long-sought enzyme that prevents cancer by enabling the breakdown of proteins that drive cell growth, and that causes cancer when disabled.
Publishing online in Nature on April 14, the new study revolves around the ability of each human cell to divide in two, with this process repeating itself until a single cell (the fertilized egg) becomes a body with trillions of cells. For each division, a cell must follow certain steps, most of which are promoted by proteins called cyclins.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the work revealed that an enzyme called AMBRA1 labels a key class of cyclins for destruction by cellular machines that break down proteins. The work finds that the enzyme's control of cyclins is essential ...
Backyard bird feeding sparks a songbird 'reverse migration'
2021-04-14
ITHACA, N.Y. - Eurasian Blackcaps are spunky and widespread warblers that breed across much of Europe. Many of them migrate south to the Mediterranean region and Africa after the breeding season. But thanks to a changing climate and an abundance of food resources offered by people across the United Kingdom and Ireland, some populations of Blackcaps have recently been heading north for the winter, spending the colder months in backyard gardens of the British Isles.
New research published this week in Global Change Biology shows some of the ways that bird feeders, fruit-bearing plants, and a warming world are changing both the movements and the physiology of the Blackcaps that spend the winter in Great Britain and Ireland.
"Many migratory birds are ...
Telling sunbathers what they don't want to hear: Tanning is bad
2021-04-14
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Most young women already know that tanning is dangerous and sunbathe anyway, so a campaign informing them of the risk should take into account their potential resistance to the message, according to a new study.
Word choice and targeting a specific audience are part of messaging strategy, but there is also psychology at play, researchers say - especially when the message is telling people something they don't really want to hear.
"A lot of thought goes into the content, but possibly less thought goes into the style," said Hillary Shulman, senior author of the study and an assistant ...
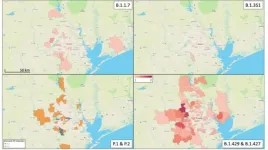
Significant spread of all coronavirus variants tracked in Houston area
2021-04-14
Philadelphia, April 14, 2021 - In late 2020, several concerning SARS-CoV-2 variants emerged globally. They are believed to be more easily transmissible, and there is concern that some may reduce the effectiveness of antibody treatments and vaccines. An extensive genome sequencing program run by the Houston Methodist health system has identified all six of the currently identified SARS-CoV-2 variants in their patients. A new study appearing in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, finds that the variants are widely spread across the Houston metropolitan area.
"Before the SARS-CoV-2 virus arrived in Houston, we planned an integrated strategy to confront ...
Channel migration plays leading role in river network evolution, study finds
2021-04-14
A new study by former University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign graduate student Jeffrey Kwang, now at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst; Abigail Langston, of Kansas State University; and Illinois civil and environmental engineering professor Gary Parker takes a closer look at the vertical and lateral – or depth and width – components of river erosion and drainage patterns. The study is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“A tree’s dendritic structure exists to provide fresh ends for leaves to grow and collect as much light as possible,” Parker said. “If you chop off some branches, they will regrow in a dendritic pattern. ...
Scientists identify potential drug candidates for deadly pediatric leukemia
2021-04-14
LA JOLLA, CALIF. - April 14, 2021 - Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute have shown that two existing drug candidates--JAK inhibitors and Mepron--hold potential as treatments for a deadly acute myeloid leukemia (AML) subtype that is more common in children. The foundational study, published in the journal Blood, is a first step toward finding effective treatments for the hard-to-treat blood cancer.
"While highly successful therapies have been found for other blood cancers, most children diagnosed with this AML subtype are still treated with harsh, toxic chemotherapies," says Ani Deshpande, Ph.D., assistant professor in Sanford Burnham Prebys' ...
Retracing his steps
2021-04-14
Half a century had passed, but UC Santa Barbara Professor Armand Kuris was sure he'd been here before. In fact, he was completely certain. After all, he had detailed notes of the location, written carefully in India ink when he was still a graduate student.
This time, though, Kuris served as a seasoned mentor for several young researchers who hadn't even been born when he first visited the site. Truth be told, many of their parents hadn't yet been born.
This was just one of many shorelines along the coast of the Pacific Northwest where the group was repeating ecological field work Kuris conducted in 1969 and 70. He teamed up with Assistant Professor Chelsea Wood of the University of Washington and her lab -- all parasite ...
How transcription factors work together in cancer formation
2021-04-14
A new study co-authored by University of Colorado Cancer Center researcher Srinivas Ramachandran, PhD, shows how DNA segments known as enhancers function in cells.
The paper published last month in Molecular Cell highlighted the work from Ramachandran, along with Satyanarayan Rao, both part of the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics at the CU School of Medicine, and Kami Ahmad from the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center.
Enhancers are DNA sequences that drive cell-type-specific gene expression, developmental transitions, and cellular responses to external stimuli. They typically have multiple binding sites for transcription factors, which are proteins that help turn specific genes "on" or "off" by binding to nearby DNA. Ramachandran ...
How we can reduce food waste and promote healthy eating
2021-04-14
URBANA, Ill. - Food waste and obesity are major problems in developed countries. They are both caused by an overabundance of food, but strategies to reduce one can inadvertently increase the other. A broader perspective can help identify ways to limit food waste while also promoting healthy nutrition, two University of Illinois researchers suggest.
"You can reduce food waste by obtaining less or eating more. Our concern was that if people are reducing waste by eating more, what does that mean for nutrition? And how do we think about these tradeoffs in a way that promotes both good nutrition outcomes and good food waste outcomes? ...
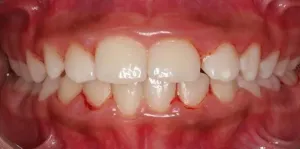
Bacteria that cause periodontitis are transmitted from parents to children
2021-04-14
By Luciana Constantino | Agência FAPESP – Adults with periodontitis transmit bacteria that can cause the disease in future to their children, and the bacteria remain in the oral cavity even when the children undergo treatment of various kinds, reinforcing the need for preventive care in the first year of a baby’s life. This is the main conclusion of a study conducted at the University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. An article on the study is published in Scientific Reports.
Periodontitis is an inflammation of the periodontium, the tissue that supports the teeth and maintains them in the maxillary and mandibular bones. The disease is triggered by bacterial infection. Symptoms include bleeding of the gums and halitosis. In severe cases, it ...
Finally, 3D-printed graphene aerogels for water treatment
2021-04-14
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Graphene excels at removing contaminants from water, but it's not yet a commercially viable use of the wonder material.
That could be changing.
In a recent study, University at Buffalo engineers report a new process of 3D printing graphene aerogels that they say overcomes two key hurdles -- scalability and creating a version of the material that's stable enough for repeated use -- for water treatment.
"The goal is to safely remove contaminants from water without releasing any problematic chemical residue," says study co-author Nirupam Aich, PhD, assistant professor of environmental engineering at the UB School of Engineering and Applied Sciences. "The aerogels ...
Adults who view TV and social media as news sources on COVID are less informed
2021-04-14
HERSHEY, Pa. -- People who trust television and Facebook to provide them with accurate news about the coronavirus pandemic are less knowledgeable about COVID-19, according to a new study, which assessed people's knowledge of the virus in the earliest stages of the pandemic.
The study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Current Medical Research & Opinion, surveyed 5,948 adults in Pennsylvania between March 25-31, 2020, and found that those who relied on social media and TV for news were less likely to get the facts right about the coronavirus.
In fact, adults that used Facebook as an additional ...
[1] ... [2418]
[2419]
[2420]
[2421]
[2422]
[2423]
[2424]
[2425]
2426
[2427]
[2428]
[2429]
[2430]
[2431]
[2432]
[2433]
[2434]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.