Alpine plants at risk of extinction following disappearing glaciers
2021-01-29
Beyond the ski slopes, one of the most iconic symbols of the Alps are the alpine flowers. These plants are not only beautiful -- they are also used in liqueurs and medicines, and they form the foundation of the local food chains. But a recent study in Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution shows that, although plant diversity may initially increase with glacier retreat, many of these species may soon become endangered.
"Our results indicate that plant diversity will ultimately decrease once the glaciers disappear -- and up to 22% of the species we analyzed may locally disappear or even go extinct once the glaciers are gone," says lead author Dr Gianalberto Losapio of Stanford University in the USA. "We show that 'not all species are equal before global warming' and that there are some species ...
Human activity caused the long-term growth of greenhouse gas methane
2021-01-29
Methane (CH4) is the second most important greenhouse gas after carbon dioxide (CO2). Its concentration in the atmosphere has increased more than twice since the preindustrial era due to enhanced emissions from human activities. While the global warming potential of CH4 is 86 times as large as that of CO2 over 20 years, it stays in the atmosphere for about 10 years, much shorter than more than centuries of CO2. It is therefore expected that emission controlling of CH4 can benefit for relatively short time period toward the Paris Agreement target to limit the global warming well below 2 degrees.
A study by an international team, published ...
Obesity may exacerbate the effects of Alzheimer's disease, new study shows
2021-01-29
New research from the University of Sheffield has found being overweight is an additional burden on brain health and it may exacerbate Alzheimer's disease.
The pioneering multimodal neuroimaging study revealed obesity may contribute toward neural tissue vulnerability, whilst maintaining a healthy weight in mild Alzheimer's disease dementia could help to preserve brain structure.
The findings, published in The Journal of Alzheimer's Disease Reports, also highlight the impact being overweight in mid-life could have on brain health in older age.
Lead author of the study, Professor Annalena Venneri from the University of Sheffield's Neuroscience Institute and NIHR Sheffield Biomedical Research Centre, ...
Genetic screening before prescribing could benefit millions
2021-01-29
Four million UK patients could benefit annually from genetic testing before being prescribed common medicines, according to new research from the University of East Anglia (UEA) in collaboration with Boots UK and Leiden University (Netherlands).
Researchers looked through 2019 NHS dispensing data across the UK to see how many patients are started on new prescriptions each year that could be potentially optimised by genetic testing.
They studied 56 medicines, including antidepressants, antibiotics, stomach ulcer treatments and painkillers where there are known drug-gene interactions.
And they found that in more than one in five occasions (21.1 ...
Imaging zebrafish movements in 3D to better understand ALS disease
2021-01-29
An interdisciplinary team of the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) used an innovative imaging technique for a better understanding of motor deficits in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). The researchers were able to follow the escape behaviour of normal and disease zebrafish models, in 3D. Their results have recently been published in Optica, the flagship journal of the Optical Society (OSA).
Professor Jinyang Liang, expert in ultra-fast imaging and biophotonics, joined an effort with Professor Kessen Patten, specialist in genetics and neurodegenerative diseases. The two groups were able to track the position of ...
Iowa and Ohio team finds strategy to protect developing brain from prenatal stress in mice
2021-01-29
New research from the University of Iowa and University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center demonstrates that offspring can be protected from the effects of prenatal stress by administering a neuroprotective compound during pregnancy.
Working in a mouse model, Rachel Schroeder, a student in the UI Interdisciplinary Graduate Program in Neuroscience, drew a connection between the work of her two mentors, Hanna Stevens, MD, PhD, UI associate professor of psychiatry and Ida P. Haller Chair of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, and Andrew A. Pieper, MD, PhD, a former UI faculty member, now Morley-Mather Chair of Neuropsychiatry at Case Western Reserve ...
The Lancet Public Health: Ethnic health disparities among older adults in England equivalent to 20-year age difference, even before COVID-19
2021-01-29
-- Experts call for policy reform to improve ethnic equity of socioeconomic opportunity, service provision, and health outcomes. They also call for long-term studies to investigate how structural and institutional racism generate these ethnic inequalities in health.
In 15 out of 17 minority ethnic groups, health-related quality of life in older age (over 55 year-olds) was worse on average for either men, women, or both, than for White British people according to an observational study published in The Lancet Public Health journal.
In five of those groups - Bangladeshi, Pakistani, ...
<i>The Lancet</i>: Study estimates that, without vaccination against 10 diseases, mortality in children under five would be 45% higher in low-income and middle-income countries
2021-01-29
Peer-reviewed / Simulation or Modelling / People
A new modelling study has estimated that from 2000 to 2030 vaccination against 10 major pathogens - including measles, rotavirus, HPV and hepatitis B - will have prevented 69 million deaths in low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs).
The study estimated that, as a result of vaccination programmes, those born in 2019 will experience 72% lower mortality from the 10 diseases over their lifetime than if there was no immunisation.
The greatest impact of vaccination was estimated to occur in children under five - mortality from the 10 diseases in ...
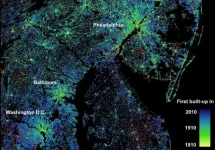
Scholars reveal the changing nature of U.S. cities
2021-01-28
Cities are not all the same, or at least their evolution isn't, according to new research from the University of Colorado Boulder.
These findings, out this week in Nature Communications Earth and Environment and Earth System Science Data, buck the historical view that most cities in the United States developed in similar ways. Using a century's worth of urban spatial data, the researchers found a long history of urban size (how big a place is) "decoupling" from urban form (the shape and structure of a city), leading to cities not all evolving the same--or even close.
The researchers hope that by providing this look at the past with this unique data set, they'll be able to glimpse the future, including the impact of population growth on cities or ...
Experiments show the record of early life could be full of "false positives"
2021-01-28
Boulder, Colo., USA: For most of Earth's history, life was limited to the microscopic realm, with bacteria occupying nearly every possible niche. Life is generally thought to have evolved in some of the most extreme environments, like hydrothermal vents deep in the ocean or hot springs that still simmer in Yellowstone. Much of what we know about the evolution of life comes from the rock record, which preserves rare fossils of bacteria from billions of years ago. But that record is steeped in controversy, with each new discovery (rightfully) critiqued, questioned, and analyzed from every angle. Even then, uncertainty ...
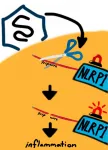
Immune system sets 'tripwire' to protect against viruses
2021-01-28
Scientists are opening new windows into understanding more about the constantly shifting evolutionary arms race between viruses and the hosts they seek to infect. Host organisms and pathogens are in a perennial chess match to exploit each other's weaknesses.
Such research holds tantalizing clues for human health since the immune system is on constant alert to deploy counter measures against new viral attacks. But unleashing too much of a defensive response can lead to self-inflicted tissue damage and disease.
A new study published in the journal eLife by biologists at the University ...
New biosensors quickly detect coronavirus proteins and antibodies
2021-01-28
Scientists have created a new way to detect the proteins that make up the pandemic coronavirus, as well as antibodies against it. They designed protein-based biosensors that glow when mixed with components of the virus or specific COVID-19 antibodies. This breakthrough could enable faster and more widespread testing in the near future. The research appears in Nature.
To diagnose coronavirus infection today, most medical laboratories rely on a technique called RT-PCR, which amplifies genetic material from the virus so that it can be seen. This technique requires specialized staff and equipment. It also consumes lab supplies ...
Study shows when housing quality is poor, children suffer
2021-01-28
Housing instability and homelessness are widely understood to have an impact on health, and certain housing problems have been linked to specific childhood health conditions, such as mold with asthma. But it has not been clear how overall housing quality may affect children--especially those who are at risk from other social determinants of health such as food insecurity or poverty.
A new nationally representative study in the Journal of Child Health Care, led by researchers at Nationwide Children's Hospital, has found poor-quality housing is independently associated with poorer pediatric health, ...
Risk analysis helps contend with uncertainty of in-person activities
2021-01-28
As states and municipalities begin to roll out mass vaccination campaigns, some people have dared to ask: When will it be safe to resume "normal" activities again? For those in most parts of the United States, the risk of COVID-19 infection remains extremely high.
People now have access to better real-time information about infection rates and transmission at the county or city level, but they still need a framework to help them decide what is safe to do. Social distancing and shutting businesses have reduced the number of cases, but there is mounting pressure to reopen businesses and classrooms.
Life is likely to continue in this limbo for some time. A new model co-authored by ...
Otago study examines attitudes toward climate change risk
2021-01-28
A University of Otago study explored factors which influence Americans' levels of concern over climate change, providing discussion on how those factors could impact mitigation efforts.
A key thread of the research examined the ability of people to visualize the future. Results showed that while 74 per cent of respondents were concerned about climate change, only 29 per cent discussed lower carbon options when asked to describe travel in the year 2050.
"This suggests actively envisioning a sustainable future was less prevalent than climate change concern. So while the majority were concerned, ...
People's acceptance of inequality affects response to company wrongdoings
2021-01-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- People who do not accept inequality are more likely to negatively evaluate companies that have committed wrongdoings than people who do accept inequality, and this response varies by culture, according to researchers at Penn State. The team also found that companies can improve their standing with consumers when they offer sincere apologies and remedies for the harm they caused to victims.
"Some prominent examples of company moral transgressions include Nike's and Apple's questionable labor practices in developing countries, BP's oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico and Volkswagen's emissions scandal," said Felix Xu, graduate student in marketing at Penn State.
In their paper, which published on Jan. 22 in the Journal of Consumer Research, the team ...
From heat to spin to electricity: Understanding spin transport in thermoelectric devices
2021-01-28
Thermoelectric materials, which can generate an electric voltage in the presence of a temperature difference, are currently an area of intense research; thermoelectric energy harvesting technology is among our best shots at greatly reducing the use of fossil fuels and helping prevent a worldwide energy crisis. However, there are various types of thermoelectric mechanisms, some of which are less understood despite recent efforts. A recent study from scientists in Korea aims to fill one such gap in knowledge. Read on to understand how!
One of these mechanisms mentioned earlier is the spin Seebeck effect (SSE), which was discovered in 2008 by a research team led by Professor Eiji Saitoh from Tokyo University, Japan. The SSE is a phenomenon in which ...
Simulation helps refine pediatric care guidelines for COVID-19
2021-01-28
DALLAS - Jan. 28, 2021 - Simulation can be a viable way to quickly evaluate and refine new medical guidelines and educate hospital staff in new procedures, a recent study from UT Southwestern's Department of Pediatrics shows. The findings, published recently in the journal Pediatric Quality and Safety and originally shaped around new COVID-19-related pediatric resuscitation procedures at UTSW and Children's Health, could eventually be used to help implement other types of guidelines at medical centers nationwide.
For decades, U.S. hospitals have used the same standard procedures ...
A glimpse into the wardrobe of King David and King Solomon, 3000 years ago
2021-01-28
"King Solomon made for himself the carriage; he made it of wood from Lebanon. Its posts he made of silver, its base of gold. Its seat was upholstered with purple, its interior inlaid with love." (Song of Songs 3:9-10)
For the first time, rare evidence has been found of fabric dyed with royal purple dating from the time of King David and King Solomon.
While examining the colored textiles from Timna Valley - an ancient copper production district in southern Israel - in a study that has lasted several years, the researchers were surprised to find remnants of woven fabric, a tassel and fibers of wool dyed with royal purple. Direct radiocarbon ...
Sotorasib provides durable clinical benefit for patients with NSCLC and KRAS mutations
2021-01-28
(For Immediate Release--Singapore--January 28, 2021)-- In the phase II CodeBreak 100 trial, sotorasib provided durable clinical benefit with a favorable safety profile in patients with pretreated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and who harbor KRAS p.G12C mutations, validating CodeBreak 100's phase I results, according to research presented today at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Outcome in patients with advanced NSCLC on second- or third-line therapies is poor, with a response rate of less than 20% and median progression-free survival of fewer than four months. Approximately 13% of patients with lung adenocarcinomas harbor KRAS p.G12C mutations.
Sotorasib is a first-in-class small molecule that specifically ...
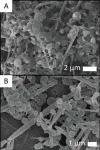
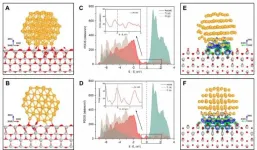
Researchers reveal in-situ manipulation of active Au-TiO<sub>2</sub> interface
2021-01-28
An international joint research team from the Shanghai Advanced Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with Zhejiang University and the Technical University of Denmark, reported an in-situ strategy to manipulate interfacial structure with atomic precision during catalytic reactions. Results were published in the latest issue of Science.
The interface between nanoparticles and substrates plays a critical role in heterogeneous catalysis because most active sites are located at the perimeter of the interface. It is generally believed that this interface is immobile and unchangeable, thus can hardly be adjusted in reactive environments. As a result, it has been challenging to promote catalytic activity through precise control of the interfacial ...
Viral sequencing can reveal how SARS-CoV-2 spreads and evolves
2021-01-28
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 virus variants that are adding twists in the battle against COVID-19 highlight the need for better genomic monitoring of the virus, says Katia Koelle, associate professor of biology at Emory University.
"Improved genomic surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 across states would really help us to better understand how the virus causing the pandemic is evolving and spreading in the United States," Koelle says. "More federal funding is needed, along with centralized standards for sample collection and genetic sequencing. Researchers need access to such metadata to better track how the virus is spreading geographically, and to identify any new variants ...
Screening asymptomatic health care personnel for COVID-19 not recommended by experts
2021-01-28
BOSTON -- Routine screening of asymptomatic health care personnel (HCP) in the absence of confirmed exposures to COVID-19 is not a recommended strategy for preventing transmission of the coronavirus causing the current global pandemic, according to a new review co-authored by an infectious disease specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). The review, published in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, found that such testing is unlikely to affect the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in health care settings and could even have unintended negative consequences.
Many universities, sports leagues and other institutions require individuals in their organization to undergo routine testing for COVID-19, whether or not they are experiencing symptoms. Current public ...
Marine heatwaves becoming more intense, more frequent
2021-01-28
When thick, the surface layer of the ocean acts as a buffer to extreme marine heating--but a new study from the University of Colorado Boulder shows this "mixed layer" is becoming shallower each year. The thinner it becomes, the easier it is to warm. The new work could explain recent extreme marine heatwaves, and point at a future of more frequent and destructive ocean warming events as global temperatures continue to climb.
"Marine heatwaves will be more intense and happen more often in the future," said Dillon Amaya, a CIRES Visiting Fellow and lead author on the study out ...
Counties with more cannabis dispensaries show reduced opioid deaths
2021-01-28
Counties with a greater number of cannabis dispensary storefronts experience reduced numbers of opioid-related deaths relative to other locales, a recent University of California, Davis, study has found. This is the first study to examine the association between active cannabis dispensary operations -- both medical and recreational -- and opioid-related mortality rates at the county level, suggesting that providing alternative pain management could improve public health outcomes, researchers said.
"While the associations documented cannot be assumed to be causal, they suggest a potential relationship between increased prevalence of medical and recreational cannabis dispensaries and reduced opioid-related ...
[1] ... [2700]
[2701]
[2702]
[2703]
[2704]
[2705]
[2706]
[2707]
2708
[2709]
[2710]
[2711]
[2712]
[2713]
[2714]
[2715]
[2716]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.