Does that 'green' plasticizer make my PVC flexible enough for you?
2015-07-06
What gives plastic objects their flexibility and reduces their brittleness is the concentration of plasticiser. For example, a chemical solvent of the phthalate family called DOP is often used. The trouble is there are concerns that phthalates present health risks. So there is a demand for more alternatives. Now, scientists from China have examined the effect of using DEHHP, a new eco-friendly plasticiser, used in combination with PVC. For a plasticiser to work, there has to be adequate hydrogen bonding with the plastic. By combining experiments and simulations, the team ...
Tel Aviv/Tsinghua University project uses crowd computing to improve water filtration
2015-07-06
Nearly 800 million people worldwide don't have access to safe drinking water, and some 2.5 billion people live in precariously unsanitary conditions, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Together, unsafe drinking water and the inadequate supply of water for hygiene purposes contribute to almost 90% of all deaths from diarrheal diseases -- and effective water sanitation interventions are still challenging scientists and engineers.
A new study published in Nature Nanotechnology proposes a novel nanotechnology-based strategy to improve water filtration. ...
Ion channel mechanics yield insights into optogenetics experiments
2015-07-06
Optogenetics techniques, which allow scientists to map and control nerve cells using light stimulation, are being used to study neural circuits in the brain with unprecedented precision. This revolutionary technology relies on light-sensitive proteins such as channelrhodopsins, and researchers at UC Santa Cruz have now determined the molecular mechanism involved in the light-induced activation of one of these proteins.
The new findings, published July 3 in two papers in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, can help scientists create tailor-made proteins optimized for ...
How the mammoth got its wool: Genetic changes are identified
2015-07-06
Evolutionary change in a gene resurrected in the lab from the extinct woolly mammoth altered the gene's temperature sensitivity and likely was part of a suite of adaptations that allowed the mammoth to survive in harsh arctic environments, according to new research. In a study published in Cell Reports on July 2, 2015, researchers determined the whole-genome sequence of two woolly mammoths and three modern Asian elephants, predicted the function of genetic changes found only in the mammoths, and then experimentally validated the function of a woolly mammoth gene reconstructed ...
Research breakthrough to treat girls-only epilepsy
2015-07-06
An international team, led by a University of Adelaide genetics expert, has made a breakthrough discovery which is expected to help thousands of young girls worldwide who are suffering from a rare yet debilitating form of epilepsy.
Professor Jozef Gecz, from the University of Adelaide's Robinson Research Institute, was a key player in identifying the responsible gene and mutations in this female-only epileptic syndrome, in 2008.
In breakthrough research published in Oxford Journals, Human Molecular Genetics, Professor Gecz has now found a treatment for this disorder. ...
tRNAs are segmented into fragments in a manner that depends on race, gender and population
2015-07-06
(PHILADELPHIA) -- Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are ancient molecules and indispensable components of all living cells - they are found in all three kingdoms of life i.e., in archaea, bacteria and eukaryotes. In a cell, they are part of the machinery that translates messenger RNA (mRNA) sequences into amino acid sequences.
In recent years advances in sequencing technology have enabled detailed investigations of the RNA molecules that are active in a cell. A study published July 6th in the journal Oncotarget reports on a newly discovered category of tRNA fragments as well as ...
Big city life: New leafhopper species found on a threatened grass in New Jersey
2015-07-06
Andrew Hicks from the Museum of Natural History at the University of Colorado and his team discovered a previously unknown leafhopper species in the New Jersey Pine Barrens, located just east of the megalopolis that extends from New York City to Washington, DC. This was the first time an insect has been reported from the state-listed threatened pinebarren smokegrass, Muhlenbergia torreyana. The study can be found in the open-access journal ZooKeys.
The discovery was made with the help of Dr. Gerry Moore of the Natural Resources Conservation Service in Greensboro, NC, ...
Emotion knowledge fosters attentiveness
2015-07-06
Young children, who possess a good understanding of their own emotions and of those of their fellow human beings early on, suffer fewer attention problems than their peers with a lower emotional understanding. Evidence of this phenomenon was found through a study of Leuphana University of Lueneburg and George Mason University, USA, under the auspices of Prof. Dr. Maria von Salisch, Professor of Developmental Psychology at Leuphana University of Lueneburg. The study was recently published in the journal Kindheit & Entwicklung (Childhood & Development).
The findings stem ...
Pazopanib improves progression-free survival without impairing HRQOL
2015-07-06
Results of EORTC trial 62072 appearing in Cancer show that in patients with soft tissue sarcoma, whose disease had progressed during or after prior chemotherapy, pazopanib improved progression-free survival but did not change health-related quality of life. This observed improvement in progression-free survival without impairment of health-related quality of life was considered a meaningful result.
There has not been a lot of research that has looked into the quality of life of patients with advanced soft tissue sarcoma. The results of this EORTC health related quality ...
New study again shows: More strokes with intracranial stents
2015-07-06
The risk of experiencing another stroke is higher if patients, after dilation of their blood vessels in the brain, receive not only clot-inhibiting drugs, but also have stents inserted. The recently published results of the VISSIT study confirm this conclusion of a rapid report by the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) of October 2014. Thus, the available studies still provide no evidence of a benefit of treatment with intracranial stents (also called "percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and stenting", PTAS). This is the conclusion of a ...
Producing biodegradable plastic just got cheaper and greener
2015-07-06
Biodegradable drinking cups or vegetable wrapping foil: the bioplastic known as polylactic acid (PLA) is already a part of our everyday lives. And yet, PLA is not yet considered a full alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics, as it is costly to produce. Researchers from the KU Leuven Centre for Surface Chemistry and Catalysis now present a way to make the PLA production process more simple and waste-free. Their findings were published in Science.
The bioplastic PLA is derived from renewable resources, including the sugar in maize and sugarcane. Fermentation ...
'Rambo' protein may not be so violent after all
2015-07-06
A protein dubbed 'Bcl-Rambo' can protect against heart failure, suggests new research from King's College London and funded by the British Heart Foundation (BHF).
The Bcl-Rambo protein (also known as Bcl2-L-13) was named by a Japanese scientist because it was thought to be involved in activating cell death - 'Rambo' also means violence in Japanese. However, it seems that the Rambo movie character's protein counterpart has actually been misjudged. New research shows for the first time that the Bcl-Rambo protein may not be so violent after all and is actually involved in ...
Structural shift elucidated with large-scale atomic simulations
2015-07-06
Iron-nickel alloys are ubiquitous: they are found at the earth's core and in meteorites. What is fascinating about such alloys is that their inner structure can change with rapid temperature swings. Heated up above 730 °C (1,340 °F), these alloys enter what is referred to as an austenitic phase. Alternatively, they can be turned into very hard alloys, referred to as a martensitic phase, by subjecting them to extremely rapid cooling. Now a team of scientists from Germany has, for the first time, created a large-scale simulation involving 275,000 atoms representing ...
Supercharging stem cells to create new therapies
2015-07-06
Researchers at the University of Adelaide have discovered a new method for culturing stem cells which sees the highly therapeutic cells grow faster and stronger.
The research, which was published in the prestigious international journal, Stem Cells, is expected to eventually lead to new treatments for transplant patients.
Kisha Sivanathan, a PhD student in the University of Adelaide's School of Medicine and the Renal Transplant Unit at the Royal Adelaide Hospital, says this is an exciting breakthrough in stem cell research.
"Adult mesenchymal stem cells, which ...
New test could predict arthritis drug failure in patients
2015-07-06
A study of 311 patients by The University of Manchester has found that it may be possible to predict early which rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients will fail to respond to the biologic drugs given to treat them. These findings could help better manage patients' symptoms.
RA is a chronic disease which affects up to 1.5% of the population. It is a significant health burden for patients, who can experience pain, reduced mobility and premature death unless they receive effective treatment.
Biologics are a relatively new form of treatment for RA. Given by injection, ...
Fingolimod in RRMS: Indication of added benefit in certain patients
2015-07-06
Pursuant to the Act on the Reform of the Market for Medicinal Products (AMNOG), the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) reassessed fingolimod (trade name: Gilenya), a drug for the treatment of adults with highly active relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). The Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) had limited its decision on the first assessment from 2012 to three years because it considered the certainty of the data as insufficient. This obliged the drug manufacturer to submit a second dossier.
It did not submit any new studies, but reanalysed ...
Significant reduction in serious crimes after juvenile offenders given emotional awareness training
2015-07-06
Scientists believe that a simple two-hour emotional awareness course aimed at making young offenders less aggressive could hold the key to significantly reducing the seriousness of their future crimes.
In the first ever study of its kind, psychologists from Cardiff University recorded a 44% drop in the severity of crimes committed by persistent reoffenders, six months following the completion of a course designed to improve their ability to recognise other people's emotions. The findings are published today in PLOS ONE journal.
Much has been published previously to ...
Waiting to harvest after a rain enhances food safety
2015-07-06
ITHACA, N.Y. - To protect consumers from foodborne illness, produce farmers should wait 24 hours after a rain or irrigating their fields to harvest crops, according to new research published in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
Rain or irrigation creates soil conditions that are more hospitable to Listeria monocytogenes, which when ingested may cause the human illness Listeriosis. Waiting to harvest crops reduces the risk of exposure to the pathogen, which could land on fresh produce.
Cornell scientists, along with other agricultural researchers from ...
Universe's hidden supermassive black holes revealed
2015-07-06
Astronomers have found evidence for a large population of hidden supermassive black holes in the Universe.
Using NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) satellite observatory, the team of international scientists detected the high-energy x-rays from five supermassive black holes previously clouded from direct view by dust and gas.
The research, led by astronomers at Durham University, UK, supports the theory that potentially millions more supermassive black holes exist in the Universe, but are hidden from view.
The findings are being presented at the ...
Cellular sentinel prevents cell division when the right machinery is not in place
2015-07-06
For cell division to be successful, pairs of chromosomes have to line up just right before being swept into their new cells, like the opening of a theater curtain. They accomplish this feat in part thanks to structures called centrioles that provide an anchor for the curtain's ropes. Researchers at Johns Hopkins recently learned that most cells will not divide without centrioles, and they found out why: A protein called p53, already known to prevent cell division for other reasons, also monitors centriole numbers to prevent potentially disastrous cell divisions.
Details ...
Aluminum clusters shut down molecular fuel factory
2015-07-06
Richland, Wash. -- Despite decades of industrial use, the exact chemical transformations occurring within zeolites, a common material used in the conversion of oil to gasoline, remain poorly understood. Now scientists have found a way to locate--with atomic precision--spots within the material where chemical reactions take place, and how these spots shut down.
Called active sites, the spots help rip apart and rearrange molecules as they pass through nanometer-sized channels, like an assembly line in a factory. A process called steaming causes these active sites to cluster, ...
Arthritis drug could be used to treat blood cancer sufferers
2015-07-06
Anti-inflammatory drug is one thousandth of the cost of the current drug which works in the same way
Discovery may open up cost effective treatment options not just for the NHS but also cancer patients across the world
Scientists at the University of Sheffield have discovered that a common drug given to arthritis sufferers could also help to treat patients with blood cancers.
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) are diagnosed in around 3,300 UK patients every year and cause an overproduction of blood cells creating a significant impact on quality-of-life, with symptoms ...
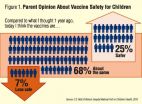
Safer, with more benefits: Parents' vaccine views shifting
2015-07-06
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- Over the same time period that multiple outbreaks of measles and whooping cough made headlines around the country, parents' views on vaccines became more favorable, according to a new nationally-representative poll.
The University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health asked parents in May how their views on vaccinations changed between 2014 and 2015 - during which two dozen measles outbreaks were reported in the U.S., including a multi-state outbreak traced to Disneyland.
One-third of parents who participated ...
Learning from biology to accelerate discovery
2015-07-06
A spider's web is one of the most intricate constructions in nature, but its precious silk has more than one use. Silk threads can be used as draglines, guidelines, anchors, pheromonal trails, nest lining, or even food. And each use requires a slightly different type of silk, optimized for its function.
"Each type of silk has similar proteins, but they are synthesized differently," said Sinan Keten, assistant professor of mechanical and civil engineering at Northwestern University's McCormick School of Engineering. "Then the spider knows how fast to reel the silk to get ...
Stronger action needed to transform the UK's energy system
2015-07-06
An ambitious policy package is essential for the UK to transform its energy system to achieve the deep reductions in carbon emissions required to avoid dangerous climate change, according to research led by UCL scientists. To meet climate targets set for 2050, policies need to ensure strong action is taken now, while preparing for fundamental changes in how energy is provided and used in the long term.
The study is part of the Deep Decarbonization Pathway Project (DDPP) which is coordinated by the Institute for Sustainable Development and International Relations (IDDRI) ...
[1] ... [2903]
[2904]
[2905]
[2906]
[2907]
[2908]
[2909]
[2910]
2911
[2912]
[2913]
[2914]
[2915]
[2916]
[2917]
[2918]
[2919]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.