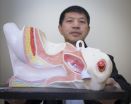
Researcher detects traces of HIV in the city
2015-07-09
This news release is available in French.
Since the treatment has become available, HIV is often described as "undetectable" and the risk of transmission has been drastically reduced. However, the epidemic is still quite present in the lives of many gay and bisexual men... and in public spaces. This often overlooked dimension of the disease has been brought to light by Gabriel Girard of the University of Montreal's Public Health Research Institute (IRSPUM) - HIV is still alive in the city, especially in the Village, Montreal's gay district. "Urban traces are significant ...
Study finds vitamin A directs immune cells to the intestines
2015-07-09
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- A key set of immune cells that protect the body from infection would be lost without directions provided by vitamin A, according to a recent study.
A team of researchers from Purdue University found retinoic acid, a metabolite that comes from digested vitamin A, is necessary for two of the three types of innate immune cells that reside in the intestine to find their proper place.
"It is known that vitamin A deficiencies lead to increased susceptibility to disease and low concentrations of immune cells in the mucosal barrier that lines the intestines," ...
Study finds violent video games provide quick stress relief, but at a price
2015-07-09
MADISON, Wis. -- A study authored by two University of Wisconsin-Madison graduate students indicates that while playing video games can improve mood, violent games may increase aggressive outcomes.
The study, authored by James Alex Bonus and Alanna Peebles, graduate students in Communication Arts, and Karyn Riddle, assistant professor in the School of Journalism and Mass Communication, was published in June in the journal Computers in Human Behavior. The researchers looked at how video games may be used to manage emotions -- specifically, whether playing the games can ...
Hearing test pinpoints middle-ear problems in newborns
2015-07-09
(Edmonton) Screening newborn babies who are in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) using a testing process called high-frequency tympanometry can help identify middle-ear problems earlier, according to newly published research from a local team of researchers.
"If people cannot hear, we need to know if the problem is with the middle ear, inner ear or hearing nerve. Obviously, a baby cannot tell you, so in the clinic it's hard to know when they have hearing loss," explained Ming Zhang, an associate professor at the U of A's Department of Communication Sciences and ...
Researchers identify new spectrum disorder called ALPIM syndrome
2015-07-09
The relationship between mental and physical health is well established. But when mental and physical illnesses co-occur, patients' accounts of physical illness are sometimes arbitrarily discredited or dismissed by physicians.
Research by Jeremy D. Coplan, MD, professor of psychiatry at SUNY Downstate Medical Center, and colleagues has documented a high rate of association between panic disorder and four domains of physical illness. The research could alter how physicians and psychiatrists view the boundaries within and between psychiatric and medical disorders.
"Patients ...
Why not build houses the environmentally friendly way?
2015-07-09
Green buildings are indeed healthy buildings. So says Dr. Joseph Allen and fellow researchers of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in the US. They conducted the first comprehensive review of studies that focused on green buildings and summarized the health benefits for the people who work and live in them. The review is published in Springer's journal Current Environmental Health Reports.
The green building movement has taken off in the past 10 years. According to Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED®), which certifies green building standards, ...
Researchers identify gene responsible for some cases of male infertility
2015-07-09
In about one-sixth of the cases of male infertility, men do not make any measurable levels of sperm, a condition called azoospermia. New research led by University of Pennsylvania scientists suggests that mutations in an X chromosome gene called TEX11 are responsible for about 1 percent of azoospermia cases.
The investigators also found that in mice bred to lack the gene, reintroducing the gene restores their fertility. Additional studies in mice revealed that a certain amount of the TEX11 protein expressed from the gene is needed for sperm to form. The protein plays ...
New recommendations addresses the diagnosis and management of testosterone deficiency
2015-07-09
An expert panel convened by the International Society for Sexual Medicine has developed a detailed "Process of Care" for the diagnosis and management of testosterone deficiency in men.
After an extensive literature review and in-depth consultations, the panel of 18 experts from a wide range of medical disciplines recommended that testosterone deficiency be defined as a clinical and biochemical syndrome characterized by both a deficiency of testosterone or testosterone action, and relevant symptoms. The panel stressed that the condition may affect multiple organ systems ...
Society has been discussing climate change's impacts long before we knew it existed
2015-07-09
For the first time, a new analysis shows an impact of climate change on human society long before we knew the climate was actually changing.
Exploring Google's scanned book collection, the analysis finds that society in general increasingly discussed some of the predicted effects of climate change--such as heat waves, drought, and flooding--long before current global weather alterations were widely known about.
The authors note that while the science of climate change and climate action has come under sustained political attack, buttressing the physical record with ...
Studies, commentary, editorial, editor's note focus on teens, adults at end of life
2015-07-09
A related package of articles published online by JAMA Oncology focuses on end-of-life care for teens and young adults and advance care planning for patients with cancer. The package of articles includes two original investigations, an invited commentary, an editorial, an accompanying editor's note and an author audio interview.
End-of-Life Care for Teens, Young Adults with Cancer
In the first study, corresponding author Jennifer W. Mack, M.D., M.P.H., of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and her coauthors looked at the intensity of end-of-life care for teens ...
Aggressive cancer treatment near end of life persists despite rise in advance planning efforts
2015-07-09
In a review of nearly 2,000 surveys with people whose loved ones died of cancer, researchers led by Johns Hopkins experts say they found a 40 percent increase over a 12-year period in the number of patients with cancer who participated in one form of advance care planning -- designating durable power of attorney privileges to a loved one -- but no corresponding impact on their rates of aggressive medical care received in the last weeks of life.
In addition, the investigators say that despite the substantial increase in patients who designated a durable power of attorney, ...
Cells help viruses during cell entry
2015-07-09
Adenoviruses cause numerous diseases, such as eye or respiratory infections, and they are widely used in gene therapy. Researchers from the University of Zurich have now discovered how these viruses penetrate the cells, a key step for infection and gene delivery The cell unwillingly supports virus entry and infection by providing lipids that are normally used to repair damaged membranes.
An intact cell membrane is essential for any cell to function. The external cell membrane can be damaged by mechanical stress, for example in muscle cells, or by pathogens, such as ...
Researchers find potential link between fat in blood and blood vessel recovery in ischemia
2015-07-09
(Philadelphia, PA) - The buildup of fat in the blood makes a bad situation worse - it not only raises a person's risk for heart attack or stroke but also impairs the growth of new blood vessels. How excess fat in the blood - a condition known as hyperlipidemia - blocks vessel growth was unclear, but new work by researchers at Temple University School of Medicine (TUSM) shows that a molecule known as caspase-1 plays a central role and that preventing its activity could be the key to building new blood vessels and restoring blood supply to oxygen-starved tissues.
"Caspase-1 ...
NOAA, partners predict severe harmful algal bloom for Lake Erie
2015-07-09
NOAA and its research partners, using an ensemble modeling approach, predict that the 2015 western Lake Erie harmful algal bloom season will be among the most severe in recent years and could become the second most severe behind the record-setting 2011 bloom.
The effects of the cyanobacterial blooms include a higher cost for cities and local governments to treat their drinking water, as well as risk to swimmers in high concentration areas, and a nuisance to boaters when blooms form. These effects will vary in locations and severity with winds, and will peak in September.
The ...
Kid swagger: How children react to winning and losing
2015-07-09
A group of preschoolers were given one shot to beat the world's fastest builder of block towers.
Unbeknownst to the children, it had already been decided who would capture the victory and who would see it slip away.
The losers shook it off without it ruining their mood.
The winners - even the two-year-olds - showed some obvious swagger: heads held high, chests puffed out, hands on hips in a victorious power pose.
But here's the thing - children show emotions much younger than they understand them. That's why the psychologists who staged the contest asked the ...
Genetic differences may help explain inconsistent effectiveness of anti-HIV drug
2015-07-09
Research with human tissue and cells suggests that genetic variations, in addition to failure to comply with treatment regimens, may account for some failures of an anti-HIV drug to treat and prevent HIV infection.
In a report described online today in the journal EBioMedicine, investigators at Johns Hopkins found that tenofovir, marketed as Viread, is processed differently according to cell location, so that if the drug is eventually marketed as a topical gel, it could work differently depending on whether it is applied to the vagina or the rectum.
Tenofovir has been ...
What makes us more likely to take the stairs?
2015-07-09
This news release is available in French. Montreal, July 9, 2015 -- Death rates due to health problems like obesity, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease are on the rise. According to the World Health Organization, that's due to our increasingly sedentary lifestyles.
Clearly, it's important to lead more active lives. Something as simple as taking the stairs can make a big difference. But can pedestrians be convinced to make healthy choices when an escalator seems so much faster and more convenient than a staircase?
Yes, say researchers from Concordia ...
Huge new survey to shine light on dark matter
2015-07-09
Around 85% of the matter in the Universe is dark [1], and of a type not understood by physicists. Although it doesn't shine or absorb light, astronomers can detect this dark matter through its effect on stars and galaxies, specifically from its gravitational pull. A major project using ESO's powerful survey telescopes is now showing more clearly than ever before the relationships between this mysterious dark matter and the shining galaxies that we can observe directly [2].
The project, known as the Kilo-Degree Survey (KiDS - http://kids.strw.leidenuniv.nl/), uses imaging ...
Blood pressure levels and prevalence among US children and adolescents declined in past decade
2015-07-09
Childhood high blood pressure (HBP) is a serious public health challenge worldwide due to associated increases in risk of end organ damages and correlation with HBP in adulthood. The prevalence of elevated blood pressure (BP) has been reported to increase significantly among United States children and adolescents from 1988-1994 to 1999-2008, but little is known about recent trends in BP values and elevated BP. The authors of a new study, "Trends in elevated blood pressure among US children and adolescents: 1999-2012," published today by the American Journal of Hypertension, ...
U-M, partners predict severe harmful algal bloom for Lake Erie
2015-07-09
ANN ARBOR--University of Michigan researchers and their colleagues predict that the 2015 western Lake Erie harmful algal bloom season will be among the most severe in recent years and could become the second-most severe behind the record-setting 2011 bloom.
The 2015 seasonal forecast uses models that translate spring nutrient loading into predicted algal blooms in the Western Basin of Lake Erie. After a relatively dry April and May, the heavy rains in June produced record discharge and nutrient loadings from the Maumee River, which runs through Toledo and northeastern ...
Graphene gets competition
2015-07-09
This news release is available in German.
Graphene, the only one atom thick carbon network, achieved overnight fame with the 2010 Nobel Prize. But now comes competition: Such layers can also be formed by black phosphorous. Chemists at the Technische Universität München (TUM) have now developed a semiconducting material in which individual phosphorus atoms are replaced by arsenic. In a collaborative international effort, American colleagues have built the first field-effect transistors from the new material.
For many decades silicon has formed the ...
Opioids may not spell relief for chronic back pain sufferers with depression, anxiety
2015-07-09
Chicago - Although opioids are frequently prescribed to treat chronic lower back pain, new research suggests these powerful medications may be less effective in some patients. A study published in the Online First edition of Anesthesiology, the official medical journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists® (ASA®), found patients who were prescribed opioids to treat chronic lower back pain experienced significantly less pain relief and were more likely to abuse their medication when they had psychiatric disorders such as depression or anxiety.
"High levels ...
Neuroscientists establish brain-to-brain networks in primates, rodents
2015-07-09
Neuroscientists at Duke University have introduced a new paradigm for brain-machine interfaces that investigates the physiological properties and adaptability of brain circuits, and how the brains of two or more animals can work together to complete simple tasks.
These brain networks, or Brainets, are described in two articles to be published in the July 9, 2015, issue of Scientific Reports. In separate experiments reported in the journal, the brains of monkeys and the brains of rats are linked, allowing the animals to exchange sensory and motor information in real time ...
Human color vision gives people the ability to see nanoscale differences
2015-07-09
The human eye is an amazing instrument and can accurately distinguish between the tiniest, most subtle differences in color. Where human vision excels in one area, it seems to fall short in others, such as perceiving minuscule details because of the natural limitations of human optics.
In a paper published today in The Optical Society's new, high-impact journal Optica, a research team from the University of Stuttgart, Germany and the University of Eastern Finland, Joensuu, Finland, has harnessed the human eye's color-sensing strengths to give the eye the ability to ...
Global trends show seabird populations dropped 70 percent since 1950s
2015-07-09
UBC research shows world's monitored seabird populations have dropped 70 per cent since the 1950s, a stark indication that marine ecosystems are not doing well.
Michelle Paleczny, a UBC master's student and researcher with the Sea Around Us project, and co-authors compiled information on more than 500 seabird populations from around the world, representing 19 per cent of the global seabird population. They found overall populations had declined by 69.6 per cent, equivalent to a loss of about 230 million birds in 60 years.
"Seabirds are particularly good indicators of ...
[1] ... [2895]
[2896]
[2897]
[2898]
[2899]
[2900]
[2901]
[2902]
2903
[2904]
[2905]
[2906]
[2907]
[2908]
[2909]
[2910]
[2911]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.