Report on treatment of patients with hemophilia published
2015-07-13
Numerous long-term randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have been conducted to investigate the long-term, factor concentrate-based treatment of patients with severe haemophilia A or B, despite the rareness of the diseases and the lack of incentives for pharmaceutical companies. These RCTs include three studies comparing prophylactic versus on-demand treatment (i.e. treatment initiated only in the event of bleeding). For patients with haemophilia A, both hints and an indication of an added benefit of prophylactic versus on-demand treatment can be inferred from these studies, ...
Stopping or reducing cocaine use associated with lower cardiovascular risk marker levels
2015-07-13
July 13, 2015 - For people who use cocaine, stopping or reducing cocaine use is associated with decreased levels of endothelin-1 (ET-1)--a protein that plays a key role in the development of coronary artery disease, reports a study in the Journal of Addiction Medicine, the official journal of the American Society of Addiction Medicine. The journal is published by Wolters Kluwer.
The findings help in understanding the high rate of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) associated with cocaine use, according to the report by Dr. Shenghan Lai and colleagues of Johns ...
New cell division mechanism discovered
2015-07-13
Canadian and British researchers have discovered that chromosomes play an active role in animal cell division. This occurs at a precise stage - cytokinesis - when the cell splits into two new daughter cells. It was observed by a team of researchers including Gilles Hickson, an assistant professor at the University of Montreal's Department of Pathology and Cell Biology and researcher at the CHU Sainte-Justine Research Centre, his assistant Silvana Jananji, in collaboration with Nelio Rodrigues, a PhD student, and Sergey Lekomtsev, a postdoc, working in the group led by Buzz ...
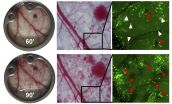
From sticks to balls: The shape of bacteria is evolving to better adapt to the throat
2015-07-13
This news release is available in French. Montréal, July 13, 2015 - It's no coincidence that the earthworm's slender shape makes it perfect for weaving through narrow tunnels. Evolution moulds the shapes of living creatures according to the benefits they offer. At the microscopic level, do the various shapes of bacteria also contribute to their survival? Does a spherical bacterium (coccus) have a better chance of infecting its host than its stick-shaped neighbour (bacillus)?
Analysis of the evolution of the pathogenic bacteria that live in the nasopharynx suggests ...
Registry data used to examine use of ICDs, cardiac rehab referral rates
2015-07-13
WASHINGTON (July 13,2015) - The American College of Cardiology's National Cardiovascular Data Registry was the source of data for research published in the first half of 2015, including a study that examines public reporting and PCI outcomes as well as research that showed implantable cardioverter-defibrillators are underutilized in older patients.
Is There a Link Between Public Reporting and PCI Outcomes?
Patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in states with mandated public reporting of outcomes had similar predicted risks but significantly ...
'Biosimilars' for children with IBD need more research, ESPGHAN expert panel states
2015-07-13
July 13, 2015 -Children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who are doing well on specific biological medications should not be switched to recently approved "biosimilar" products, concludes an expert consensus statement of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN). The statement appears in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, the official journal of the European Society of Paediatric Gatroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition and the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and ...
Discovery of young family gives hope to world's rarest ape
2015-07-13
The world's rarest ape has an increased chance of survival after a team led by international conservation charity the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) found a new family group of Hainan gibbons (Nomascus hainanus).
Until last month, it was thought that there were just 25 Hainan gibbons living in three social groups on an island off the Chinese mainland.
The discovery of a new fourth group, a mating pair with a young baby, sighted within Bawangling National Nature Reserve, Hainan Province, increases the known population by almost 12%.
The discovery of this fourth ...
Report on treatment of patients with haemophilia published
2015-07-13
Numerous long-term randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have been conducted to investigate the long-term, factor concentrate-based treatment of patients with severe haemophilia A or B, despite the rareness of the diseases and the lack of incentives for pharmaceutical companies. These RCTs include three studies comparing prophylactic versus on-demand treatment (i.e. treatment initiated only in the event of bleeding). For patients with haemophilia A, both hints and an indication of an added benefit of prophylactic versus on-demand treatment can be inferred from these studies, ...
Plump cartoon characters provoke indulgent eating in kids, says CU-Boulder-led study
2015-07-13
Children consume more low-nutrition, high-calorie food such as cookies and candy after observing seemingly overweight cartoon characters, according to a first-of-its-kind study led by the University of Colorado Boulder.
The results of the new study, involving Colorado State University and published online in the Journal of Consumer Psychology, show that kids are responsive to the apparent bodyweight of cartoon characters like the aptly named Grimace, a rotund, milkshake-loving creature created by McDonald's restaurant in the 1970s.
Children tend to perceive ovoid, or ...
Immune cell journey has bloody consequences
2015-07-13
Immune cells that creep across blood vessels trigger potentially fatal bleeding in platelet-deficient mice, according to a report published in The Journal of Experimental Medicine. If the same is true in humans, blocking the passage of these cells could prevent dangerous complications in patients undergoing transplants or chemotherapy.
Bone marrow transplantation and chemotherapy are known to deplete blood-clotting cells called platelets, resulting in potentially fatal bleeding (hemorrhage) in some patients. Previous studies showed that inflammation was required for bleeding ...
Teaching reflection to doctors to improve physician-patient interactions
2015-07-13
BOSTON (July 13, 2015)--Physicians in their medical residency training programs often focus on scientific reasoning and research evidence in their efforts to provide medical care. While appropriate, this focus may overshadow subtle and indirect communication that reveals important information about the patient's experience with their illness that will help the physician provide better care. A new study by researchers at Tufts University School of Medicine and Boston College presents the results of a strategy to train medical residents to reflect on interactions with patients ...
Mysterious black leopards finally reveal their spots
2015-07-13
James Cook University scientists have helped invent a clever technique to tell black leopards apart - a trick that may end up saving their skins.
Scientists from JCU in Australia and others have been studying the leopards on the Malay Peninsula - where almost all of the big cats are jet black.
Experts have no idea why the leopards are black and, until recently, could not tell them apart, hindering research and conservation efforts.
But researchers have now devised a simple method to solve the problem by manipulating the mechanism of automatic cameras.
"Most automatic ...
Invasions out of center of diversity increase the risk of disease epidemics in wheat
2015-07-13
Scientists have found that strains of the wheat pathogen causing severe yellow rust epidemics in Europe have their origin in the centre of diversity in the Himalayan region. This disease can have a great impact on wheat production in Europe, including organic crop production in Denmark.
Wheat is the most widely cultivated food crop in the world. However, the global production of wheat is under constant threat from devastating fungal diseases. The ever more frequent and severe large-scale epidemics caused by these fungi pose a severe threat to global food security.
Scientists ...
Cancer survivors may face unique challenges when trying to adopt
2015-07-13
A new study has found that cancer survivors' options for adoption may be limited by adoption agencies' policies. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the study also indicates that a training program for oncology healthcare providers can help them provide valuable information to patients who are making decisions about fertility and adoption.
Because cancer and the therapies used to treat it can leave some patients infertile, many young cancer survivors may turn to adoption when hoping to start--or add to--a family. Adoption ...
Nixoncare vs. Obamacare: Comparing the rhetoric and reality of 2 health plans
2015-07-13
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- Few people today would dare call President Richard Nixon a radical liberal. But 44 years ago, he proposed a health plan that went far beyond what today's Affordable Care Act includes. After the first plan failed, he did it again three years later.
And just like today's heated rhetoric from opponents of the ACA, also called "Obamacare" after the president who introduced it, Nixon's plans were met with inflamed opposition from the other party.
In a new article in the journal Pediatrics, a team from the Child Health Evaluation and Research Unit at ...
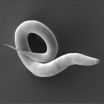
Worms hitch rides on slugs when traveling to far flung places
2015-07-13
This news release is available in German.
Slugs and other invertebrates provide essential public transport for small worms in the search for food, according to research published in the open access journal BMC Ecology.
Nematode worms (including Caenorhabditis elegans) are around a millimeter long and commonly found in short-lived environments, such as decomposing fruit or other rotting plant material. The worms face a high level of unpredictability in these environments as temperature and food availability fluctuate, and frequently need to move to new locations. ...
Ultrasound accelerates skin healing -- especially for diabetics and the elderly
2015-07-13
Treatment could save the NHS £3.1 billion every year
More than 200,000 patients in the UK suffer with chronic wounds
Healing time can be reduced by a third
Healing times for skin ulcers and bedsores can be reduced by a third with the use of low-intensity ultrasound, scientists from the University of Sheffield and University of Bristol have found.
Researchers from the University of Sheffield's Department of Biomedical Science discovered the ultrasound transmits a vibration through the skin and wakes up cells in wounds helping to stimulate and accelerate the healing ...
What happens when cosmic giants meet galactic dwarfs?
2015-07-13
When two different sized galaxies smash together, the larger galaxy stops the smaller one making new stars, according to a study of more than 20,000 merging galaxies.
The research, published today, also found that when two galaxies of the same size collide, both galaxies produce stars at a much faster rate.
Astrophysicist Luke Davies, from The University of Western Australia node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR), says our nearest major galactic neighbour, Andromeda, is hurtling on a collision course with the Milky Way at about 400,000 ...
The Lancet: Study reveals dramatic shortfall in donor funding for key global health issues
2015-07-13
As the world's leaders gather in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, for the Financing for Development Conference [1], a study published in The Lancet demonstrates that a new approach is needed for classifying funding that reflects the function the funding serves, rather than the specific disease or country. The study is the first in-depth assessment of how donor funding is spent on global versus country-specific functions of health [2].
The paper also presents an expanded definition of official development assistance (ODA) for health, which is used to identify important underfunded ...
Study finds donor funds fall short for key global health functions
2015-07-13
As experts debate the slow response to the Ebola outbreak in West Africa and call for better international coordination, a new analysis estimates that $22 billion was spent on global health aid in 2013, yet only a fifth of this went toward such global imperatives as research on diseases that disproportionally affect the poor, outbreak preparedness and global health leadership.
The analysis, by Dean Jamison, PhD, a global health economist at UC San Francisco (UCSF); Lawrence Summers, PhD, a former US Treasury Secretary now at Harvard University; and researchers at SEEK ...
Tommy John surgeries increasing for youth athletes
2015-07-12
ORLANDO, FL - Surgeries related to overuse elbow injuries, i.e. Tommy John Surgery, are more common among youth athletes than previously believed, according to research presented today at the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine's (AOSSM) Annual Meeting in Orlando, Florida.
"Our results showed that 15-19 year-olds accounted for 56.7 percent of the Ulnar Collateral Ligament Reconstruction (UCLR) or Tommy John surgeries performed in the U.S. between 2007-2011. This is a significant increase over time with an average increase of 9.12 percent per year," said lead ...
Surgeries before college athletics may result in more injuries during college play
2015-07-12
ORLANDO, FL - Athletes who've had lower extremity surgeries before going on to play in college, might be at a higher risk for another surgery independent of gender and sport, say researchers presenting their work today at the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine's (AOSSM) Annual Meeting in Orlando, FL.
"This is the first study to look at the relationship between precollegiate surgery and future injury requiring surgery in collegiate athletes. Our results suggest that athletes injured before college might be left with a functional deficit that puts them at ...
Documentation of hospital patients' malnutrition helps maximize care and reimbursement
2015-07-12
Nutrition support professionals who are well-versed in proper documentation of malnutrition diagnoses in hospital patients can help ensure that hospitals receive maximum funding for patient care according to a new review.
The review, recently published in Nutrition in Clinical Practice (NCP), a peer-reviewed, interdisciplinary journal of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.) that publishes articles about the scientific basis and clinical application of nutrition and nutrition support, found that proper documentation and coding of malnutrition ...
Surgery a better treatment option for some hamstring injuries
2015-07-11
ORLANDO, FL - Patients treated surgically for a hamstring rupture demonstrated better results than those treated only with therapy, according to a study presented today at the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine's (AOSSM) Annual Meeting in Orlando, FL.
"Overall, patients in this study treated with surgery had a trend towards better lower extremity function as well as a higher likelihood of returning to re-injury activities than those treated non-surgically," commented corresponding author Joshua Olsen, MD, from the New England Baptist Hospital. "Most notably, ...
Older athletes able to return to sport after rotator cuff repair
2015-07-11
ORLANDO, FL - Outcomes following the arthroscopic repair of rotator cuff tears in older athletes appears to be successful a majority of the time, according to research presented today at the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine's (AOSSM) Annual Meeting in Orlando, Florida.
"Seventy-seven percent of our patients who had an arthroscopic repair of a full thickness rotator cuff tear, were able to return to their sport at a similar level of intensity," said lead author, Peter Millett, MD, MSc, from the Steadman Philippon Research Institute in Vail, Colorado.
Forty-nine ...
[1] ... [2887]
[2888]
[2889]
[2890]
[2891]
[2892]
[2893]
[2894]
2895
[2896]
[2897]
[2898]
[2899]
[2900]
[2901]
[2902]
[2903]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.