Cancer survivors may face unique challenges when trying to adopt
2015-07-13
A new study has found that cancer survivors' options for adoption may be limited by adoption agencies' policies. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the study also indicates that a training program for oncology healthcare providers can help them provide valuable information to patients who are making decisions about fertility and adoption.
Because cancer and the therapies used to treat it can leave some patients infertile, many young cancer survivors may turn to adoption when hoping to start--or add to--a family. Adoption ...
Nixoncare vs. Obamacare: Comparing the rhetoric and reality of 2 health plans
2015-07-13
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- Few people today would dare call President Richard Nixon a radical liberal. But 44 years ago, he proposed a health plan that went far beyond what today's Affordable Care Act includes. After the first plan failed, he did it again three years later.
And just like today's heated rhetoric from opponents of the ACA, also called "Obamacare" after the president who introduced it, Nixon's plans were met with inflamed opposition from the other party.
In a new article in the journal Pediatrics, a team from the Child Health Evaluation and Research Unit at ...
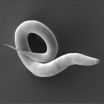
Worms hitch rides on slugs when traveling to far flung places
2015-07-13
This news release is available in German.
Slugs and other invertebrates provide essential public transport for small worms in the search for food, according to research published in the open access journal BMC Ecology.
Nematode worms (including Caenorhabditis elegans) are around a millimeter long and commonly found in short-lived environments, such as decomposing fruit or other rotting plant material. The worms face a high level of unpredictability in these environments as temperature and food availability fluctuate, and frequently need to move to new locations. ...
Ultrasound accelerates skin healing -- especially for diabetics and the elderly
2015-07-13
Treatment could save the NHS £3.1 billion every year
More than 200,000 patients in the UK suffer with chronic wounds
Healing time can be reduced by a third
Healing times for skin ulcers and bedsores can be reduced by a third with the use of low-intensity ultrasound, scientists from the University of Sheffield and University of Bristol have found.
Researchers from the University of Sheffield's Department of Biomedical Science discovered the ultrasound transmits a vibration through the skin and wakes up cells in wounds helping to stimulate and accelerate the healing ...
What happens when cosmic giants meet galactic dwarfs?
2015-07-13
When two different sized galaxies smash together, the larger galaxy stops the smaller one making new stars, according to a study of more than 20,000 merging galaxies.
The research, published today, also found that when two galaxies of the same size collide, both galaxies produce stars at a much faster rate.
Astrophysicist Luke Davies, from The University of Western Australia node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR), says our nearest major galactic neighbour, Andromeda, is hurtling on a collision course with the Milky Way at about 400,000 ...
The Lancet: Study reveals dramatic shortfall in donor funding for key global health issues
2015-07-13
As the world's leaders gather in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, for the Financing for Development Conference [1], a study published in The Lancet demonstrates that a new approach is needed for classifying funding that reflects the function the funding serves, rather than the specific disease or country. The study is the first in-depth assessment of how donor funding is spent on global versus country-specific functions of health [2].
The paper also presents an expanded definition of official development assistance (ODA) for health, which is used to identify important underfunded ...
Study finds donor funds fall short for key global health functions
2015-07-13
As experts debate the slow response to the Ebola outbreak in West Africa and call for better international coordination, a new analysis estimates that $22 billion was spent on global health aid in 2013, yet only a fifth of this went toward such global imperatives as research on diseases that disproportionally affect the poor, outbreak preparedness and global health leadership.
The analysis, by Dean Jamison, PhD, a global health economist at UC San Francisco (UCSF); Lawrence Summers, PhD, a former US Treasury Secretary now at Harvard University; and researchers at SEEK ...
Tommy John surgeries increasing for youth athletes
2015-07-12
ORLANDO, FL - Surgeries related to overuse elbow injuries, i.e. Tommy John Surgery, are more common among youth athletes than previously believed, according to research presented today at the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine's (AOSSM) Annual Meeting in Orlando, Florida.
"Our results showed that 15-19 year-olds accounted for 56.7 percent of the Ulnar Collateral Ligament Reconstruction (UCLR) or Tommy John surgeries performed in the U.S. between 2007-2011. This is a significant increase over time with an average increase of 9.12 percent per year," said lead ...
Surgeries before college athletics may result in more injuries during college play
2015-07-12
ORLANDO, FL - Athletes who've had lower extremity surgeries before going on to play in college, might be at a higher risk for another surgery independent of gender and sport, say researchers presenting their work today at the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine's (AOSSM) Annual Meeting in Orlando, FL.
"This is the first study to look at the relationship between precollegiate surgery and future injury requiring surgery in collegiate athletes. Our results suggest that athletes injured before college might be left with a functional deficit that puts them at ...
Documentation of hospital patients' malnutrition helps maximize care and reimbursement
2015-07-12
Nutrition support professionals who are well-versed in proper documentation of malnutrition diagnoses in hospital patients can help ensure that hospitals receive maximum funding for patient care according to a new review.
The review, recently published in Nutrition in Clinical Practice (NCP), a peer-reviewed, interdisciplinary journal of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.) that publishes articles about the scientific basis and clinical application of nutrition and nutrition support, found that proper documentation and coding of malnutrition ...
Surgery a better treatment option for some hamstring injuries
2015-07-11
ORLANDO, FL - Patients treated surgically for a hamstring rupture demonstrated better results than those treated only with therapy, according to a study presented today at the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine's (AOSSM) Annual Meeting in Orlando, FL.
"Overall, patients in this study treated with surgery had a trend towards better lower extremity function as well as a higher likelihood of returning to re-injury activities than those treated non-surgically," commented corresponding author Joshua Olsen, MD, from the New England Baptist Hospital. "Most notably, ...
Older athletes able to return to sport after rotator cuff repair
2015-07-11
ORLANDO, FL - Outcomes following the arthroscopic repair of rotator cuff tears in older athletes appears to be successful a majority of the time, according to research presented today at the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine's (AOSSM) Annual Meeting in Orlando, Florida.
"Seventy-seven percent of our patients who had an arthroscopic repair of a full thickness rotator cuff tear, were able to return to their sport at a similar level of intensity," said lead author, Peter Millett, MD, MSc, from the Steadman Philippon Research Institute in Vail, Colorado.
Forty-nine ...
Neutrons find 'missing' magnetism of plutonium
2015-07-10
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., July 10, 2015 -- Groundbreaking work at two Department of Energy national laboratories has confirmed plutonium's magnetism, which scientists have long theorized but have never been able to experimentally observe. The advances that enabled the discovery hold great promise for materials, energy and computing applications.
Plutonium was first produced in 1940 and its unstable nucleus allows it to undergo fission, making it useful for nuclear fuels as well as for nuclear weapons. Much less known, however, is that the electronic cloud surrounding the plutonium ...
NASA's Fermi sees record flare from a black hole in a distant galaxy
2015-07-10
Five billion years ago, a great disturbance rocked a region near the monster black hole at the center of galaxy 3C 279. On June 14, the pulse of high-energy light produced by this event finally arrived at Earth, setting off detectors aboard NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope and other satellites. Astronomers around the world turned instruments toward the galaxy to observe this brief but record-setting flare in greater detail.
"One day 3C 279 was just one of many active galaxies we see, and the next day it was the brightest thing in the gamma-ray sky," said Sara ...
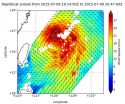
Satellite shows newborn Tropical Depression 02C form in Central Pacific
2015-07-10
NOAA's GOES-West satellite saw that Hawaii is in the middle of a triangle of tropical cyclones. Tropical Depression 02C formed over 700 hundred miles south-southeast of Hawaii on July 10.
There are three tropical cyclones in the Central Pacific Ocean and Hawaii is in the middle of them. On July 10, newborn Tropical Depression 01C was west of Hawaii, while newborn Tropical Depression 02C was south of the Big Island. Post-Tropical Depression Ela was fizzling northeast of Hawaii.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite provided an infrared image of the newborn depression that showed ...
Satellite shows newborn Tropical Depression 01C form in Central Pacific
2015-07-10
NOAA's GOES-West satellite saw that Hawaii is in the middle of a triangle of tropical cyclones. Tropical Depression 01C formed hundreds of miles southwest of Hawaii on July 10.
There are three tropical cyclones in the Central Pacific Ocean and Hawaii is in the middle of them. On July 10, newborn Tropical Depression 01C was west of Hawaii, while newborn Tropical Depression 02C was south of the Big Island. Post-Tropical Depression Ela was fizzling northeast of Hawaii.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite provided an infrared image of the newborn depression that showed fragmented ...
Spotting the elephant not in the room
2015-07-10
An automated thermal detection system that can discern wild elephants from background and other animals in infrared images could save lives in parts of the world where the animals roam free and often enter villages and other human habitation, according to research published in the International Journal of Electronic Security and Digital Forensics.
Siva Mangai and colleagues at Karunya University, in Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India, explain how encounters between humans and elephants is a critical safety issue in the Western Ghats region of Tamil Nadu. "The movement of wild ...
NASA sees Typhoon Nangka leaving the Marianas
2015-07-10
NASA's Aqua satellite saw the massive Typhoon Nangka moving out of the Marianas Islands, while NASA's RapidScat instrument pinpointed the location of its strongest winds.
On July 9, the RapidScat instrument that flies aboard the International Space Station, observed Nangka's strongest winds on the western side of the storm, reaching speeds of more than 30 meters per second (108 kph/67 mph). RapidScat scanned the storm's surface winds for about 90 minutes from 1:41 p.m. to 3:14 p.m. EDT.
When Aqua passed over Typhoon Nangka on July 10 at 01:10 UTC (9:10 a.m. EDT ...
Satellite shows Post-Tropical Depression Ela northeast of Hawaii
2015-07-10
NOAA's GOES-West satellite saw that Hawaii is in the middle of a triangle of tropical cyclones. Post-Tropical Depression Ela was located northeast of Hawaii on July 10, and the forecast calls for the storm to move west toward the islands over the weekend of July 11 and 12 and dissipate.
There are three tropical cyclones in the Central Pacific Ocean and Hawaii is in the middle of them. On July 10, newborn Tropical Depression 01C was west of Hawaii, while newborn Tropical Depression 02C was south of the Big Island. Post-Tropical Depression Ela was northeast of the islands ...
NASA looks at Typhoon Chan-Hom's strongest winds on approach to China
2015-07-10
RapidScat is an instrument that sits on the International Space Station and reads surface winds over the ocean. It has been invaluable to tropical cyclone forecasters, showing where the strongest winds are located in storms. RapidScat spotted Chan-Hom's strongest winds away from Taiwan as it approached mainland China for landfall.
On July 9, the RapidScat instrument that flies aboard the International Space Station, observed Chan-Hom's strongest winds stretched from the northwestern to southeastern side of the storm, reaching speeds of more than 30 meters per second (108 ...
Improved sperm diagnostic test may pinpoint best fertility treatment for couples
2015-07-10
DETROIT - A Wayne State University School of Medicine professor, in collaboration with researchers at CReAte Fertility Center, University of Toronto, Harvard University and Georgia Reagents University, has developed the first diagnostic test for sperm RNA based on next-generation sequencing. For couples with unexplained infertility, the test may help determine the best infertility treatment for couples having difficulty conceiving.
Published this week in Science Translational Medicine, "Absence of sperm RNA elements correlates with idiopathic male infertility," by the ...
Can you actually hear 'inaudible' sound?
2015-07-10
This news release is available in German.
Are wind farms harmful to humans? Some believe so, others refute this; this controversial topic makes emotions run high. To give the debate more objectivity, an international team of experts dealt with the fundamentals of hearing in the lower limit range of the audible frequency range (i.e. infrasound), but also in the upper limit range (i.e. ultrasound). The project, which is part of the European Metrology Research Programme (EMRP), was coordinated by the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB). At PTB, not only acoustics ...
Study shows variation in rates of secondary cleft lip and palate surgery
2015-07-10
July 10, 2015 - For children with cleft lip and palate, the chances of undergoing secondary surgery vary depending on the center where they're treated, reports a study in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery--Global Open®, the official open-access medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
When secondary surgeries are performed, they don't necessarily improve the child's final facial appearance, according to the new research by ASPS Member Surgeon Dr. Thomas J. Sitzman of Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center and colleagues.
Secondary ...
Cutting cost and power consumption for big data
2015-07-10
Random-access memory, or RAM, is where computers like to store the data they're working on. A processor can retrieve data from RAM tens of thousands of times more rapidly than it can from the computer's disk drive.
But in the age of big data, data sets are often much too large to fit in a single computer's RAM. The data describing a single human genome would take up the RAM of somewhere between 40 and 100 typical computers.
Flash memory -- the type of memory used by most portable devices -- could provide an alternative to conventional RAM for big-data applications. It's ...
Findings identify receptors modulating macrophage responses to spinal cord injury
2015-07-10
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Jul. 10, 2015) -- Macrophages are cellular sentinels in the body, assigned to identify "attacks" from viruses, bacteria, or fungi and sound the alarm when they are present. However, these cells are a "double edged sword" in spinal cord injury, providing both neural repair-promoting properties and pathological functions that destroy neuronal tissue
"We know from previous research that macrophages are versatile, and signals at the injury site can stimulate repair or destruction--or confusingly, both," said John Gensel Ph.D., Assistant Professor of Physiology ...
[1] ... [2879]
[2880]
[2881]
[2882]
[2883]
[2884]
[2885]
[2886]
2887
[2888]
[2889]
[2890]
[2891]
[2892]
[2893]
[2894]
[2895]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.