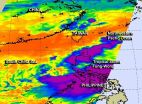
(Press-News.org) Tropical Storm Fung-Wong continued to affect the Philippines while moving north through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. NASA's Aqua satellite provided infrared data on the storm's clouds that showed some high, strong thunderstorms with the potential for heavy rainfall over the northern and central regions of the country. The storm is now expected to affect three more countries over the next several days.
The AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite uses infrared light to read cloud top temperatures in tropical cyclones. When Aqua passed over Fung-Wong infrared data saw some very cold cloud top temperatures and strong storms. Those storms had cloud top temperatures near -63F/-53C indicating they were high into the troposphere and had the potential to generate heavy rain.
On Sept. 19 at 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT) Fung-Wong had maximum sustained winds near 40 knots (46 mph/74 kph). It was centered near 18.9 north latitude and 121.0 east longitude, about 247 nautical miles north of Manila, Philippines. Fung-Wong was moving to the west-northwest at 13 knots (15 mph/24 kph).
Now that Fung-Wong is departing the Philippines, it is now forecast to affect Taiwan, China and Japan. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center now forecasts the center of Fung-Wong to track through Taiwan from south to north over Sept. 20 and 21 and make another landfall near Shanghai, China on Sept. 23 before curving back over the ocean and head toward southern Japan.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA eyes Tropical Storm Fung-Wong move through Northwestern Pacific
2014-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dwindling wind may tip predator-prey balance
2014-09-19
MADISON, Wis. — Bent and tossed by the wind, a field of soybean plants presents a challenge for an Asian lady beetle on the hunt for aphids. But what if the air — and the soybeans — were still?
Rising temperatures and shifting precipitation patterns may get the lion's share of our climate change attention, but predators may want to give some thought to wind, according to a University of Wisconsin Madison zoologist's study, which is among the first to demonstrate the way "global stilling" may alter predator-prey relationships.
"There are all sorts of other things that ...
A two generation lens: Current state policies fail to support families with young children
2014-09-19
September 19, 2014 -- Recent two-generation approaches to reducing poverty that help children and their parents are receiving increasing attention from researchers, advocates, and foundations. By combining education and training for parents to enable them to move to jobs that offer a path out of poverty with high-quality early care and education for children, these programs aim to improve the life opportunities of both. However, according to a new report from the National Center for Children in Poverty (NCCP), State Policies through a Two-Generation Lens, while research ...
Soft robotics 'toolkit' features everything a robot-maker needs
2014-09-19
A new resource unveiled today by researchers from several Harvard University labs in collaboration with Trinity College Dublin provides both experienced and aspiring researchers with the intellectual raw materials needed to design, build, and operate robots made from soft, flexible materials.
With the advent of low-cost 3D printing, laser cutters, and other advances in manufacturing technology, soft robotics is emerging as an increasingly important field. Using principles drawn from conventional rigid robot design, but working with pliable materials, engineers are pioneering ...
Fingertip sensor gives robot unprecedented dexterity
2014-09-19
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- Researchers at MIT and Northeastern University have equipped a robot with a novel tactile sensor that lets it grasp a USB cable draped freely over a hook and insert it into a USB port.
The sensor is an adaptation of a technology called GelSight, which was developed by the lab of Edward Adelson, the John and Dorothy Wilson Professor of Vision Science at MIT, and first described in 2009. The new sensor isn't as sensitive as the original GelSight sensor, which could resolve details on the micrometer scale. But it's smaller — small enough to fit on a robot's ...
Mayo researchers reveal pathway that contributes to Alzheimer's disease
2014-09-19
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. — Researchers at Jacksonville's campus of Mayo Clinic have discovered a defect in a key cell-signaling pathway they say contributes to both overproduction of toxic protein in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients as well as loss of communication between neurons — both significant contributors to this type of dementia.
Their study, in the online issue of Neuron, offers the potential that targeting this specific defect with drugs "may rejuvenate or rescue this pathway," says the study's lead investigator, Guojun Bu, Ph.D., a neuroscientist at Mayo ...
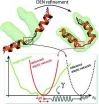
A refined approach to proteins at low resolution
2014-09-19
Membrane proteins and large protein complexes are notoriously difficult to study with X-ray crystallography, not least because they are often very difficult, if not impossible, to crystallize, but also because their very nature means they are highly flexible. The result is that when a structure can be obtained it is often of low resolution, ambiguous and reveals a mosaic-like spread of protein domains that sometimes create more puzzles than they solve. [Schröder, Levitt & Brunger. (2014), Acta Cryst. D70, 2241-2255; doi: 10.1107/S1399004714016496 ]
Now, Gunnar Schröder ...
Reflected smartphone transmissions enable gesture control
2014-09-19
With almost all of the U.S. population armed with cellphones – and close to 80 percent carrying a smartphone – mobile phones have become second-nature for most people.
What's coming next, say University of Washington researchers, is the ability to interact with our devices not just with touchscreens, but through gestures in the space around the phone. Some smartphones are starting to incorporate 3-D gesture sensing based on cameras, for example, but cameras consume significant battery power and require a clear view of the user's hands.
UW engineers have developed a ...
Patients with advanced, incurable cancer denied palliative care
2014-09-19
Many patients with advanced, incurable cancer do not receive any palliative care, reveals new research to be presented later this month at the ESMO 2014 Congress in Madrid, Spain, 26-30 September. The findings are astonishing as they come at the same time as 15 new oncology centres in Europe, Canada, South America and Africa are being awarded the prestigious title of 'ESMO Designated Centre of Integrated Oncology and Palliative Care.'
SR I Dr Alexandru Grigorescu, medical oncology consultant at the Institute of Oncology Bucharest, Romania, member of the ESMO Palliative ...
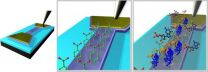
Graphene sensor tracks down cancer biomarkers
2014-09-19
An ultrasensitive biosensor made from the wonder material graphene has been used to detect molecules that indicate an increased risk of developing cancer.
The biosensor has been shown to be more than five times more sensitive than bioassay tests currently in use, and was able to provide results in a matter of minutes, opening up the possibility of a rapid, point-of-care diagnostic tool for patients.
The biosensor has been presented today, 19 September, in IOP Publishing's journal 2D Materials.
To develop a viable bionsensor, the researchers, from the University of ...
Simple test can help detect Alzheimer's before dementia signs show: York U study
2014-09-19
TORONTO, Sept. 19, 2014 — York University researchers say a simple test that combines thinking and movement can help to detect heightened risk for developing Alzheimer's disease in a person, even before there are any telltale behavioural signs of dementia.
Faculty of Health Professor Lauren Sergio and PhD candidate Kara Hawkins who led the study asked the participants to complete four increasingly demanding visual-spatial and cognitive-motor tasks, on dual screen laptop computers. The test aimed at detecting the tendency for Alzheimer's in those who were having cognitive ...