Researchers grind nanotubes to get nanoribbons
2015-06-15
A simple way to turn carbon nanotubes into valuable graphene nanoribbons may be to grind them, according to research led by Rice University.
The trick, said Rice materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan, is to mix two types of chemically modified nanotubes. When they come into contact during grinding, they react and unzip, a process that until now has depended largely on reactions in harsh chemical solutions.
The research by Ajayan and his international collaborators appears in Nature Communications.
To be clear, Ajayan said, the new process is still a chemical reaction ...
People living in disadvantaged cities are at greater risk of suicide
2015-06-15
The city where an individual lives can influence the risk of dying by suicide, according to a new study from sociologists at Rice University and the University of Colorado at Boulder.
"Suicide in the City: Do Characteristics of Place Really Influence Risk?" appears in the latest edition of Social Science Quarterly. The study found that adults living in cities with more socio-economic disadvantages and fewer families living together have higher odds of suicidal death than adults living in less-disadvantaged cities and cities with more families living together.
The findings ...
Underground ants can't take the heat
2015-06-15
PHILADELPHIA (June 15, 2015) - Army ants, the nomadic swarming predators underfoot in the jungle, can take down a colony of prey animals without breaking a sweat. But certain army ant species can't take the heat.
According to a new study from Drexel University, underground species of army ants are much less tolerant of high temperatures than their aboveground relatives--and that difference in thermal tolerance could mean that many climate change models lack a key element of how animal physiology could affect responses to changing environments.
At face value, this is ...
What fish ears can tell us about sex, surveillance and sustainability
2015-06-15
Scientists at the University of Southampton have found a way to pry into the private lives of fish - by looking in their ears.
By studying ear stones in fish, which act as tiny data recorders, scientists can now reveal migration patterns and even provide insights into their sex life.
Managing fish stocks in a sustainable way is a major challenge facing scientists, conservationists, policy makers and fishermen. To get the best results, accurate information about the movements of fish in the wild is needed but gathering this information is extremely difficult.
Tiny ...
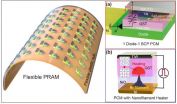
A KAIST research team develops the first flexible phase-change random access memory
2015-06-15
Daejeon, Republic of Korea, Jun 15, 2015 -- Phase change random access memory (PRAM) is one of the strongest candidates for next-generation nonvolatile memory for flexible and wearable electronics. In order to be used as a core memory for flexible devices, the most important issue is reducing high operating current. The effective solution is to decrease cell size in sub-micron region as in commercialized conventional PRAM. However, the scaling to nano-dimension on flexible substrates is extremely difficult due to soft nature and photolithographic limits on plastics, thus ...
Secrets of innovation revealed in study of global video game industry
2015-06-15
From the adventures of Lara Croft in Tomb Raider to the apocalyptic drama of Fallout - new research from the University of Warwick has revealed the secret to how some of the world's most iconic video games were created.
Professor David Stark says it is because the creative teams behind these ground-breaking titles had the ideal mix of career backgrounds and working relationships.
He claims his research offers a fresh insight into the factors which
stimulate innovation - theories that can also apply away from the video gaming industry.
The 'Big Data' analysis looked ...
Self-awareness not unique to mankind
2015-06-15
Humans are unlikely to be the only animal capable of self-awareness, a new study has shown.
Conducted by University of Warwick researchers, the study found that humans and other animals capable of mentally simulating environments require at least a primitive sense of self. The finding suggests that any animal that can simulate environments must have a form of self-awareness.
Often viewed as one of man's defining characteristics, the study strongly suggests that self-awareness is not unique to mankind and is instead likely to be common among animals.
The researchers, ...
Mount Sinai scientists develop new technique for analyzing the epigenetics of bacteria
2015-06-15
Scientists from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have developed a new technique to more precisely analyze bacterial populations, to reveal epigenetic mechanisms that can drive virulence. The new methods hold the promise of a potent new tool to offset the growing challenge of antibiotic resistance by bacterial pathogens. The research was published today in the journal Nature Communications, and conducted in collaboration with New York University Langone Medical Center and Brigham and Women's Hospital of Harvard Medical School.
The information content of the ...
How the Epstein-Barr virus hides in human cells
2015-06-15
Scientists at Helmholtz Zentrum München have now discovered how Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) conceals itself in human cells. A main culprit for its bad visibility by the immune system is the viral protein LMP2A. As published in the scientific journal PLOS Pathogens, the protein helps EBV-infected cells hide from T cells. This camouflage through the LMP2A protein may play a major role in the causation of cancer by EBV.
„We suspected that a viral protein was behind EBV's camouflage in cancerous cells", says Dr. Andreas Moosmann from the Research Unit Gene Vectors ...
Majority of adults favor ban on powdered alcohol
2015-06-15
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- After this year's legalization of powdered alcohol, some states have already banned it -- a move that the majority of the public supports, according to a new University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health.
Adults across the country share the same top concern about the new alcohol-on-the-go product: potential misuse among underage youth.
Packaged in travel-friendly pouches, powdered alcohol will be available in flavors of distilled spirits like vodka and rum and also mixed drinks. One packet of powdered alcohol ...
Uterine transplantation: Subjects have 'adjusted well to their new life situation'
2015-06-15
Lisbon, 15 June 2015: In October last year the Gothenburg, Sweden, group of Mats Bra?nnstro?m announced the world's first live birth following the transplantation of a donated uterus.(1) In an editorial accompanying the report, The Lancet listed this remarkable achievement as comparable to only three other landmarks in the history of reproductive medicine: "the arrival of in-vitro fertilisation (IVF) in the late 1970s; the development of intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) in the early 1990s; the first ovarian transplant a decade ago; and [now] the first live birth ...
Assisted reproduction not associated with reduced academic performance in adolescence
2015-06-15
Lisbon, 15 June 2015: The academic performance of children conceived by assisted reproduction techniques (ART) is no better or worse than that of spontaneously conceived children when assessed at the ninth grade of their school education.(1) Similarly, ART singletons and ART twins also had comparable test scores, suggesting, say the investigators, that "the higher obstetric risk" identified in ART pregnancies - and particularly in twins - "is not associated with poorer academic performance in adolescence".(2)
"These findings are very important for infertile patients," ...
Poor sleep associated with increased risk of heart attack and stroke
2015-06-15
EuroHeartCare is the official annual meeting of the Council on Cardiovascular Nursing and Allied Professions (CCNAP) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). The 2015 meeting is held 14 to 15 June in Dubrovnik, Croatia, in collaboration with the Croatian Association of Cardiology Nurses.
Professor Gafarov said: "Mortality from cardiovascular diseases accounts for nearly 50% of the total mortality among the population. Nearly 80% of deaths from cardiovascular disease are due to myocardial infarction (heart attack) and stroke. It means that today we are talking about ...
Visualizing calcified coronary arteries may be wake-up call to change lifestyle
2015-06-15
"It is my coronary artery and my coronary artery calcification and I am facing a real risk and challenge," said one patient.
EuroHeartCare is the official annual meeting of the Council on Cardiovascular Nursing and Allied Professions (CCNAP) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). The 2015 meeting is held 14 to 15 June in Dubrovnik, Croatia, in collaboration with the Croatian Association of Cardiology Nurses.
Ms Mols said: "Patients with non-obstructive coronary artery disease and hyperlipidaemia (high blood lipids) urgently need to improve their lifestyles and ...
American Thoracic Society issues recommendations on healthy sleep
2015-06-15
The American Thoracic Society has released a policy statement with recommendations for clinicians and the general public on achieving good quality sleep and getting an adequate quantity of sleep.
"Sleep plays a vital role in human health, yet there is a lack of sufficient guidance on promoting good sleep health," said Sutapa Mukherjee, MBBS, PhD, chair of the committee that produced the statement. "In this statement, with an eye towards improving public health, we address the importance of good quality sleep with a focus on sleep health in adults and children; the effects ...
New calculations to improve CO2 monitoring from space
2015-06-15
How light of different colours is absorbed by carbon dioxide (CO2) can now be accurately predicted using new calculations developed by a UCL-led team of scientists. This will help climate scientists studying Earth's greenhouse gas emissions to better interpret data collected from satellites and ground stations measuring CO2.
By improving the understanding of how much radiation CO2 absorbs, uncertainties in modelling climate change will be reduced and more accurate predictions can be made about how much Earth is likely to warm over the next few decades.
Previous methods ...
Blood antibodies may predict HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer survival
2015-06-15
Background: According to Sturgis, the incidence of HPV-positive oropharyngeal carcinoma has increased dramatically in recent years. Although patients with HPV-positive disease have a better prognosis than those with HPV-negative disease, researchers are still seeking a better understanding of what group of patients is more likely to respond to treatment.
How the Study Was Conducted: Sturgis and colleagues used blood samples from 209 patients with previously untreated oropharyngeal carcinoma, including 96 who had confirmed HPV-positive disease, and screened the samples ...
ALK1 protein may play a role in breast cancer metastasis
2015-06-15
Background: Pietras said that although prognosis for breast cancer is relatively good when detected in its early stages, metastatic disease is the cause of 90 percent of all cancer-related deaths. Therefore, learning more about the metastatic process and finding new cures to inhibit disease spread is at the center of clinical attention.
He explained that in order for a tumor to spread, a cancer cell must detach and traverse the vascular wall to escape into the blood stream, exit the vasculature to enter the metastatic site, and colonize the new tissue. The fact that ...
Endometriosis associated with a greater risk of complications in pregnancy
2015-06-15
Lisbon, 15 June 2015: Women with endometriosis are at an increased risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy, according to results of a huge nationwide study presented today. Moreover, women with a history of endometriosis whose pregnancies progressed beyond 24 weeks were found to be at a higher than average risk of complications, including haemorrhage (ante- and postpartum) and preterm birth.
"These results indicate that endometriosis predisposes women to an increased risk of early pregnancy loss and later pregnancy complications," said the study's first author Dr Lucky ...
Lack of evidence on how to care for hip fracture patients with dementia
2015-06-15
Medical guidance on how to care for elderly people with dementia following a hip fracture is 'sadly lacking' according to researchers at the University of East Anglia.
Almost half of all people who suffer hip fractures also have dementia. But a Cochrane Review published today reveals there is no conclusive evidence on how to care for this particularly vulnerable group.
The review, which was funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), highlights an urgent need for better research into what strategies improve post-operative care - both within hospital ...
Power of the media's impact on medicine use revealed
2015-06-14
More than 60,000 Australians are estimated to have reduced or discontinued their use of prescribed cholesterol-lowering statin medications following the airing of a two-part series critical of statins by ABC TV's science program, Catalyst, a University of Sydney study reveals in the latest Medical Journal of Australia.
The analysis of the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme medication records of 191,000 people revealed that there was an immediate impact after Catalyst was aired in October 2013, with 14,000 fewer people dispensed statins per week than expected.
"In the eight ...
One in 5 young VTE patients require psychotropic drugs within 5 years
2015-06-14
EuroHeartCare is the official annual meeting of the Council on Cardiovascular Nursing and Allied Professions (CCNAP) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). The 2015 meeting is held 14 to 15 June in Dubrovnik, Croatia, in collaboration with the Croatian Association of Cardiology Nurses.
Ms Arbjerg Højen said: "Young VTE patients are scared of having another VTE and of dying. We treat these patients in our Thrombosis Research Unit and have seen how anxious and mentally unwell they can be, even a long time after the VTE occurs. They are troubled and have a hard ...
Patients with primary hand OA should not be prescribed hydroxychloroquine
2015-06-13
Rome, Italy, 13 June 2015: The results of an interventional trial presented today at the European League Against Rheumatism Annual Congress (EULAR 2015) showed that use of the disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug hydroxychloroquine for 24 weeks did not diminish mild-moderate pain from primary hand osteoarthritis (OA). Furthermore, treatment did not improve overall physical, social and emotional wellbeing. These findings suggest that hydroxychloroquine should no longer be routinely prescribed for patients with this form of arthritis.
OA is the most common type of arthritis, ...
Dose reduction strategy can substantially reduce high cost of TNF inhibitor therapy in RA
2015-06-13
Rome, Italy, 13 June 2015: The results of a study presented today at the European League Against Rheumatism Annual Congress (EULAR 2015) showed that, in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, a good clinical response to maintenance treatment with a tumour necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) was maintained even when the dose was reduced by one-third.
Reducing the TNFi dose by two-thirds resulted in more flares (exacerbations of symptoms and signs) but these subsided when the higher dose of TNFi was restarted, and did not adversely affect subsequent progression of any disability. ...
Severely impaired stroke survivors regain arm function after intensive physical therapy
2015-06-13
Time may heal all wounds, but in the case of stroke survivors, the key to better recovery is to spend more time in an intensive physical therapy program, according to a University of Florida Health study.
After a stroke, the brain and body can start recovering immediately and can show improvement up to six months afterward, said UF Health researcher Janis Daly, Ph.D. But this study focused on people who had persistent disability even a year or more after completing standard care. The study found that extensive physical therapy helped them recover motor function, even ...
[1] ... [2939]
[2940]
[2941]
[2942]
[2943]
[2944]
[2945]
[2946]
2947
[2948]
[2949]
[2950]
[2951]
[2952]
[2953]
[2954]
[2955]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.