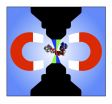
How dividing cells end up the same size
2015-06-04
DURHAM, NC -- There aren't any giants or midgets when it comes to the cells in your body, and now Duke University scientists think they know why.
A new study appearing June 3 in Nature shows that a cell's initial size determines how much it will grow before it splits into two.
This finding goes against recent publications suggesting cells always add the same amount of mass, with some random fluctuations, before beginning division.
"It's like students going through college," said Lingchong You, the Paul Ruffin Scarborough Associate Professor of Engineering in the ...
Study points to human impact on evolution of freshwater fish
2015-06-04
The most aggressive largemouth bass in the lake are also the ones most prized by anglers. These are the fish that literally 'take the bait' and put the fun into both competitive and casual sport fishing.
Then, according to the rules of catch-and-release, the captive is unhooked and tossed back to swim away without any lasting consequences. But a new UConn study says there is an impact; the evolutionary path of a species may be on the line.
In a recent paper published in the journal PLOS ONE, a team of researchers led by Jan-Michael Hessenauer and Jason Vokoun of the ...
Preventive neuroradiology: Brain imaging bolsters efforts to lower Alzheimer's risk
2015-06-04
Armed with new knowledge about how neurodegenerative diseases alter brain structures, increasing numbers of neurologists, psychiatrists and other clinicians are adopting quantitative brain imaging as a tool to measure and help manage cognitive declines in patients. These imaging findings can help spur beneficial lifestyle changes in patients to reduce risk for Alzheimer's disease.
The concept that cognitive decline can be identified early and prevented by applying quantitative brain imaging techniques is the focus of "Hot Topics in Research: Preventive Neuroradiology ...
Cancer screening increase may reflect Affordable Care Act provision
2015-06-04
ATLANTA - June 4, 2015- Screening for colorectal cancer increased in lower socioeconomic status (SES) individuals after 2008, perhaps reflecting the Affordable Care Act's removal of financial barriers to screening according to a new analysis. The study, by American Cancer Society investigators, appears online in the journal Cancer.
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) included a cost-sharing provision intended to reduce financial barriers for preventive services, including screening for colorectal cancer (CRC) and breast cancer (BC). To investigate whether ...
Withholding angiotensin receptor blockers after surgery increases risk of postoperative death
2015-06-04
Withholding angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) for longer than two days after surgery is associated with a significantly increased risk of postoperative death, according to a study of more than 30,000 patients in the VA health care system by researchers at UC San Francisco and the San Francisco VA Medical Center (SFVAMC).
ARBs are prescribed for high blood pressure, heart disease and kidney disease, explained lead author Susan M. Lee, MD, an SFVAMC anesthesiologist and UCSF clinical instructor.
"For non-cardiac surgery, ARBs are commonly stopped on the day of surgery ...
A microscopic approach to the magnetic sensitivity of animals
2015-06-04
Researchers at the University of Tokyo have succeeded in developing a new microscope capable of observing the magnetic sensitivity of photochemical reactions believed to be responsible for the ability of some animals to navigate in the Earth's magnetic field, on a scale small enough to follow these reactions taking place inside sub-cellular structures.
Several species of insects, fish, birds and mammals are believed to be able to detect magnetic fields - an ability known as magnetoreception. For example, birds are able to sense the Earth's magnetic field and use it to ...
Social networking against cancer
2015-06-04
The advent of online social networks has led to the rapid development of tools for understanding the interactions between members of the network, their activity, the connections, the hubs and nodes. But, any relationships between lots of entities, whether users of Facebook and Twitter, bees in a colony, birds in a flock, or the genes and proteins in our bodies can be analyzed with the same tools.
Now, research published in International Journal of Data Mining and Bioinformatics shows how social network analysis can be used to understand and identify the biomarkers in ...
Penn study maps the types of physical activity associated with better sleep
2015-06-04
SEATTLE - Physical activities, such as walking, as well as aerobics/calisthenics, biking, gardening, golfing, running, weight-lifting, and yoga/Pilates are associated with better sleep habits, compared to no activity, according to a new study from researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. In contrast, the study shows that other types of physical activity - such as household and childcare -- work are associated with increased cases of poor sleep habits. The full results of the study (Abstract #0246) will be presented during the poster ...
Bee warned -- Study finds pesticides threaten native pollinators
2015-06-04
ITHACA, N.Y. - A new Cornell study of New York state apple orchards finds that pesticides harm wild bees, and fungicides labeled "safe for bees" also indirectly may threaten native pollinators.
The research, published June 3 in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, finds the negative effects of pesticides on wild bees lessens in proportion to the amount of natural areas near orchards.
Thirty-five percent of global food production benefits from insect pollinators, and U.S. farmers have relied exclusively on European honeybees, whose populations have been in decline for ...
Parent-reported symptoms gauge features of the food allergic disease EoE
2015-06-04
CINCINNATI - Researchers have identified that parent-reported responses to a questionnaire called the Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis Symptom Score (PEESS® v2.0) correspond to clinical and biologic features of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) - a severe and often painful food allergy that renders children unable to eat a wide variety of foods.
This study, published online in Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, was led by researchers at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center.
Eosinophils are normal cellular components of the blood, but when the body ...
Extra DNA creates cucumber with all female flowers
2015-06-04
ITHACA, N.Y. - Ask a plant researcher how the sex of a cucumber plant is determined and the person will tell you, "It's complicated." Depending on a complex mix of genetic and environmental factors, cucumbers can be seven different sexes. Some high-yield cucumber varieties produce only female flowers, and a new study identifies the gene duplication that causes this unusual trait.
The study, led by Zhangjun Fei of the Boyce Thompson Institute at Cornell University, and Sanwen Huang of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, in Beijing, appeared recently in The Plant ...
Resuming blood pressure medicine promptly after surgery reduces risk of death
2015-06-04
Chicago - June 4, 2015 - It may be better for patients to resume taking their blood pressure medication sooner after surgery than previously thought. A new study published in the Online First edition of Anesthesiology, the official medical journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists® (ASA®), found resuming angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), common medications used to treat high blood pressure, within two days after surgery decreased death rates in the first month following surgery.
"Sometimes doctors briefly stop ARB medications around the time of ...
Australian fossil forces rethink on our ancestors' emergence onto land
2015-06-04
A 333-million year old broken bone is causing fossil scientists to reconsider the evolution of land-dwelling vertebrate animals, says a team of palaeontologists, including QUT evolutionary biologist Dr Matthew Phillips, and colleagues at Monash University and Queensland Museum.
Analysis of a fractured and partially healed radius (front-leg bone) from Ossinodus pueri, a large, primitive, four-legged (tetrapod), salamander-like animal, found in Queensland, pushes back the date for the origin of demonstrably terrestrial vertebrates by two million years, said Dr Phillips, ...
Bristol undergraduate identifies Gloucestershire fossil as new species of ancient reptile
2015-06-04
Research by Catherine Klein, an undergraduate in Bristol's School of Earth Sciences, shows that fossils from the previously unstudied Woodleaze Quarry belong to a new species of the 'Gloucester lizard' Clevosaurus (named in 1939 after Clevum, the Latin name for Gloucester).
In the Late Triassic, the hills of the South West of the UK formed an archipelago that was inhabited by small dinosaurs and relatives of the Tuatara, a living fossil from New Zealand. The limestone quarries of the region have many caves or fissures containing sediments filled with the bones of abundant ...
'Vampire' plants can have positive impacts up the food chain
2015-06-04
New research has revealed that parasitic 'vampire' plants that attach onto and derive nutrients from another living plant may benefit the abundance and diversity of surrounding vegetation and animal life.
By altering the densities of the hemiparasite (a parasitic plant that also photosynthesises) Rhinanthus minor, in the Castle Hill National Nature Reserve in Sussex, ecologists from the Universities of York, Sussex and Lincoln were able to assess the impacts of the 'vampire' plants on the biodiversity of a species-rich semi-natural grassland. The scientists compared ...
Research points to effective methods of freezing avian red blood cells
2015-06-04
NORTH GRAFTON, Mass. (June 4, 2015)--Birds, like people, can suffer from conditions where a blood transfusion is a necessary life-saving measure. But in many instances, unless an avian donor is readily available, accessing blood is impossible because of the challenges associated with storing the species' red blood cells.
New research published in the American Journal of Veterinary Research has found that a substance called dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) shows promise as a potential cryopreservant for freezing avian blood.
"Birds are susceptible to various causes of blood ...
DNA which only females have
2015-06-04
In many animal species, the chromosomes differ between the sexes. The male has a Y chromosome. In some animals, however, for example birds, it is the other way round. In birds, the females have their own sex chromosome, the W chromosome. For the first, researchers in Uppsala have mapped the genetic structure and evolution of the W chromosome.
Every individual of a species has the same sorts of chromosomes, with one exception. In many species, the way the sexes differ is that males have their own sex chromosome, the Y chromosome. This contains genes which result in the ...
Household items, toys key to infant motor skill development, research finds
2015-06-04
ARLINGTON, Texas -- Toys, appliances, and even a sofa and coffee table can impact the way or when a baby first crawls, walks or achieves other growth milestones, but a new UT Arlington study finds that many parents are unaware of the significant role household items play in their infant's motor skill development.
Priscila Caçola, an assistant professor of kinesiology in the UT Arlington College of Nursing and Health Innovation, co-developed a simple questionnaire for caregivers of infants aged 3 to 18 months that she says can aid in the evaluation of toys and other ...
This week from AGU: Gulf of Mexico erosion, Grand Canyon sandbars, rainfall fluctuations
2015-06-04
From AGU's blogs: Flooding, erosion risks rise as Gulf of Mexico waves loom larger
Waves in the northern Gulf of Mexico are higher than they were 30 years ago, contributing to a greater risk of coastal erosion and flooding in Florida, Alabama, Mississippi and Louisiana, according to a new study in Geophysical Research Letters.
From Eos.org: Building Sandbars in the Grand Canyon
Annual controlled floods from one of America's largest dams are rebuilding the sandbars of the iconic Colorado River, according to a new article by U.S. Geological Survey scientists in Eos. ...
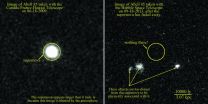
Exiled stars explode far from home
2015-06-04
Sharp images obtained by the Hubble Space Telescope confirm that three supernovae discovered several years ago exploded in the dark emptiness of intergalactic space, having been flung from their home galaxies millions or billions of years earlier.
Most supernovae are found inside galaxies containing hundreds of billions of stars, one of which might explode per century per galaxy.
These lonely supernovae, however, were found between galaxies in three large clusters of several thousand galaxies each. The stars' nearest neighbors were probably 300 light years away, nearly ...
CU Anschutz study shows low-cost weight loss program has long-term results
2015-06-04
AURORA, Colo. June 3 -- As America's obesity epidemic continues to grow, a new study from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus shows that a low-cost, non-profit weight loss program offers the kind of long-term results that often elude dieters.
'We know that people lose weight and then gain it back,' said study author Nia S. Mitchell, M.D., MPH, a researcher with the Division of General Internal Medicine at the Anschutz Health and Wellness Center at CU Anschutz. 'In this case, we found that people who renewed their annual membership in the program lost a ...
New tool brings standards to epigenetic studies
2015-06-04
One of the most widely used tools in epigenetics research - the study of how DNA packaging affects gene expression - is chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), a technique that allows researchers to examine interactions between specific proteins and genomic regions. However, ChIP is a relative measurement, and has significant limitations that can lead to errors, poor reproducibility and an inability to be compared between experiments.
To address these issues, scientists from the University of Chicago have developed a new technique that calibrates ChIP experiments with an ...
Developing delirium in the ICU linked to fatal outcomes
2015-06-04
About one-third of patients admitted to an intensive care unit (ICU) will develop delirium, a condition that lengthens hospital stays and substantially increases one's risk of dying in the hospital, according to a new study led by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers appearing in the British Medical Journal.
"Every patient who develops delirium will on average remain in the hospital at least one day longer," says one of the study's authors, Robert Stevens, M.D., a specialist in critical care and an associate professor at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. ...
Thirty years of AIDS data highlight survival gains, room for improvement
2015-06-04
[EMBARGOED UNTIL THURSDAY, JUNE 4] Although treatment advances have dramatically reduced deaths from opportunistic infections related to AIDS, a new study drawing on 30 years of data from more than 20,000 patients in San Francisco suggests there is still ample room to improve. About a third--35 percent--of AIDS patients diagnosed with their first opportunistic infection from 1997 to 2012 in that city died within five years, according to the study, published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
"While recent research suggests that many opportunistic infections in the ...
Is dietary supplementation appropriate for children with autism spectrum disorder?
2015-06-04
Philadelphia, PA, June 4, 2015 - Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) are often picky eaters, which can lead parents to suspect that their children might not be getting adequate amounts of vitamins and minerals. This sometimes leads parents of children with ASD to try nutritional supplements and dietary regimens such as gluten-free and casein-free (GFCF) diets without professional supervision. In the largest study of its kind, published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, researchers report that these well-intentioned efforts can result in ...
[1] ... [2944]
[2945]
[2946]
[2947]
[2948]
[2949]
[2950]
[2951]
2952
[2953]
[2954]
[2955]
[2956]
[2957]
[2958]
[2959]
[2960]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.