In search of memory storage
2015-06-03
The hippocampus plays a crucial role in memory formation. However, it is not yet fully understood in what way that brain structure's individual regions are involved in the formation of memories. Neuroscientists at the Collaborative Research Center 874 at RUB have recreated this process with the aid of computer simulations. Their findings challenge the model of memory forming in the hippocampus established to date. Their results have been published in the journal PLOS Computational Biology.
Unique anatomy of the hippocampus
The hippocampus' importance for memory forming ...
Study supports IDH gene as prognostic marker in anaplastic astrocytoma
2015-06-03
COLUMBUS, Ohio - New findings suggest that a gene called IDH1 might be prognostic marker for a rare form of brain cancer. Patients in this study who had a mutated IDH gene lived an average of 7.9 years after diagnosis versus 2.8 years for patients with unaltered IDH.
The IDH study was done as part of the phase III clinical trial RTOG 9813, which involved 301 patients with anaplastic astrocytoma. The duel-arm trial evaluated the effectiveness of radiation therapy plus either of two chemotherapy drugs: temozolomide and nitrosourea.
"We found that IDH status is not only ...
Re-inflating balloon after carotid stenting appears to double risk of stroke and death
2015-06-03
After reviewing outcomes from thousands of cases, researchers at Johns Hopkins report that patients with blocked neck arteries who undergo carotid stenting to prop open the narrowed blood vessels fare decidedly worse if their surgeons re-inflate a tiny balloon in the vessel after the mesh stent is in place.
Although the overall risk of stroke and death is low in patients who undergo carotid stenting, the common practice of "ballooning" the vessel after the wire mesh is inserted can double the risk of death and stroke during or shortly after the procedure, according to ...
The Lancet: Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) Seminar
2015-06-03
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) has recently returned to the headlines as new cases have been exported to Korea and China. Experts are concerned that MERS cases continued to be detected in Saudi Arabia throughout the past year, and there appears to be little reduction in the number of cases since its first discovery three years ago. As the month of Ramadan approaches, with 1 million pilgrims expected to arrive in Saudi Arabia in June and July 2015, MERS remains a threat to global health security. The Lancet today publishes a new Seminar on MERS, outlining the current ...
Intravenous nutrition source could reduce side effects of chemotherapy
2015-06-03
PITTSBURGH -- A single dose of an FDA-approved intravenous nutrition source may be able to significantly reduce the toxicity and increase the bioavailability of platinum-based cancer drugs, according to a study by Carnegie Mellon University biologists published in Scientific Reports.
Platinum-based drugs, including cisplatin, carboplatin and oxyplatin, have been used to treat cancer for more than 35 years. While they remain among the most prescribed and most potent chemotherapy drugs, they also cause serious side effects, including kidney damage.
Many of the side effects ...
Cooking up cognition
2015-06-03
These days, cooking dinner requires no more thought than turning a knob on a stovetop, but for early humans the notion that - simply by applying heat or fire - foods could be transformed into something both tastier and easier to digest demanded huge cognitive insight - insights often believed to be limited to humans.
New evidence, however, suggests that, when it comes to cooking, humans may need to make more room at the table.
A new study, co-authored by Felix Warneken, the John L. Loeb Associate Professor of the Social Sciences, and Alexandra Rosati '05, currently ...
The early bird catches the sperm
2015-06-03
Getting up later in the morning might gain you more sleep, but it could mean you end up fathering fewer offspring--at least if you are a songbird called the great tit. Ecologists from the United States and Germany have discovered that compared with early birds, late risers are more likely to be cuckolded, meaning that they unknowingly end up raising young in their nest that had been fathered by another male. It appears that in the early morning hours, they're still asleep rather than being awake and defending their mate.
The study, published in the British Ecological ...
One's ability to identify different smells may impact longevity
2015-06-03
In a recent study of older adults, those with a reduced ability to identify certain odors had an increased risk of dying during an average follow-up of 4 years. The mortality rate was 45% in participants with the lowest scores on a 40-item smell test, compared with 18% of participants with the highest scores.
The study included 1169 Medicare beneficiaries who scratched and sniffed individuals odorant strips and chose the best answer from 4 items listed as multiple-choice.
"The increased risk of death increased progressively with worse performance in the smell identification ...
Cat got your tongue? New research says 'no'
2015-06-03
Cat taste receptors respond in a unique way to bitter compounds compared with human receptors, according to research published in the open access journal BMC Neuroscience. The study represents the first glimpse into how domestic cats perceive bitterness in food at a molecular level, and could explain why cats are sometimes such picky eaters.
The ability to detect bitter chemicals is thought to have evolved because of its utility in avoiding toxic compounds often found in plants. All cats, from pets to wild tigers, are carnivores that consume little plant material. Domestic ...
Endurance athletes should be tested while exercising for potentially fatal heart condition
2015-06-03
Some athletes who take part in endurance exercise such as marathon running, endurance triathlons or alpine cycling can develop irregularities in their heartbeats that can, occasionally, lead to their sudden death.
Now, new evidence published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Wednesday) has shown that doctors who try to detect these heartbeat irregularities (known as arrhythmias) by focusing on the left ventricle of the heart, or on the right ventricle while an athlete is resting, will miss important signs of right ventricular dysfunction that can only be detected ...
Birds cry wolf to scare predators
2015-06-03
One of Australia's smallest birds has found a cunning way to protect its nest from predators by crying wolf, or rather hawk, and mimicking the warning calls of other birds.
Researchers from The Australian National University (ANU) found that the tiny brown thornbill mimics the hawk warning call of a variety of birds to scare off predators threatening its nest, such as the larger pied currawong.
"It's not superbly accurate mimicry, but it's enough to fool the predator," said Dr Branislav Igic, who carried out the study during his PhD at ANU Research School of Biology.
"A ...
Are commercial conflicts of interests justifiable in medical journals?
2015-06-03
A group of former senior editors, writing in The BMJ today, criticise a "seriously flawed and inflammatory attack" by The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) on what that journal believes have become overly stringent policies on conflicts of interest.
The NEJM was the first major medical journal to introduce conflict of interest policies in 1984. It required all authors to disclose any financial ties to health industries and made conflict of interests more transparent.
But recently the NEJM published a series of commentaries and an editorial that attempt to justify ...
Nearly one-third of early adulthood depression could be linked to bullying in teenage years
2015-06-03
Bullying in teenage years is strongly associated with depression later on in life, suggests new research published in The BMJ this week.
Depression is a major public health problem with high economic and societal costs. There is a rapid increase in depression from childhood to adulthood and one contributing factor could be bullying by peers. But the link between bullying at school and depression in adulthood is still unclear due to limitations in previous research.
So a team of scientists, led by Lucy Bowes at the University of Oxford, carried out one of the largest ...
No evidence that smoking drug linked to increased risk of suicide or traffic accidents
2015-06-03
There is no strong evidence that the popular smoking cessation drug varenicline is associated with increased risks of suicidal behaviours, criminal offending, transport accidents, traffic-related offences, and psychoses, finds a study in The BMJ this week.
The findings are based on over 69,000 individuals in Sweden who were prescribed varenicline between 2006 and 2009. Previous reports suggesting a link may not have taken full account of underlying risk factors, say the authors.
Varenicline is widely prescribed for the treatment of nicotine dependence, but reports that ...
Study shows helping pregnant moms with depression doesn't help kids
2015-06-03
DURHAM, N.C. -- A long-term study of mother-child pairs in Pakistan has found that the children turn out pretty much the same, whether or not their mothers received treatment for depression during pregnancy.
An earlier study of the same population found that the mothers themselves benefited from the treatment, with less depression, and demonstrating related healthy behaviors with their newborns, such as breastfeeding. But those improvements were short-lived.
The "Thinking Healthy Programme" is a successful depression intervention evaluated through a randomized trial ...
Compensatory rehabilitation limits motor recovery after stroke
2015-06-03
Washington, DC--Relying on the better-functioning side of the body after a stroke can cause brain changes that hinder rehabilitation of the impaired side, according to an animal study published June 3 in the Journal of Neuroscience. Strokes that occur in one brain hemisphere can result in poor motor function on the opposite side of the body, leading to heavy reliance on the "good" side. This study, led by Soo Young Kim and performed at the University of Texas at Austin and the University of California, Berkeley, found that such compensation produces structural brain changes ...
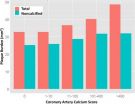
CT angiography links arterial plaque with diabetes, blood pressure, cholesterol
2015-06-02
OAK BROOK, Ill. -- Non-calcified arterial plaque is associated with diabetes, high systolic blood pressure and elevated 'bad' cholesterol levels in asymptomatic individuals, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the leading cause of death in men and women worldwide, accounting for 17 million deaths annually. Current treatment strategies focus on cardiovascular risk and serum cholesterol levels rather than direct assessment of extent of disease in the coronary arteries.
Plaque that forms in the arterial walls ...
Autism struck by surprise
2015-06-02
A new study shows that social and sensory overstimulation drives autistic behaviors. The study, conducted on rats exposed to a known risk factor in humans, supports the unconventional view of the autistic brain as hyper-functional, and offers new hope with therapeutic emphasis on paced and non-surprising environments tailored to the individual's sensitivity.
For decades, autism has been viewed as a form of mental retardation, a brain disease that destroys children's ability to learn, feel and empathize, thus leaving them disconnected from our complex and ever-changing ...
Brain's reaction to certain words could replace passwords
2015-06-02
You might not need to remember those complicated e-mail and bank account passwords for much longer. According to a new study, the way your brain responds to certain words could be used to replace passwords.
In "Brainprint," a newly published study in academic journal Neurocomputing, researchers from Binghamton University observed the brain signals of 45 volunteers as they read a list of 75 acronyms, such as FBI and DVD. They recorded the brain's reaction to each group of letters, focusing on the part of the brain associated with reading and recognizing words, and found ...
Alice instrument's ultraviolet close-up provides a surprising discovery about comet's atmosphere
2015-06-02
San Antonio -- June 2, 2015 -- A close-up of Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko by NASA's ultraviolet instrument surprised scientists by revealing that electrons close to the comet's surface -- not photons from the Sun as had been believed -- cause the rapid breakup of water and carbon dioxide molecules spewing from the surface.
Since last August, the European Space Agency's Rosetta spacecraft has orbited within a hundred miles of the comet in this historic mission. The spectrograph onboard, named Alice, specializes in the far-ultraviolet wavelength band and was developed ...
No improvement in cognition with post-menopausal hormones
2015-06-02
Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) given to recently postmenopausal women in the US for up to four years does not improve cognition, but may have some positive benefits for some mood symptoms, according to a study published by Carey Gleason and colleagues from the University of Wisconsin, Madison, USA, in this week's PLOS Medicine.
The researchers reached these conclusions by conducting a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial (the KEEPS-Cog trial), including 693 recently postmenopausal women living in the US who were randomly assigned to receive either oral estrogen ...
How to weigh the Milky Way
2015-06-02
What if your doctor told you that your weight is somewhere between 100 and 400 lbs.? With any ordinary scale every patient can do better at home. Yet, one patient can't: the Milky Way. Even though today we peer deeper into space than ever before, our home galaxy's weight is still unknown to about a factor of four. Researchers at Columbia University's Astronomy Department have now developed a new method to give the Milky Way a more precise physical checkup.
The Milky Way consists of roughly 100 billion stars that form a huge stellar disk with a diameter of 100-200 thousand ...
'Master controller' behind DNA structure reorganization during senescence identified
2015-06-02
PHILADELPHIA--(June 2, 2015)--Senescence, a phenomenon in which cells cease to divide and grow, can be caused by everything from natural DNA damage to treatment with chemotherapy. However, several mechanisms allow for cells to bypass senescence and grow out of control, eventually becoming cancerous. Now, scientists at The Wistar Institute have identified how a specific variant of a key protein complex found in human cells called condensin can reorganize a cell's genetic architecture in such a way as to promote senescence, making it an important facilitator in a cell's ...
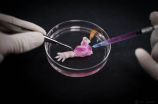
Mass. General team develops transplantable bioengineered forelimb in an animal model
2015-06-02
A team of Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators has made the first steps towards development of bioartificial replacement limbs suitable for transplantation. In their report, which has been published online in the journal Biomaterials, the researchers describe using an experimental approach previously used to build bioartificial organs to engineer rat forelimbs with functioning vascular and muscle tissue. They also provided evidence that the same approach could be applied to the limbs of primates
"The composite nature of our limbs makes building a functional ...
UF study shows benefits of multi-tasking on exercise
2015-06-02
Who says you can't do two things at once and do them both well?
A new University of Florida study challenges the notion that multi-tasking causes one or both activities to suffer. In a study of older adults who completed cognitive tasks while cycling on a stationary bike, UF researchers found that participants' cycling speed improved while multi-tasking with no cost to their cognitive performance.
Results of the study, which was supported by a grant from the National Institute on Aging, were published May 13 in the journal PLOS ONE.
The discovery was a surprise finding ...
[1] ... [2952]
[2953]
[2954]
[2955]
[2956]
[2957]
[2958]
[2959]
2960
[2961]
[2962]
[2963]
[2964]
[2965]
[2966]
[2967]
[2968]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.