Toothbrush contamination in communal bathrooms
2015-06-02
New Orleans, Louisiana - June 2, 2015 - Data confirms that there is transmission of fecal coliforms in communal bathrooms at Quinnipiac University and that toothbrushes can serve as a vector for transmission of potentially pathogenic organisms. This research is presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Microbiology.
"The main concern is not with the presence of your own fecal matter on your toothbrush, but rather when a toothbrush is contaminated with fecal matter from someone else, which contains bacteria, viruses or parasites that are not part of your ...
Scary TV's impact on kids is overstated, say psychologists
2015-06-02
The impact of scary TV on children's wellbeing has been overstated, according to University of Sussex psychologists.
While research has shown that a small minority of children can have extreme reactions to a scary programme or film, the researchers found that, overall, children show very little sign of increased anxiety, fear, sadness or sleep problems.
University of Sussex research student, Laura Pearce, and Andy Field, Professor of Child Psychopathology at the University, reviewed all research into the topic carried out over the past 25 years.
Their findings, ...
How Microprocessor precisely initiates miRNA production
2015-06-02
A scientific group from the Center for RNA Research within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and School of Biological Sciences in Seoul National University has reported an insightful molecular mechanism of how Microprocessor, the DROSHA-DGCR8 complex, precisely determines cleavage sites on miRNA-containing primary transcripts allowing faithful initiation of microRNA biogenesis.
The group's findings, published in Cell on 28th May as Advance Online Publication, not only reveal the function of each part of human Microprocessor, but also outline future work on the molecular ...
Weight-loss surgery puts spark back into relationships
2015-06-02
Bariatric surgery does not only benefit the health of patients who undergo this weight loss procedure. It also leads to greater intimacy between them and their life partners, and adds a spark to their sex life. It's all in all a shared journey that brings partners closer together, says Mary Lisa Pories of East Carolina University in the US, lead author of a study providing insights into the experience of couples after one of the partners underwent weight loss surgery. The findings are published in Springer's journal Obesity Surgery.
Bariatric surgery is the most effective ...
Intermountain Healthcare participating in White House forum on antibiotics
2015-06-02
SALT LAKE CITY - Intermountain Healthcare is one of 150 organizations in the nation that was invited to the White House to help develop national policy to address the growing problem of the overuse of antibiotics.
Intermountain has been studying this issue extensively for the past several years and is one the of leading healthcare organizations in the United States to research best practices to help curb the inappropriate use of antibiotics, which is contributing to the growing problem of resistant bacteria.
Intermountain will participate in a one-day antibiotic stewardship ...
Single 30-day hospital readmission metric fails to reflect changing risk factors
2015-06-02
BOSTON - A new study from researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) suggests that risk factors for readmission change significantly over the course of the 30 days following hospital discharge. Thirty-day hospital readmission rates have become a federal quality metric intended to reflect inpatient quality of care and unnecessary health care utilization.
Published today in the Annals of Internal Medicine, the research suggests that two distinct 8-day and 30-day readmission rates would serve as better inpatient quality measurements and would better inform ...
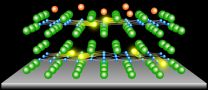
QLEDs meet wearable devices
2015-06-02
The scientific team, from the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and Seoul National University, has developed an ultra-thin wearable quantum dot light emitting diodes (QLEDs). The electronic tattoo is based on current quantum dot light emitting diode (QLED) technology. Colloidal quantum dot (QLED's) have attracted great attention as next generation displays. The quantum dots (QDs) have unique properties such as the color tunability, photo/air stability, and are printability on various substrates. The device is paper thin and can be applied to human skin like a sticker.
The ...
Story tips from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory, June 2015
2015-06-02
To arrange for an interview with a researcher, please contact the Communications staff member identified at the end of each tip. For more information on ORNL and its research and development activities, please refer to one of our media contacts. If you have a general media-related question or comment, you can send it to news@ornl.gov.
SOLAR - Suitability mapping ...
Using remote sensing data, researchers can efficiently determine optimum sites for solar power plants, according to a study led by Olufemi Omitaomu of Oak Ridge National Laboratory. With the target of solar ...
Genetic causes of cerebral palsy trump birth causes
2015-06-02
University of Adelaide researchers have discovered cerebral palsy has an even stronger genetic cause than previously thought, leading them to call for an end to unnecessary caesareans and arbitrary litigation against obstetric staff.
In an authoritative review published in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology, members of the Australian Cerebral Palsy Research Group, based at the University of Adelaide's Robinson Research Institute, argue that up to 45% of cerebral palsy cases can have genetic causes.
This builds on research published in February this year ...
Many endangered species are back -- but face new struggles
2015-06-02
A study of marine mammals and other protected species finds that several once endangered species, including the iconic humpback whale, the northern elephant seal and green sea turtles, have recovered and are repopulating their former ranges.
The research, published in the June edition of Trends in Ecology and Evolution, suggests that some species, including humpback whales, have reached population levels that may warrant removal from endangered species lists.
But returning species, which defy global patterns of biodiversity loss, create an urgent new challenge for policymakers ...
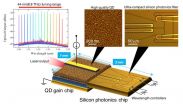
New heterogeneous wavelength tunable laser diode for high-frequency efficiency
2015-06-02
Researchers at Tohoku University and the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) in Japan, have developed
a novel ultra-compact heterogeneous wavelength tunable laser diode. The heterogeneous laser diode was realized through a combination
of silicon photonics and quantum-dot (QD) technology, and demonstrates a wide-range tuning-operation.
The researchers presented their work at a Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO) in San Jose, California, on May 13. The related
paper was also be published in Applied Physics Express ...
High-temperature superconductivity in atomically thin films
2015-06-02
A research group at Tohoku University has succeeded in fabricating an atomically thin, high-temperature superconductor film with a superconducting transition temperature (Tc) of up to 60 K (-213°C). The team, led by Prof. Takashi Takahashi (WPI-AIMR) and Asst. Prof. Kosuke Nakayama (Dept. of Physics), also established the method to control/tune the Tc.
This finding not only provides an ideal platform for investigating the mechanism of superconductivity in the two-dimensional system, but also paves the way for the development of next-generation nano-scale superconducting ...
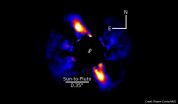
Astronomers discover a young solar system around a nearby star
2015-06-02
An international team led by Thayne Currie of the Subaru Telescope and using the Gemini South telescope, has discovered a young planetary system that shares remarkable similarities to our own early solar system. Their images reveal a ring-like disk of debris surrounding a Sun-like star, in a birth environment similar to the Sun's. The disk appears to be sculpted by at least one unseen solar system-like planet, is roughly the same size as our solar system's Edgeworth-Kuiper Belt (commonly called the Kuiper Belt), and may contain dust and icy particles. This work provides ...
'Climate-change skeptics are more ambivalent than we thought'
2015-06-02
Using a brand new survey method, researchers in Bergen have asked a broad spectrum of people in Norway about their thoughts on climate change. The answers are quite surprising.
Some 2,000 Norwegians have been asked about what they think when they hear or read the words "climate change". There were no pre-set answers or "choose the statement that best describes your view" options. Instead the respondents had to formulate their views on climate change in their own words. The answers have provided striking new insight into what the average person on the street in Norway ...
Childhood trauma gets under the skin
2015-06-02
Long-term changes in immune function caused by childhood trauma could explain increased vulnerability to a range of health problems in later life, according to new research by the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King's College London and the NIHR Maudsley BRC.
The study, published today in Molecular Psychiatry, found heightened inflammation across three blood biomarkers in adults who had been victims of childhood trauma. High levels of inflammation can lead to serious and potentially life-threatening conditions such as type-2 diabetes, cardiovascular ...
FDA addresses concerns on approval of drugs to treat chronic hepatitis C
2015-06-02
Treatment options for chronic hepatitis C, a serious and life-threatening infection, have improved substantially and several new regimens with shorter durations and improved efficacy and safety profiles are now available.
Groups have raised concerns about the evidence used to support the approval of some newer drugs, however, and the issue has been used to cast doubt on their efficacy and even to question treatment or deny reimbursement.
To address these concerns, the US Food and Drug Administration's Division of Antiviral Products in the Center for Drug Evaluation ...
Douglas study on cerebral astrocytes in depression and suicide
2015-06-02
This news release is available in French. Montreal, June 2 -- A new study published by the team of Naguib Mechawar, Ph.D., a researcher with the McGill Group for Suicide Studies (MGSS) of the Douglas Institute (CIUSSS de l'Ouest-de-l'Ile de Montreal) and associate professor in the Department of Psychiatry at McGill University, sheds new light on the disruption of astrocytes in depression. Astrocytes, a class of non-neuronal cells, have previously been implicated in depression and suicide.
However, it was not known whether these cells were affected throughout the brain ...
Interpersonal conflict is the strongest predictor of community crime and misconduct
2015-06-02
Los Angeles, CA (June 2, 2015) Neighborhoods with more interpersonal conflict, such as domestic violence and landlord/tenet disputes, see more serious crime according to a new study out today in Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency (JRCD). Private conflict was a better predictor of neighborhood deterioration than public disorder, such as vandalism, suggesting the important role that individuals play in community safety.
"Private conflicts, for example, domestic violence or friendship disputes over money or girlfriends, can and do spill over into public spaces, ...
Infant brains develop years faster than we thought
2015-06-02
Scientists from the University of Louvain have discovered that a key element of infant brain development occurs years earlier than previously thought.
The way we perceive faces -- using the right hemisphere of the brain -- is unique and sets us apart from non-human primates. It was thought that this ability develops as we learn to read, but a new study published in the journal eLife shows that in babies as young as four months it is already highly evolved.
"Just as language is impaired following damage to the brain's left hemisphere, damage to the right hemisphere ...
Kids' altruism linked with better physiological regulation, less family wealth
2015-06-02
Children as young as 4 years old may reap better health from altruistic giving, a behavior that tends to be less common among kids from high-income families, according to new research on the nature and nurture of altruism published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"The findings provide us with a new understanding of how children's altruistic behaviors, family wealth, and physiological health are intertwined," says psychological scientist and lead researcher Jonas Miller of the University of California Davis.
Previous ...
Teens turn to Internet to cope with health challenges
2015-06-02
EVANSTON, Ill. --- At a time when teenagers are grappling with new and often confusing health concerns, the overwhelming majority -- 84 percent -- turn to the Internet, according to the first national study in more than a decade to examine how adolescents use digital tools for health information.
But while most teens tap online sources to learn more about puberty, drugs, sex, depression and other issues, a surprising 88 percent said they do not feel comfortable sharing their health concerns with Facebook friends or on other social networking sites, according to the study ...
Neuroimaging findings generally nondiagnostic in kids with sports-related concussions
2015-06-02
CHARLOTTESVILLE, VA (JUNE 2, 2015). Researchers from the Canada North Concussion Network in Manitoba examined neuroimaging studies obtained in children and adolescents with sports-related concussions and found that the images appeared normal in 78% of cases. Detailed findings of this study are reported and discussed in "Neuroimaging findings in pediatric sports-related concussion" by Michael J. Ellis, MD, and colleagues, published today online, ahead of print, in the Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics.
Expert opinion among physicians specializing in sports-related concussion ...
Vestibulo-ocular dysfunction in children and adolescents with sports-related concussion
2015-06-02
CHARLOTTESVILLE, VA (JUNE 2, 2015). Researchers from the Canada North Concussion Network in Manitoba investigated the frequency of vestibulo-ocular dysfunction in children and adolescents with sports-related concussion and found that its presence was predictive of a prolonged recovery. Findings in this study are reported and discussed in "Vestibulo-ocular dysfunction in pediatric sports-related concussion" by Michael J. Ellis, MD, and colleagues, published today online, ahead of print, in the Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics.
Normally, if you are asked to focus on ...
Study shows public access defibrillators are increasing survival but are not being used enough
2015-06-02
New research presented at this year's Euroanaesthesia shows that use of public access defibrillation on people suffering cardiac arrest is associated with a large increase in chances of survival. However, despite the great potential, publicly accessible Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) are not being used enough, concludes research by Dr Marianne Agerskov and colleagues at Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Denmark.
Publicly accessible AEDs are now commonplace in many European countries, and they are often found in sport centres, transportation hubs, and ...
Get up and stand up for at least 2 hours daily during working hours
2015-06-02
Office workers should be on their feet for a minimum of 2 hours daily during working hours, recommends the first ever UK guidance designed to curb the health risks of too much cumulative sitting time, and published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
This daily quota should eventually be bumped up to 4 hours a day, breaking up prolonged periods of sitting with the use of sit-stand desks, standing based work, and regular walk-abouts, it says.
The guidance, which evaluates and distils the available evidence, was drawn up by a panel of international experts, ...
[1] ... [2949]
[2950]
[2951]
[2952]
[2953]
[2954]
[2955]
[2956]
2957
[2958]
[2959]
[2960]
[2961]
[2962]
[2963]
[2964]
[2965]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.