Pathbreaking study by Israeli and American neuroscientists reveals autism's 'noisy' secret
2015-05-26
Strapped into a motion-enabled simulator and wearing 3D glasses, 36 adolescent volunteers recently experienced what it was like to "travel" through a field of virtual stars. The experiments provided new and convention-busting data about how sensory stimuli are processed by the brains of individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
The study, entitled "Self-motion perception in autism is compromised by visual noise but integrated optimally across multiple senses," was published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on May 4th, 2015. The authors of ...
Genomic data reveals emergence in Africa of drug resistant strain of typhoid
2015-05-26
The team has completed two genomics studies on the tropical disease, a condition that is estimated to cause up to 30 million illnesses and over a quarter of a million deaths globally each year.
The first study, published in the journal Nature Genetics, suggests that the H58-strain, which is likely to have emerged in Asia approximately thirty years ago, is now rapidly spreading across Africa, where it has been introduced on several separate occasions. A key feature of this strain appears to be its ability to acquire resistance to commonly available antibiotics.
Dr Melita ...
ER doctors stress need for good communications with police
2015-05-26
TORONTO, May 27, 2015--A good working relationship with police is essential for the smooth operation of a busy Emergency Department. Police are in and out of EDs regularly, supporting EMS, transporting patients and helping to provide a safe environment for hospital staff.
Not surprisingly, differences of opinion arise from time to time over a health care worker's duty to protect patient privacy and the police need to conduct a criminal investigation.
That's why it's essential to develop strategies to optimize communications between police and ED workers, according to ...
Changes in forest structure affect bees and other pollinators
2015-05-26
ATHENS, GA - Over the past century, many forests have shifted from open to closed canopies. The change in forest structure could be contributing to declines in pollinator species, especially native bees, according to a new study by U.S. Forest Service scientists.
The study shows how common present-day forest conditions affect pollinators, especially bees. "Bees prefer open forests," says Jim Hanula, a research entomologist at the Southern Research Station (SRS) Insects, Diseases, and Invasive Plants research unit. "We found that total tree basal area was the best predictor ...
Debunking 3 common food myths (video)
2015-05-26
WASHINGTON, May 26, 2015 -- You might have heard that microwaving your food is dangerous. Maybe your health nut friend told you that eating frozen veggies is less healthful than eating fresh ones. Is a glass of red wine really good for your heart? This week, Reactions is here to sort out the "old wives' tales" from the facts, taking on a swath of food myths. Check out the videos here: http://bit.ly/ACSFoodMyths.
Subscribe to the series at http://bit.ly/ACSReactions, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
INFORMATION:
The ...
New urine test could reduce need for blood samples
2015-05-26
CLEMSON, S.C. -- If you've been to the doctor, you probably know what to do when you're handed a plastic cup and shown to the bathroom.
Most patients hand over the sample and give little thought to what happens when it's shipped to the lab for analysis.
Ken Marcus and his students are the exceptions. They have developed a new testing method that they believe will reduce costs, get faster results and lower the volume of urine needed for a sample.
Marissa Pierson, a master's student, closes the lid on a centrifuge while working in a Clemson University lab with Ken Marcus.
It's ...
Squeezed quantum cats
2015-05-26
This news release is available in German.
Quantum physics is full of fascinating phenomena. Take, for instance, the cat from the famous thought experiment by the physicist Erwin Schrodinger. The cat can be dead and alive at once, since its life depends on the quantum mechanically determined state of a radioactively decaying atom which, in turn, releases toxic gas into the cat's cage. As long as one hasn't measured the state of the atom, one knows nothing about the poor cat's health either - atom and kitty are intimately "entangled" with each other.
Equally striking, ...
Researchers solve another piece of the puzzle how forests can effect our climate
2015-05-26
This news release is available in German.
Leipzig / Helsinki. A first global scale study has estimated how forest emitted compounds affecting cloud seeds via formation of low-volatility vapours. According to the latest projections, terrestrial vegetation emits several million tons of extremely low-volatility organic compounds (ELVOCs) per year to the atmosphere. These oxidation products of compounds such as monoterpenes results in an increase of condensing vapours that can further form cloud condensation nuclei over the continents and thus has an influence ...
A scientific breakthrough helps explain how DNA is organized in our cells
2015-05-26
Montréal, May 25, 2015 - A team of researchers at the IRCM led by François Robert, PhD, uncovered a critical role for two proteins in chromatin structure. Their breakthrough, recently published in the scientific journal Molecular Cell, helps explain how DNA is organized in our cells. This discovery could lead to a better understanding of what causes certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma.
Dr. Robert and his team study chromatin, the structure composed of DNA and proteins that makes up chromosomes. Its main role is to package DNA molecules containing all the ...
Nanotechnology identifies brain tumor types through MRI 'virtual biopsy' in animal studies
2015-05-26
LOS ANGELES (May 26, 2015) - Biomedical researchers at Cedars-Sinai have invented a tiny drug-delivery system that can identify cancer cell types in the brain through "virtual biopsies" and then attack the molecular structure of the disease.
If laboratory research with mice is borne out in human studies, the results could be used to deliver nano-scale drugs that can distinguish and fight tumor cells in the brain without resorting to surgery.
"Our nanodrug can be engineered to carry a variety of drugs, proteins and genetic materials to attack tumors on several fronts ...
Monitoring magnetospheres
2015-05-26
Queen's University PhD student Matt Shultz is researching magnetic, massive stars, and his research has uncovered questions concerning the behaviour of plasma within their magnetospheres.
Drawing upon the extensive dataset assembled by the international Magnetism in Massive Stars (MiMeS) collaboration, led by Mr. Shultz's supervisor, Queen's professor Gregg Wade, along with some of his own observations collected with both the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope and the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope, Mr. Shultz is conducting the first systematic population ...
Researchers identify new target for Ebola drugs
2015-05-26
Washington, D.C. -- May 26, 2015 -- A new study has demonstrated that a protein called Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) is critical for the Ebola virus to infect a host. The study, published in the May/June issue of mBio, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, suggests that drugs that block NPC1 could be used to treat this deadly disease.
"The science behind the concept of blocking the interaction between NPC1 and the virus is solid. Now, it is just a matter of powering through and identifying drugs that can inhibit NPC1 and moving them forward," ...
Study identifies Ebola virus's Achilles' heel
2015-05-26
An international team including scientists from Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University and the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID) has identified the molecular "lock" that the deadly Ebola virus must pick to gain entry to cells. The findings, made in mice, suggest that drugs blocking entry to this lock could protect against Ebola infection. The study was published in today's edition of the online journal mBio.
The researchers found that the Ebola virus can't infect cells unless it first attaches to a host protein called ...
Nearly indestructible virus yields tool to treat diseases
2015-05-26
By unlocking the secrets of a bizarre virus that survives in nearly boiling acid, scientists at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have found a blueprint for battling human disease using DNA clad in near-indestructible armor.
"What's interesting and unusual is being able to see how proteins and DNA can be put together in a way that's absolutely stable under the harshest conditions imaginable," said Edward H. Egelman, PhD, of the UVA Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics. "We've discovered what appears to be a basic mechanism of resistance - to ...
Therapy-resistant breast cancer mechanism revealed
2015-05-26
Mitsuyoshi Nakao, Director of the Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics in Kumamoto University and Associate Professor Noriko Saitoh revealed that a cluster of defined, non-coding RNAs are mechanistically involved in endocrine therapy resistance in human breast cancer cells. Furthermore, resveratrol, a kind of polyphenol, was found to repress these RNAs and inhibit the proliferative activity of breast cancer cells which had acquired resistance. The work was published in Nature Communications on April 29th, 2015.
Breast cancer is one of the most common types ...
You're driving yourself to burnout, literally
2015-05-26
This news release is available in French.
Commuting length, distance, and means are stress factors that can lead to burnout, says Annie Barreck of the University of Montreal's School of Industrial Relations. "A correlation exists between commuting stress factors and the likelihood of suffering from burnout. But their importance varies according to the individual, the conditions in which their trips take place, and the place where the individual works," she explained. Barreck will present her research today at the 83rd congress of the Association francophone pour ...
New national study finds autoimmune disease severely impacts patients
2015-05-26
In a new national survey of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, Health Union found a severe impact on quality of life, employment, and ability to afford treatment. The autoimmune condition attacks the body, resulting in joint inflammation, pain, stiffness, and swelling, but may also harm other organs. About 1.3 million Americans or about one percent of the global population have RA.
Ninety-four percent of respondents with RA said they cannot do as much as they were able before acquiring the disease. Additionally, 67% said others do not understand the severity of their ...
CBD targets protect biodiversity only if new protected areas are more than 'paper parks'
2015-05-26
Protected areas are the cornerstone to prevent species extinctions. The Convention on Biological Diversity have set a target to protect 17% of all terrestrial land by 2020.
Many of the international recommendations concerning protection goals are provided for single countries to take action individually. Researchers in the University of Helsinki, Finland, stress the importance of international collaborations in the protected area expansion process.
"It has been shown that working at the country level is less efficient than promoting transnational collaborations. As ...
Research 'challenges assumption that arthritis patients take their medication regularly'
2015-05-26
New UK research has challenged the assumption that people with rheumatoid arthritis always take their medication as prescribed.
Researchers from the Arthritis Research UK Centre for Epidemiology at The University of Manchester found that 40% of patients scored low on an adherence questionnaire at least once during their time in a recent study, indicating that they might not be taking their expensive biological therapies as regularly as prescribed.
Their research is published online in the journal Rheumatology.
The findings have prompted Arthritis Research UK's head ...
Herpes offers big insights on coughing -- and potential new remedies
2015-05-26
Cough treatments could change dramatically after the herpes virus helped researchers discover that the respiratory tract links to two different parts of the nervous system.
A research team led by The University of Queensland's Dr Stuart Mazzone made the important breakthrough after setting out to learn more about the triggers behind excessive coughing.
"Different physical sensations arise from the upper and lower respiratory tracts in people with respiratory diseases," said Dr Mazzone, from the School of Biomedical Sciences.
"The irritating sensations from the upper ...
Fine-tuned molecular orientation is key to more efficient solar cells
2015-05-26
Polymer solar cells are a hot area of research due to both their strong future potential and the significant challenges they pose. It is believed that thanks to lower production costs, they could become a viable alternative to conventional solar cells with silicon substrates when they achieve a power conversion efficiency--a measure that indicates how much electricity they can generate from a given amount of sunlight--of between 10 and 15 percent. Now, using carefully designed materials and an "inverted" architecture, a team of scientists has achieved efficiency of 10 percent, ...
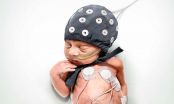
Earthquakes -- an unexpected help in interpreting the brain activity of premature babies
2015-05-26
Giant strides have been taken in the early care of very premature infants in postnatal intensive care units during the past two decades. Doctors can now support the function of especially the lungs, heart and the circulatory system so as to guarantee the survival of most of even extremely premature infants.
Despite a good start, many of these may still have lifelong problems with brain function, such as attention deficit disorders or difficulty with visual function. For this reason, the primary focus of developing care for premature infants has been on securing brain ...
Dartmouth researchers create first smartphone app that predicts GPA
2015-05-26
HANOVER, N.H. - If you're a college student wondering how your study and party habits will affect your GPA, wonder no longer. Dartmouth researchers and their colleagues have built the first app that automatically predicts college students' grade point average based on their smartphone data.
The findings offer new ways to improve students' performance, providing real-time feedback on their studying, partying, sleeping, exercising and other conscious and unconscious behaviors to help them stay on track academically.
Dartmouth computer science Professor Andrew Campbell, ...
Researchers say anti-pollution rules have uncertain effects
2015-05-26
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- Air pollution regulations issued by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency are estimated to save thousands of lives annually. A new study by researchers at Indiana University says these estimates are more uncertain than commonly believed.
Researchers Kerry Krutilla, David H. Good and John D. Graham of the IU School of Public and Environmental Affairs analyzed the costs and expected lifesavings of nine regulations issued between 2011 and 2013. The bulk of these regulations require national emissions standards for hazardous air pollutants. The analysis ...
Pitt team IDs two new and very large classes of RNAs linked to cancer biomark
2015-05-26
PITTSBURGH, May 26, 2015 - Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine have identified two new classes of RNAs that are closely associated with a protein known to be a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer and could play a role in progression of prostate cancer. Their findings were published in the June issue of the scientific journal RNA.
Levels of human Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1), which is involved in many cellular functions, have been shown to correlate with drug resistance and poor patient outcomes in a variety of cancers. The observation that ...
[1] ... [2962]
[2963]
[2964]
[2965]
[2966]
[2967]
[2968]
[2969]
2970
[2971]
[2972]
[2973]
[2974]
[2975]
[2976]
[2977]
[2978]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.