Creating bright X-ray pulses in the laser lab
2014-11-11
This news release is available in German. X-rays are widely used in medicine and in materials science. To take a picture of a broken bone, it is enough to create a continuous flux of X-ray photons, but in order to study time-dependent phenomena on very short timescales, short X-ray pulses are required. One possibility to create short hard X-ray pulses is hitting a metal target with laser pulses. The laser rips electrons out of the atoms and makes them emit X-ray radiation. Electrical engineers at the Vienna University of Technology (TU Wien) together with researchers ...
Multiple models reveal new genetic links in autism
2014-11-11
With the help of mouse models, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and the "tooth fairy," researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have implicated a new gene in idiopathic or non-syndromic autism. The gene is associated with Rett syndrome, a syndromic form of autism, suggesting that different types of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may share similar molecular pathways.
The findings are published in the Nov. 11, 2014 online issue of Molecular Psychiatry.
"I see this research as an example of what can be done for cases of non-syndromic ...
Breakthrough shows how the 'termites of the sea' digest wood
2014-11-11
An inter­na­tional research team led by Dan Distel, director of the Ocean Genome Legacy Center of New Eng­land Bio­labs at North­eastern Uni­ver­sity, has dis­cov­ered a novel diges­tive strategy in ship­worms. The break­through, the researchers say, may also be a game-​​changer for the indus­trial pro­duc­tion of clean biofuels.
To start, it's impor­tant to note that ship­worms, the so-​​called "ter­mites of the sea," aren't actu­ally worms--they're bizarre clams that ...
Hospital workers wash hands less frequently toward end of shift, study finds
2014-11-11
WASHINGTON - Hospital workers who deal directly with patients wash their hands less frequently as their workday progresses, probably because the demands of the job deplete the mental reserves they need to follow rules, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
Researchers led by Hengchen Dai, a PhD candidate at the University of Pennsylvania, looked at three years of hand-washing data from 4,157 caregivers in 35 U.S. hospitals. They found that "hand-washing compliance rates" dropped by an average of 8.7 percentage points from the beginning ...
Too many people, not enough water: Now and 2,700 years ago
2014-11-10
The Assyrian Empire once dominated the ancient Near East. At the start of the 7th century BC, it was a mighty military machine and the largest empire the Old World had yet seen. But then, before the century was out, it had collapsed. Why? An international study now offers two new factors as possible contributors to the empire's sudden demise - overpopulation and drought.
Adam Schneider of the University of California, San Diego and Selim Adalı of Koç University in Istanbul, Turkey, have just published evidence for their novel claim.
"As far as we know, ...
Smoking associated with elevated risk of developing a second smoking-related cancer
2014-11-10
Results of a federally-funded pooled analysis of five prospective cohort studies indicate that cigarette smoking prior to the first diagnosis of lung (stage I), bladder, kidney or head and neck cancer increases risk of developing a second smoking-associated cancer. This is the largest study to date exploring risk of second cancers among current smokers.
An analysis of five large, prospective cohort studies indicates that lung (stage I), bladder, kidney and head and neck cancer survivors who smoked 20 or more cigarettes a day prior to their cancer diagnoses have an up ...
ALMA finds best evidence yet for galactic merger in distant protocluster
2014-11-10
Nestled among a triplet of young galaxies more than 12.5 billion light-years away is a cosmic powerhouse: a galaxy that is producing stars nearly 1,000 times faster than our own Milky Way. This energetic starburst galaxy, known as AzTEC-3, together with its gang of calmer galaxies may represent the best evidence yet that large galaxies grow from the merger of smaller ones in the early Universe, a process known as hierarchical merging.
An international team of astronomers observed these remarkable objects with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA).
"The ...
Lung cancer screening with low-dose CT could be cost effective says Dartmouth study
2014-11-10
VIDEO:
Dartmouth researchers say lung cancer screening in the National Lung Screening Trial meets a commonly accepted standard for cost effectiveness as reported in the Nov. 6 issue of the New...
Click here for more information.
Dartmouth researchers say lung cancer screening in the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) meets a commonly accepted standard for cost effectiveness as reported in the Nov. 6 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine. This relatively new screening ...
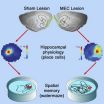
The brain's 'inner GPS' gets dismantled
2014-11-10
Imagine being able to recognize your car as your own but never being able to remember where you parked it. Researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have induced this all-too-common human experience - or a close version of it - permanently in rats and from what is observed perhaps derive clues about why strokes and Alzheimer's disease can destroy a person's sense of direction.
The findings are published online in the current issue of Cell Reports.
Grid cells and other specialized nerve cells in the brain, known as "place cells," comprise ...
The cat's meow: Genome reveals clues to domestication
2014-11-10
Cats and humans have shared the same households for at least 9,000 years, but we still know very little about how our feline friends became domesticated. An analysis of the cat genome by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis reveals some surprising clues.
The research appears Nov. 10 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Early Edition.
Cats have a relatively recent history of domestication compared with dogs; canines arose from wolves over 30,000 years ago.
"Cats, unlike dogs, are really only semidomesticated," said ...
Study ties conflict risk in sub-Saharan Africa to climate change, economics, geography
2014-11-10
A massive new University of Colorado Boulder study indicates there is a statistical link between hotter temperatures generated by climate change and the risk of armed conflicts in sub-Saharan Africa.
CU-Boulder Professor John O'Loughlin led a research team that assessed more than 78,000 armed conflicts between 1980 and 2012 in the Sahel region of Africa - a semi-arid belt just south of the Saharan Desert that spans about 3,000 miles and more than a dozen countries from the Atlantic to the Indian oceans.
The team was looking for links between armed conflicts and temperature ...
ACA health insurance plans differ in cost, coverage and hospital access across Texas
2014-11-10
HOUSTON - (Nov. 10, 2014) - An analysis of more than 100 health insurance plans across Texas offered under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) shows that plans can differ significantly in premium cost and the number of hospitals included in insurance networks. That's just one of the findings of a report released today by the Episcopal Health Foundation and Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy.
The report examined "Silver" health insurance plans offered by insurers within the ACA's Marketplace. Texas is divided into 26 different geographic areas, with different ...
Beta-blockers have no mortality benefit in post-heart attack patients, say researchers
2014-11-10
Philadelphia, PA, November 10, 2014 - Beta-blockers have been a cornerstone in the treatment of heart attack survivors for more than a quarter of a century. However, many of the data predate contemporary medical therapy such as reperfusion, statins, and antiplatelet agents, and recent data have called the role of beta-blockers into question. Two new studies published in The American Journal of Medicine evaluated the traditional management of these patients after their discharge from the hospital and in the light of changing medical treatment, as well as the impact of the ...
We are not alone
2014-11-10
The adult human body is made up of about 37 trillion cells. Microbes, mainly bacteria, outnumber body cells by 10 to 1. Increasingly, scientists recognize that this huge community of microbes, called the microbiome, affects the health, development and evolution of all multicellular organisms, including humans.
Studies show symbiotic microbes can help prevent infection by disease-causing pathogens. But sometimes the interaction goes the other way, with a pathogen or disease disrupting the normal community of symbiotic bacteria. In a new study, a team of scientists from ...
Microbot muscles: Chains of particles assemble and flex
2014-11-10
ANN ARBOR--In a step toward robots smaller than a grain of sand, University of Michigan researchers have shown how chains of self-assembling particles could serve as electrically activated muscles in the tiny machines.
So-called microbots would be handy in many areas, particularly medicine and manufacturing. But several challenges lie between current technologies and science fiction possibilities. Two of the big ones are building the 'bots and making them mobile.
"We are inspired by ideas of microscopic robots," said Michael Solomon, a professor of chemical engineering. ...
Sweet music or sour notes? The test will tell
2014-11-10
BUFFALO, N.Y. - Most people rarely sing publicly outside of a duty-bound rendition of "Happy Birthday." And since that particular song is usually offered as a group performance, even the reluctant join in the spirit of the occasion, hoping their individual shortcomings will be cloaked by the chorus.
"I can't sing," says the hesitant performer. But a University at Buffalo psychologist believes that most people are not as bad at singing as they might think and he is collaborating on the development of an online test that will evaluate participants' ability to match specific ...
SwRI-led team telescope effort reveals asteroid's size for the first time
2014-11-10
Boulder, Colo. -- Nov. 10, 2014 -- When the double asteroid Patroclus-Menoetius passed directly in front of a star on the night of Oct. 20, a team of volunteer astronomers across the U.S. was waiting.
Observing the event, known as an occultation, from multiple sites where each observer recorded the precise time the star was obscured, yielded the first accurate determination of the two objects' size and shape. The analysis was led by Dr. Marc W. Buie, staff scientist in Southwest Research Institute's (SwRI) Space Studies Department in Boulder, Colo.
The team effort was ...
Baby photos of a scaled-up solar system
2014-11-10
Scientists at the University of Arizona have discovered what might be the closest thing to "baby photos" of our solar system. A young star called HD 95086 is found to have two dust belts, analogous to the asteroid and Kuiper belts in the Solar System, surrounded by a large dust halo that only young planetary systems have.
Similar dust structures are also found around another, slightly older star called HR 8799, where four massive planets occupy the large gap between the two belts. HR 8799, the first star found to host four directly imaged planets, is often referred ...
Wireless devices used by casual pilots vulnerable to hacking, computer scientists find
2014-11-10
A new class of apps and wireless devices used by private pilots during flights for everything from GPS information to data about nearby aircraft is vulnerable to a wide range of security attacks, which in some scenarios could lead to catastrophic outcomes, according to computer scientists at the University of California, San Diego and Johns Hopkins University. They presented their findings Nov. 5 at the 21st ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security in Scottsdale, Ariz.
`
Researchers examined three combinations of devices and apps most commonly used by private ...
Changes in a single gene's action can control addiction and depression-related behaviors
2014-11-10
Regulation of a single, specific gene in a brain region related to drug addiction and depression is sufficient to reduce drug and stress responses, according to a study conducted at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and published October 27 online in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
The Mount Sinai study focuses on epigenetics, the study of changes in the action of human genes caused, not by changes in DNA code we inherit from our parents, but instead by molecules that regulate when, where and to what degree our genetic material is activated.
Previous research ...
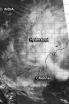
NASA sees System 05B fizzle in Bay of Bengal
2014-11-10
System 05B degenerated into a remnant low pressure area on Nov. 8 and lingered near the east-central coast of India for two days before dissipating on Nov. 10.
The tropical cyclone's western edge spread over land on Sunday, Nov. 9 while the center of the low-level circulation remained over open waters of the Bay of Bengal. On that day, 05B's remnants were centered near 14.0 north latitude and 83.8 east longitude, about 215 miles east-northeast of Chennai, India.
Infrared imagery from satellites on Nov. 9 indicated that the low-level circulation center of the storm was ...
Is your relationship moving toward marriage? If it isn't, you probably can't admit it
2014-11-10
URBANA, Ill. - Dating couples who have moved toward marriage over the course of their relationship remember accurately what was going on at each stage of their deepening commitment. But couples whose commitment to each other has stagnated or regressed are far less accurate in their memories of their relationships, says a new University of Illinois study.
"People like to feel that they're making progress as a couple. If they're not--if, in fact, the relationship is in trouble--they may have distorted recollections that help them feel like they're moving forward because ...
'Antibiogram' use in nursing facilities could help improve antibiotic use, effectiveness
2014-11-10
PORTLAND, Ore. - Use of "antibiograms" in skilled nursing facilities could improve antibiotic effectiveness and help address problems with antibiotic resistance that are becoming a national crisis, researchers conclude in a new study.
Antibiograms are tools that aid health care practitioners in prescribing antibiotics in local populations, such as a hospital, nursing home or the community. They are based on information from microbiology laboratory tests and provide information on how likely a certain antibiotic is to effectively treat a particular infection.
The recent ...
EARTH magazine: Solar storms cause spike in insurance claims
2014-11-10
Alexandria, Va. -- On March 13, 1989, a geomagnetic storm spawned by a solar outburst struck Earth, triggering instabilities in the electric-power grid that serves much of eastern Canada and the U.S. The storm led to blackouts for more than 6 million customers and caused tens of millions of dollars in damages and economic losses. More than 25 years later, the possibility of another such catastrophe still looms, and the day-to-day effects of space weather on electrical systems remain difficult to quantify. Now, a new study correlating electrical insurance claims with geomagnetic ...
Robotic ocean gliders aid study of melting polar ice
2014-11-10
The rapidly melting ice sheets on the coast of West Antarctica are a potential major contributor to rising ocean levels worldwide. Although warm water near the coast is thought to be the main factor causing the ice to melt, the process by which this water ends up near the cold continent is not well understood.
Using robotic ocean gliders, Caltech researchers have now found that swirling ocean eddies, similar to atmospheric storms, play an important role in transporting these warm waters to the Antarctic coast--a discovery that will help the scientific community determine ...
[1] ... [3207]
[3208]
[3209]
[3210]
[3211]
[3212]
[3213]
[3214]
3215
[3216]
[3217]
[3218]
[3219]
[3220]
[3221]
[3222]
[3223]
... [8825]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.