Interstitial lung disease is a significant risk factor for lung inflammation
2014-11-10
Interstitial lung disease is a significant risk factor for lung inflammation following stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung cancer.
DENVER - Pretreatment interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a significant risk factor for developing symptomatic and severe radiation pneumonitis in stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) alone.
ILD is a group of diseases that cause scarring and stiffing of the tissue and space around the air sacs in the lungs, which results in diminished gas exchange. The incidence ...
Noise in a microwave amplifier is limited by quantum particles of heat
2014-11-10
As part of an international collaboration, scientists at Chalmers University of Technology have demonstrated how noise in a microwave amplifier is limited by self-heating at very low temperatures. The results will be published in the prestigious journal Nature Materials. The findings can be of importance for future discoveries in many areas of science such as quantum computers and radio astronomy.
Many significant discoveries in physics and astronomy are dependent upon registering a barely detectable electrical signal in the microwave regime. A famous example of this ...
Production of human motor neurons from stem cells is gaining speed
2014-11-10
This news release is available in French. The motor neurons that innervate muscle fibres are essential for motor activity. Their degeneration in many diseases causes paralysis and often death among patients. Researchers at the Institute for Stem Cell Therapy and Exploration of Monogenic Diseases (I-Stem - Inserm/AFM/UEVE), in collaboration with CNRS and Paris Descartes University, have recently developed a new approach to better control the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells, and thus produce different populations of motor neurons from these cells in only ...
Lighter, cheaper radio wave device could transform telecommunications
2014-11-10
AUSTIN, Texas -- Researchers at the Cockrell School of Engineering at The University of Texas at Austin have achieved a milestone in modern wireless and cellular telecommunications, creating a radically smaller, more efficient radio wave circulator that could be used in cellphones and other wireless devices, as reported in the latest issue of Nature Physics.
The new circulator has the potential to double the useful bandwidth in wireless communications by enabling full-duplex functionality, meaning devices can transmit and receive signals on the same frequency band at ...
New electron spin secrets revealed
2014-11-10
Researchers from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) and the University of Cambridge in the UK have demonstrated that it is possible to directly generate an electric current in a magnetic material by rotating its magnetization.
The findings reveal a novel link between magnetism and electricity, and may have applications in electronics.
The electric current generation demonstrated by the researchers is called charge pumping. Charge pumping provides a source of very high frequency alternating electric currents, and its magnitude and external magnetic ...
Catalyst-where-you-want-it method expands the possibilities for new drug development
2014-11-10
LA JOLLA, CA--November 10, 2014--Chemists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) and the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry have described a method for creating and modifying organic compounds that overcomes a major limitation of previous methods. The advance opens up a large number of novel chemical structures for synthesis and evaluation, for example, as candidate pharmaceuticals.
The new method was designed to avoid an unwanted side effect--a diversion of a catalyst molecule to the wrong location--that prevents chemists from manipulating many organic compounds ...
Iron fertilization less efficient for deep-sea CO2 storage than previously thought?
2014-11-10
The Southern Ocean plays an important role in the exchange of carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and the ocean. One aspect of this is the growth of phytoplankton, which acts as a natural sponge for carbon dioxide, drawing the troublesome greenhouse gas from the atmosphere into the sea. When these plankton die they can sink to the bottom of the ocean and store some of the carbon dioxide they have absorbed, a process scientists call the "biological carbon pump".
Although many areas of the Southern Ocean are rich in nutrients, they often lack iron, which limits phytoplankton ...
Some neurons can multitask, raising questions about the importance of specialization
2014-11-10
Cold Spring Harbor, NY - Think about all the things you are doing at this moment. As your eyes scan across the lines of this article, maybe your brain is processing the smell of coffee brewing down the hall and the sound of leaf blowers outside your window. Maybe you are tapping your foot and spinning a pen between your fingers. At any given moment, your brain is simultaneously processing a multitude of information from your senses while supporting a dizzying array of behaviors.
How is all this information processed at once? The provisional answer, for decades, has centered ...
A billion holes can make a battery
2014-11-10
COLLEGE PARK, Md. -- Researchers at the University of Maryland have invented a single tiny structure that includes all the components of a battery that they say could bring about the ultimate miniaturization of energy storage components.
The structure is called a nanopore: a tiny hole in a ceramic sheet that holds electrolyte to carry the electrical charge between nanotube electrodes at either end. The existing device is a test, but the bitsy battery performs well. First author Chanyuan Liu, a graduate student in materials science & engineering, says that it can be ...
Good vibrations give electrons excitations that rock an insulator to go metallic
2014-11-10
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Nov. 10, 2014--For more than 50 years, scientists have debated what turns particular oxide insulators, in which electrons barely move, into metals, in which electrons flow freely. Some scientists sided with Nobel Prize-winning physicist Nevill Mott in thinking direct interactions between electrons were the key. Others believed, as did physicist Rudolf Peierls, that atomic vibrations and distortions trumped all. Now, a team led by the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory has made an important advancement in understanding a classic transition-metal ...
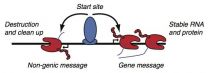
Re-learning how to read a genome
2014-11-10
Cold Spring Harbor, NY - There are roughly 20,000 genes and thousands of other regulatory "elements" stored within the three billion letters of the human genome. Genes encode information that is used to create proteins, while other genomic elements help regulate the activation of genes, among other tasks. Somehow all of this coded information within our DNA needs to be read by complex molecular machinery and transcribed into messages that can be used by our cells.
Usually, reading a gene is thought to be a lot like reading a sentence. The reading machinery is guided ...
Thousands of never-before-seen human genome variations uncovered
2014-11-10
Thousands of never-before-seen genetic variants in the human genome have been uncovered using a new genome sequencing technology. These discoveries close many human genome mapping gaps that have long resisted sequencing.
The technique, called single-molecule, real-time DNA sequencing (SMRT), may now make it possible for researchers to identify potential genetic mutations behind many conditions whose genetic causes have long eluded scientists, said Evan Eichler, professor of genome sciences at the University of Washington, who led the team that conducted the study.
"We ...
Statins reverse learning disabilities caused by genetic disorder
2014-11-10
UCLA neuroscientists discovered that statins, a popular class of cholesterol drugs, reverse the learning deficits caused by a mutation linked to a common genetic cause of learning disabilities. Published in the Nov. 10 advance online edition of Nature Neuroscience, the findings were studied in mice genetically engineered to develop the disease, called Noonan syndrome.
The disorder can disrupt a child's development in many ways, often causing unusual facial features, short stature, heart defects and developmental delays. No treatment is currently available.
"Noonan ...
A greasy way to take better protein snapshots
2014-11-10
Thanks to research performed at RIKEN's SACLA x-ray free electron laser facility in Japan, the dream of analyzing the structure of large, hard-to-crystallize proteins and other bio molecules has come one step closer to reality. In the study published in Nature Methods, researchers used a newly developed grease to suspend small crystals of lysozyme, glucose isomerase, thaumatin, and fatty acid-binding protein type-3, which they then analyzed using the revolutionary serial femtosecond crystallography method.
Crystallography, which was first performed just a century ago, ...
Heat transfer sets the noise floor for ultrasensitive electronics
2014-11-10
A team of engineers and scientists has identified a source of electronic noise that could affect the functioning of instruments operating at very low temperatures, such as devices used in radio telescopes and advanced physics experiments.
The findings, detailed in the November 10 issue of the journal Nature Materials, could have implications for the future design of transistors and other electronic components.
The electronic noise the team identified is related to the temperature of the electrons in a given device, which in turn is governed by heat transfer due to packets ...
For enterics, adaptability could be an Achilles heel
2014-11-10
In research published in Nature Chemical Biology, scientists from RIKEN in Japan have discovered a surprisingly simple mechanism through which enterics can adjust to the very different oxygen environments inside the human gut and outside. This research, which was led by Shigeyuki Yokoyama and Wataru Nishii of the Structural Biology Laboratory, opens a new potential target against these bacteria, which are the most-frequently encountered causative microorganisms of infectious diseases. The family includes well-known symbionts and facultative or obligate pathogens such as ...
Kīlauea, 1790 and today
2014-11-10
Boulder, Colo., USA - Scores of people were killed by an explosive eruption of Kīlauea Volcano, Hawai'i, in 1790. Research presented in GSA Bulletin by D.A. Swanson of the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory and colleagues suggests that most of the fatalities were caused by hot, rapidly moving surges of volcanic debris and steam that engulfed the victims. Deposits of such surges occur on the surface on the west summit area and cover an ash bed indented with human footprints.
The footprints, made by warriors and their families, appear along a major trail in use at the time. ...
Researchers discover new target for blood cancer treatment
2014-11-10
Scientists at the University of York have identified a therapeutic target which could lead to the development of new treatments for specific blood cancers.
The study, by researchers from the Centre for Immunology and Infection at York working with scientists in the Department of Medicine at Stony Brook University in the USA, could lead to improved therapies for a group of haematological cancers called myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs).
These are characterised by increases in one or more blood cell types, usually red blood cells, which carry oxygen around the body ...
Anxiety can damage brain
2014-11-10
Toronto, Canada - People with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) are at increased risk of converting to Alzheimer's disease within a few years, but a new study warns the risk increases significantly if they suffer from anxiety.
The findings were reported on Oct. 29 online by The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, ahead of print publication, scheduled for May 2015.
Led by researchers at Baycrest Health Sciences' Rotman Research Institute, the study has shown clearly for the first time that anxiety symptoms in individuals diagnosed with MCI increase the risk of a ...
Rhode Island, Miriam hospitals, other researchers: Opioid OD cause for over 100,000 ED visits in '10
2014-11-10
PROVIDENCE, R.I. - Researchers from Rhode Island and The Miriam hospitals and the Stanford University School of Medicine have found that prescription opioids, including methadone, were involved in 67.8 percent of (or over 135,971 visits to) nationwide emergency department (ED) visits in 2010, with the highest proportion of opioid overdoses occurring in the South.
Additionally, several concurrent health conditions were identified as common among overdose victims. These include chronic respiratory diseases and mental health/mood disorders -suggesting that opioids should ...
Mothers' education significant to children's academic success
2014-11-10
ANN ARBOR--A mother knows best--and the amount of education she attains can predict her children's success in reading and math. In fact, that success is greater if she had her child later in life, according to a new University of Michigan study.
Sandra Tang, a U-M psychology research fellow and the study's lead author, said children of mothers 19 and older usually enter kindergarten with higher levels of achievement. These kids continue to excel in math and reading at higher levels through eighth grade when compared to children of mothers 18 and younger.
"These results ...
Can HIV be transmitted via manicure instruments?
2014-11-10
New Rochelle, NY, November 10, 2014--The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) lists numerous potential alternative sources of HIV transmission in addition to the known classical modes for acquiring the AIDS virus. Although manicure instruments is not on this list of alternative sources, a case of HIV transmission that may be linked to sharing of manicure instruments is presented in AIDS Research and Human Retroviruses, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article appears in special issue on HIV Prevention Science and is available ...
A sea change for marine conservation
2014-11-10
Harnessing 'people power' to manage fisheries in the developing world has significantly benefited local communities and coral reefs, according to new research.
"Studies about the environment, and particularly fisheries, abound with bad news, but here, we see a glimmer of hope," says lead author Professor Joshua Cinner, from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies at James Cook University.
Historically, fisheries management in East Africa has followed a 'top down' approach, but in 2006, the Kenyan government introduced a pilot program that gave communities ...
Moderate drinking is healthy only for some people
2014-11-10
The study included 618 Swedes with coronary heart disease and a control group of 3,000 healthy subjects. The subjects were assigned to various categories based on the amount of alcohol they consumed (ethanol intake). Meanwhile, they were tested in order to identify a particular genotype (CETP TaqIB) that previous studies had found to play a role in the health benefits of alcohol consumption.
Protective effect
The results, which have been published in Alcohol, confirm the findings of the earlier studies. Moderate consumption of alcohol helps protect people with the genotype ...
Low levels of the DHEA prohormone predict coronary heart disease
2014-11-10
Men with low levels of DHEA in the blood run an increased risk of developing coronary heart disease events. The Sahlgrenska Academy study has been published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The term prohormone refers to the precursor of a hormone. DHEA is a prohormone that is produced by the adrenal glands and can be converted to active sex hormones. While the tendency of DHEA levels to fall with age was discovered long ago, the biological role of the prohormone is largely unknown.
Researchers at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, have ...
[1] ... [3208]
[3209]
[3210]
[3211]
[3212]
[3213]
[3214]
[3215]
3216
[3217]
[3218]
[3219]
[3220]
[3221]
[3222]
[3223]
[3224]
... [8825]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.