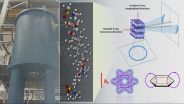
Migration negation
2014-11-06
Most cancer deaths occur because of metastasis, yet progress in preventing and treating migratory cancer cells has been slow.
"It's been particularly challenging to design drugs that work against metastasis," said Taran Gujral, research fellow in systems biology at Harvard Medical School.
"Unfortunately, many cancers aren't detected until after they've already metastasized."
Gujral and colleagues have now identified a cellular culprit that should help researchers better understand how metastasis begins. Their findings may also inform the design of new treatments ...
Study shows integrative medicine relieves pain and anxiety for cancer inpatients
2014-11-06
Pain is a common symptom of cancer and side effect of cancer treatment, and treating cancer-related pain is often a challenge for health care providers.
The Penny George Institute for Health and Healing researchers found that integrative medicine therapies can substantially decrease pain and anxiety for hospitalized cancer patients. Their findings are published in the current issue of the Journal of the National Cancer Institute Monographs.
"Following Integrative medicine interventions, such as medical massage, acupuncture, guided imagery or relaxation response ...
Greater use of social media gets science, scientists noticed, study says
2014-11-06
MADISON, Wis. -- Here is an idea worth following: "share" for tenure; "like" to get cited.
Academic researchers are turning to social media more and more, according to Dominique Brossard, and not just to post family photos or crack wise via hashtag.
"I've been in science communication for a while now, and I am really seeing a change -- especially among the younger scientists -- in their willingness to share their work," says Brossard, a University of Wisconsin-Madison professor of life sciences communication.
It's the venue for that sharing that has inspired work ...
ORNL thermomagnetic processing method provides path to new materials
2014-11-06
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Nov. 6, 2014 - For much the same reason LCD televisions offer eye-popping performance, a thermomagnetic processing method developed at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory can advance the performance of polymers.
Polymers are used in cars, planes and hundreds of consumer products, and scientists have long been challenged to create polymers that are immune to shape-altering thermal expansion. One way to achieve this goal is to develop highly directional crystalline structures that mimic those of transparent liquid crystal diode, or ...
The tiger beetle: Too fast to see
2014-11-06
PITTSBURGH--Speed is an asset for a predator. Except when that predator runs so fast that it essentially blinds itself.
The tiger beetle, relative to its size, is the fastest creature on Earth. Some of these half-inch-long beetles cover about 120 body lengths per second (at about five miles per hour). The fastest human can do about five body lengths. To take the sprinting gold from the tiger beetle, a person would have to hit 480 miles per hour.
BUT! The tiger beetle has a problem. At peak speeds, everything becomes a blur. They can't gather enough light with their ...
Black, Hispanic kids underrepresented in autism identification
2014-11-06
LAWRENCE -- The number of children diagnosed with autism has increased in recent years, but a new study co-authored by a University of Kansas professor shows that while the number of students with autism increased in every state from 2000 to 2007, black and Hispanic children were significantly underrepresented.
Jason Travers, assistant professor of special education, co-authored a study that analyzed administrative identification of autism in every state under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act for the years 2000 and 2007. The disparity in the odds of white ...
Who will come to your bird feeder in 2075?
2014-11-06
The distribution of birds in the United States today will probably look very different in 60 years as a result of climate, land use and land cover changes.
A new U.S. Geological Survey study predicts where 50 bird species will breed, feed and live in the conterminous U.S. by 2075. While some types of birds, like the Baird's sparrow, will likely lose a significant amount of their current U.S. range, other ranges could nearly double. Human activity will drive many of these shifts. The study was published today in the journal PLOS ONE.
"Habitat loss is a strong predictor ...
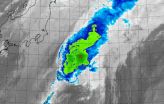
NASA sees Tropical Storm Nuri resemble a frontal system
2014-11-06
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Tropical Storm Nuri on Nov. at captured an infrared picture of the storm. The storm looked more like a frontal system as it stretched from northeast to southwest.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite flew over Nuri on Nov. 6 at 1240 UTC (7:40 a.m. EST). The MODIS image showed some strong thunderstorms remaining in a small area around Nuri's center, but the storm appeared stretched out from northeast to southwest. Wind shear was affecting the storm, stretching it ...
'Rewriting' the way to make natural drug compounds
2014-11-06
(SALT LAKE CITY)--One of the big hurdles in bringing drugs to market is the difficulty of producing large enough quantities of potential compounds to conduct clinical trials. This is particularly true with compounds made by organisms, which usually are produced in exceedingly small amounts and are difficult to synthesize in the laboratory.
Researchers from the University of Utah College of Pharmacy have made an important stride in addressing those problems. In a study in ACS Synthetic Biology, researchers led by Eric W. Schmidt, Ph.D., professor of medicinal chemistry, ...
NASA see birth of Tropical Cyclone 5B in Bay of Bengal
2014-11-06
The fifth tropical cyclone of the Northern Indian Ocean season formed in the Bay of Bengal as NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead and captured an image of the storm.
When Terra passed over Tropical Cyclone 5B on Nov. 6 at 05:05 UTC (12:05 a.m. EST), the MODIS instrument aboard took a visible image of the storm. The MODIS image showed a concentrated storm with strong thunderstorms circling tight around the center and in the northeastern quadrant.
By 1500 UTC (10 a.m. EST), Tropical Cyclone 5B was located near 13.4 north latitude and 87.9 east longitude. That's about ...
Study highlights prevalence of mistreatment between nursing home residents
2014-11-06
NEW YORK (November 6, 2014) -- Inappropriate, disruptive, or hostile behavior between nursing home residents is a sizable and growing problem, according to new research from Weill Cornell Medical College and Cornell University.
The study found that nearly one in five nursing home residents were involved in at least one negative and aggressive encounter with one or more fellow residents over the previous four weeks. These included acts of verbal or physical abuse, inappropriate sexual behavior, or invasion of privacy, among other incidents, known collectively as resident-to-resident ...
Denying problems when we don't like the political solutions
2014-11-06
DURHAM, N.C. -- There may be a scientific answer for why conservatives and liberals disagree so vehemently over the existence of issues like climate change and specific types of crime.
A new study from Duke University finds that people will evaluate scientific evidence based on whether they view its policy implications as politically desirable. If they don't, then they tend to deny the problem even exists.
"Logically, the proposed solution to a problem, such as an increase in government regulation or an extension of the free market, should not influence one's belief ...
Koala study reveals clues about origins of the human genome
2014-11-06
Eight percent of your genome derives from retroviruses that inserted themselves into human sex cells millions of years ago. Right now the koala retrovirus (KoRV) is invading koala genomes, a process that can help us understand our own viral lineage and make decisions about managing this vulnerable species.
In a recent study scientists from the University of Illinois discovered that 39 different KoRVs in a koala's genome were all endogenous, which means passed down to the koala from one parent or the other; one of the KoRVs was found in both parents.
Koalas are the ...
Retaining military veteran employees is all about the right fit
2014-11-06
It's a difficult career transition that can lead to more professional frustration and shorter tenure on the job for many of the newest generation of veterans employed with the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) compared to their non-veteran co-workers.
New research from the University of Cincinnati is helping VA analyze the process of reintegrating veterans into civilian careers and evaluate methods for easing that transition. That's good news for all veterans as the nation prepares to observe Veterans Day on Nov. 11.
"This period of time within our labor force ...
Nutrients that feed red tide 'under the microscope' in major study
2014-11-06
The "food" sources that support Florida red tides are more diverse and complex than previously realized, according to five years' worth of research on red tide and nutrients published recently as an entire special edition of the scientific journal Harmful Algae.
The multi-partner project was funded by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's ECOHAB program* (described below) and included 14 research papers from seven institutions.
The research team studied four red tide blooms caused by the harmful algae species Karenia brevis in 2001, '07, '08 and '09, ...
Gut bacteria: How genes determine the fit of your jeans
2014-11-06
Our genetic makeup influences whether we are fat or thin by shaping which types of microbes thrive in our body, according to a Cornell-led study published today in the journal Cell.
By studying pairs of twins, researchers identified the Christensenellaceae bacterial family, which is highly heritable and more common in lean individuals. Moreover, a member of this class of bacteria, Christensenellaceae minuta, protected against weight gain when transplanted into mice.
The findings pave the way for personalized probiotic therapies that are optimized to reduce the risk ...
For tiger populations, a new threat
2014-11-06
Along with the pressures of habitat loss, poaching and depletion of prey species, a new threat to tiger populations in the wild has surfaced in the form of disease, specifically, canine distemper virus (CDV). According to a new study from the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) and its partners, CDV has the potential to be a significant driver in pushing the animals toward extinction.
While CDV has recently been shown to lead to the deaths of individual tigers, its long-term impacts on tiger populations had never before been studied.
The authors evaluated these impacts ...
Arm pain in young baseball players is common, preventable
2014-11-06
NEW YORK, NY (November 6, 2014) --The most in-dept survey of its kind found that arm pain is common among supposedly healthy young baseball players and nearly half have been encouraged to keep playing despite arm pain. The findings suggest that more detailed and individualized screening is needed to prevent overuse injury in young ballplayers. The study, led by Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) researchers, was published this week in the online edition of the American Journal of Sports Medicine.
"Both nationally and internationally, we're witnessing a troubling ...
Biodiversity offsets need a national strategy to succeed
2014-11-06
In a paper published by PLOS ONE, researchers concluded that a national strategy must be implemented in order to compensate for environmental damage caused by development projects in Africa.
Studying these issues and other serious ethical concerns, the research discovered that current offset programs - which are planned and designed on a project-by-project basis - fail to take into account the cumulative impacts of various conservations projects taking place in the same country or region.
The scientists from the universities of California, Stirling and Kent alongside ...
From single cells to multicellular life
2014-11-06
This news release is available in German.
All multicellular creatures are descended from single-celled organisms. The leap from unicellularity to multicellularity is possible only if the originally independent cells collaborate. So-called cheating cells that exploit the cooperation of others are considered a major obstacle. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology in Plön, Germany, together with researchers from New Zealand and the USA, have observed in real time the evolution of simple self-reproducing groups of cells from previously ...
Is violent injury a chronic disease? Study suggests so & may aid efforts to stop the cycle
2014-11-06
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- Teens and young adults who get seriously injured in an assault are nearly twice as likely as their peers to end up back in the emergency room for a violent injury within the next two years, a new University of Michigan Injury Center study finds.
The researchers call this repeating pattern of violent injury a reoccurring disease, but their landmark study also suggests potentially powerful opportunities to intervene in ways that could stop the cycle.
The first six months after a young person seeks care for a violence-related injury is an especially ...
Novel 3D printing process enables metal additive manufacturing for consumer market
2014-11-06
New Rochelle, NY, November 6, 2014--Lower-cost 3D printers for the consumer market offer only a limited selection of plastic materials, while industrial additive manufacturing (AM) machines can print parts made of high-performance metals. The application of a novel process called Selective Inhibition Sintering (SIS) in a consumer-priced metal AM machine is described in an article in 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing website until ...
Synthetic biology for space exploration
2014-11-06
Does synthetic biology hold the key to manned space exploration of Mars and the Moon? Berkeley Lab researchers have used synthetic biology to produce an inexpensive and reliable microbial-based alternative to the world's most effective anti-malaria drug, and to develop clean, green and sustainable alternatives to gasoline, diesel and jet fuels. In the future, synthetic biology could also be used to make manned space missions more practical.
"Not only does synthetic biology promise to make the travel to extraterrestrial locations more practical and bearable, it could also ...
New insights into an old bird
2014-11-06
Berlin, Germany (November, 2014) - The dodo is among the most famous extinct creatures, and a poster child for human-caused extinction events. Despite its notoriety, and the fact that the species was alive during recorded human history, little is actually known about how this animal lived, looked, and behaved. A new study of the only known complete skeleton from a single bird takes advantage of modern 3-D laser scanning technology to open a new window into the life of this famous extinct bird. The study was presented at the 74th Annual Meeting of the Society of Vertebrate ...
Complete 9,000-year-old frozen bison mummy found in Siberia
2014-11-06
Berlin, Germany (November, 2014) - Many large charismatic mammals went extinct at the end of the Ice Age (approx 11,000 years ago), including the Steppe bison, Bison priscus. A recent find in Eastern Siberia has uncovered one of these bison, literally, frozen in time.
The most complete frozen mummy of the Steppe bison yet known, dated to 9,300 years before present, was recently uncovered in the Yana-Indigirka Lowland and a necropsy was performed to learn about how this animal lived and died at the end of the Ice Age. The Yukagir bison mummy, as it is named, has a complete ...
[1] ... [3213]
[3214]
[3215]
[3216]
[3217]
[3218]
[3219]
[3220]
3221
[3222]
[3223]
[3224]
[3225]
[3226]
[3227]
[3228]
[3229]
... [8825]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.