Parents' reported food preparation time is inversely associated with energy density
2014-07-30
7/29/2014, Seatle, WA. Research to be presented at the Annual Meeting of the Society for the Study of Ingestive Behavior (SSIB), the foremost society for research into all aspects of eating and drinking behavior, suggests that the amount time parents spend on food preparation at home influences children's food intake decisions made in the laboratory without parental supervision.
"In general, research shows that children tend to eat inadequate amounts of nutrient-rich foods while eating large amounts of sugary and fatty foods," Shehan said. "It's encouraging to see that ...
Research shows impact of soft drinks in meal planning
2014-07-30
Seattle, WA. 7/29/20134. New research by academics in the University of Bristol's Nutrition and Behaviour Unit (NBU) has looked into whether we take liquid calories into account when planning meals.
The research, to be presented at the Society for the Study of Ingestive Behavior Conference (SSIB 2014) in Seattle, USA this week [29 July to 2 August], argues that we do.
The team was led by Professor Jeff Brunstrom, and is based in the School of Experimental Psychology.
As part of a Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) grant, the researchers looked ...
Time of arrival at hospital impacts time to treatment and survival of heart attack patients
2014-07-29
Going to the hospital for a heart attack during evenings, weekends and holidays increases your risk of dying 13 percent compared with people arriving during workday hours, according to new research in the American Heart Association journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Every year, more than 250,000 people experience an ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), the most severe type of heart attack caused by a complete blockage of blood flow to the heart. To prevent death, it's critical to restore blood flow as quickly as possible by surgically opening ...
Reducing kidney injury using a quality improvement method
2014-07-29
LEBANON, NH (July 29, 2014) – Using quality improvement measures in eight of the 10 hospitals in the Northern New England Cardiovascular Disease Study Group, researchers have found a way to reduce kidney injury in patients undergoing a procedure with contrast dye.
Currently, 7-15 percent of these patients who undergo a coronary stent procedure with contrast-dye end up with kidney injury, which can result in death or rapid decline in kidney function leading to temporary or permanent dialysis, says a study published in the July issue of Circulation Cardiovascular Quality ...
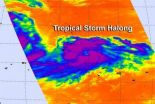
NASA sees developing Tropical Storm Halong causing warning
2014-07-29
NASA infrared satellite data revealed that Tropical Storm Halong is surrounded by strong thunderstorms and an eye appears to be developing.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Halong on July 29 at 03:29 UTC (July 28 at 11:29 p.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument captured data on the cloud cover. The infrared data showed very cold, high thunderstorm cloud top temperatures of powerful storms surrounding the center, with what appears to be an eye developing. Microwave satellite data also shows a small eye, with tightly-curved bands of ...
Good outcomes with multiple limb salvage after severe combat injuries, reports Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
2014-07-29
July 29, 2014 – For survivors of severe combat injuries threatening more than one limb, reconstructive surgical procedures using tissue flaps have a good record of safety and effectiveness in avoiding amputation, reports a paper in the August issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
Experience with multiple limb salvage procedures in solders injured in Iraq and Afghanistan shows good success rates, with no increase in complications compared to single-flap techniques, report Dr. Ian Valerio ...
Beware of claims about cosmetic stem cells procedures, says review in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
2014-07-29
July 29, 2014 – Advertising claims for cosmetic procedures using stem cells are running far ahead of the scientific evidence for safety and effectiveness, according to a review in the August issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
"Stem cells offer tremendous potential, but the marketplace is saturated with unsubstantiated and sometimes fraudulent claims that may place patients at risk," write Dr Michael T. Longaker of Stanford University Medical Center and colleagues.
'Worrying advertisements' ...
NASA-funded X-ray instrument settles interstellar debate
2014-07-29
VIDEO:
This animation illustrates solar wind charge exchange in action. An atom of interstellar helium (blue) collides with a solar wind ion (red), losing one of its electrons (yellow) to the...
Click here for more information.
New findings from a NASA-funded instrument have resolved a decades-old puzzle about a fog of low-energy X-rays observed over the entire sky. Thanks to refurbished detectors first flown on a NASA sounding rocket in the 1970s, astronomers have now confirmed ...
Revolutionary microshutter technology hurdles significant challenges
2014-07-29
NASA technologists have hurdled a number of significant technological challenges in their quest to improve an already revolutionary observing technology originally created for the James Webb Space Telescope.
The team, led by Principal Investigator Harvey Moseley, a scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, has demonstrated that electrostatically actuated microshutter arrays — that is, those activated by applying an specific voltage — are as functional as the current technology's magnetically activated arrays. This advance makes them a highly ...
Study: Contrary to image, city politicians do adapt to voters
2014-07-29
Political scientists have long wondered whether city governments in the U.S. are really responsive to their voters. Aren't local governments simply mired in machine politics, or under the sway of local big-money interests? Does ideology matter?
Now a uniquely comprehensive study co-authored by an MIT political scientist has produced a pair of distinctive findings: first, that the policies of city governments do closely match the politics of their citizens, and second, that this occurs regardless of the exact form of government than a city has.
That means that urban ...
Short sellers not to blame for 2008 financial crisis, study finds
2014-07-29
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Contrary to widespread media reports, the collapse of several financial firms during the 2008 economic crisis was not triggered by unsettled stock trades, according to new research from the University at Buffalo School of Management.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Financial Economics, analyzed the open interest of fails-to-deliver — stock trades in which shares are not delivered within the three-day trading cycle — in the days before and after the stock crashes of American Insurance Group, Bear Stearns, Lehman Brothers and Merrill Lynch.
The ...
Informal child care significantly impacts rural economies, MU study finds
2014-07-29
COLUMBIA, Mo. – The child care industry has grown significantly in recent years, contributing considerably to the national economy through job creation and increased opportunities for parents to work. However, little knowledge exists of the size and economic impact of child care, especially informal child care, on rural economies. Now, University of Missouri researchers have studied the child care sector in Kansas, particularly in rural areas, and have found that informal child care services create a large economic impact in the state.
Tom Johnson, a professor in the ...
Malaria vaccine shows continued protection during 18 months of follow-up
2014-07-29
A vaccine previously shown to reduce malaria in young infants and children reduces larger numbers of malaria cases in areas of higher malaria transmission, according to results from an ongoing clinical trial published in PLOS Medicine. The effect of vaccination diminished over time, but protection against clinical malaria remained evident 18 months after vaccination.
In the new report, the RTS,S Clinical Trials Partnership* update estimates of vaccine efficacy (the reduction in the risk of malaria in participants who received the vaccine compared to those who received ...
Small increases in Ugandan urbanicity tied to CVD risk factors
2014-07-29
Urban dwellers tend to have higher risk for cardiovascular diseases than people living in more rural locations. In a new study published in PLOS Medicine, Johanna Riha and colleagues, researchers from the University of Cambridge and the MRC/UVRI Research Unit in Uganda, have found that even within rural communities in Uganda that all lacked paved roads and running water, people living in villages with relatively more urban features—such as schools and health facilities –were more likely to have risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as physical inactivity, lower ...
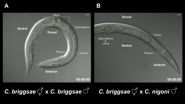
'Killer sperm' prevents mating between worm species
2014-07-29
VIDEO:
These are time-lapse videos of Caenorhabditis hermaphrodites that were (A) mated with the same species and (B) mated with a different species. Male sperm were fluorescently labeled and appear as...
Click here for more information.
The classic definition of a biological species is the ability to breed within its group, and the inability to breed outside it. For instance, breeding a horse and a donkey may result in a live mule offspring, but mules are nearly always sterile ...
Urbanization of rural Africa associated with increased risk of heart disease and diabetes
2014-07-29
The increasing urbanisation of rural areas in sub-Saharan Africa could lead to an explosion in incidences of heart disease and diabetes, according to a new study carried out in Uganda which found that even small changes towards more urban lifestyles was associated with increased risk of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
Over 530 million people live in rural areas of sub-Saharan Africa, where rates of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases tend to be much lower than in urban areas. However, many of these areas are becoming increasingly urbanised, with people living ...
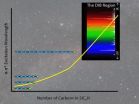
Mysterious molecules in space
2014-07-29
WASHINGTON D.C., July 29, 2014 – Over the vast, empty reaches of interstellar space, countless small molecules tumble quietly though the cold vacuum. Forged in the fusion furnaces of ancient stars and ejected into space when those stars exploded, these lonely molecules account for a significant amount of all the carbon, hydrogen, silicon and other atoms in the universe. In fact, some 20 percent of all the carbon in the universe is thought to exist as some form of interstellar molecule.
Many astronomers hypothesize that these interstellar molecules are also responsible ...
This week from AGU: Cell tower rain gauges, lightning channels, North Sea storm surge
2014-07-29
This Week From AGU: Cell phone tower rain gauges, lightning channels, North Sea storm surge
From AGU's blogs: Dropped cell phone calls become rain gauges in West Africa
A shaky cell phone connection during a rainstorm can be an annoying nuisance. But now scientists are showing that these weakened signals can be used to monitor rainfall in West Africa, a technique that could help cities in the region better prepare for floods and combat weather-related diseases, according to a new study accepted for publication in Geophysical Research Letters, a journal of the American ...
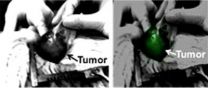
Penn team makes cancer glow to improve surgical outcomes
2014-07-29
The best way to cure most cases of cancer is to surgically remove the tumor. The Achilles heel of this approach, however, is that the surgeon may fail to extract the entire tumor, leading to a local recurrence.
With a new technique, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have established a new strategy to help surgeons see the entire tumor in the patient, increasing the likelihood of a positive outcome. This approach relies on an injectable dye that accumulates in cancerous tissues much more so than normal tissues. When the surgeon shines an infrared light on the ...
Huge waves measured for first time in Arctic Ocean
2014-07-29
As the climate warms and sea ice retreats, the North is changing. An ice-covered expanse now has a season of increasingly open water which is predicted to extend across the whole Arctic Ocean before the middle of this century. Storms thus have the potential to create Arctic swell – huge waves that could add a new and unpredictable element to the region.
A University of Washington researcher made the first study of waves in the middle of the Arctic Ocean, and detected house-sized waves during a September 2012 storm. The results were recently published in Geophysical Research ...
Underwater elephants
2014-07-29
In the high-tech world of science, researchers sometimes need to get back to basics. UC Santa Barbara's Douglas McCauley did just that to study the impacts of the bumphead parrotfish (Bolbometopon muricatum) on coral reef ecosystems at two remote locations in the central Pacific Ocean.
Using direct observation, animal tracking and computer simulation, McCauley, an assistant professor in the Department of Ecology, Evolution and Marine Biology, and his colleagues sought to understand whether the world's largest parrotfish is necessary for positively shaping the structure ...
Vision-correcting display makes reading glasses so yesterday
2014-07-29
BERKELEY — What if computer screens had glasses instead of the people staring at the monitors? That concept is not too far afield from technology being developed by computer and vision scientists at the University of California, Berkeley.
The researchers are developing computer algorithms to compensate for an individual's visual impairment, and creating vision-correcting displays that enable users to see text and images clearly without wearing eyeglasses or contact lenses. The technology could potentially help hundreds of millions of people who currently need corrective ...
Researchers take steps toward development of a vaccine against tick-transmitted disease
2014-07-29
Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine researchers have made an important advancement toward developing a vaccine against the debilitating and potentially deadly tick-transmitted disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis (HGA).
During the past several years, experts have seen a steady rise in the incidence of human infections caused by tick-transmitted bacterial pathogens — making the need for a vaccine critical. Successful vaccine development hinges on knowing what to target to prevent disease, and the VCU team has identified three such proteins on the surface ...
Brainwaves can predict audience reaction for television programming
2014-07-29
Media and marketing experts have long sought a reliable method of forecasting responses from the general population to future products and messages. According to a study conducted at the City College of New York (CCNY) in partnership with Georgia Tech, it appears that the brain responses of just a few individuals are a remarkably strong predictor.
By analyzing the brainwaves of 16 individuals as they watched mainstream television content, researchers were able to accurately predict the preferences of large TV audiences, up to 90 percent in the case of Super Bowl commercials. ...
Socialization relative strength in fragile X longitudinal study
2014-07-29
Standard scores measuring "adaptive behavior" in boys with fragile X syndrome tend to decline during childhood and adolescence, the largest longitudinal study of the inherited disorder to date has found.
Adaptive behavior covers a range of everyday social and practical skills, including communication, socialization, and completing tasks of daily living such as getting dressed. In this study, socialization emerged as a relative strength in boys with fragile X, in that it did not decline as much as the other two domains of adaptive behavior measured: communication and daily ...
[1] ... [3452]
[3453]
[3454]
[3455]
[3456]
[3457]
[3458]
[3459]
3460
[3461]
[3462]
[3463]
[3464]
[3465]
[3466]
[3467]
[3468]
... [8831]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.