Sustained efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety for GlaxoSmithKline's HPV vaccine
2014-07-31
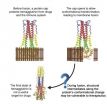
A long-term follow-up study (HPV-023; NCT00518336) shows the sustained efficacy, immunogenicity and safety of GlaxoSmithKline's human papilloma virus (HPV) vaccine Cervarix. Women vaccinated with the HPV-16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine were followed for more than nine years, and vaccine efficacy (VE) against incident infection was 100%. This is the longest follow-up report for a licensed HPV vaccine. Visit https://www.landesbioscience.com/journals/vaccines/article/29532/ for the full paper.
HPV and vaccination
Persistent infection with HPV has been clearly established ...
Algorithm reduces use of CT scans when diagnosing children with appendicitis
2014-07-31
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Implementation of an algorithm aimed to diagnose pediatric patients with suspected appendicitis reduces the utilization of computed tomography (CT) scans, without affecting diagnostic accuracy, Mayo Clinic Children's Center researchers have found. The study was recently published in the journal Surgery.
Acute appendicitis is the most common cause of acute abdominal pain in children. Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes inflamed and filled with pus. CT scans are often used to diagnose acute appendicitis because they are accurate, widely available ...
Study of bigeye tuna in Northwest Atlantic uses new tracking methods
2014-07-31
AMHERST, Mass. – A first-of-its-kind study of bigeye tuna movements in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean led by Molly Lutcavage, director of the Large Pelagics Research Center at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, found among other things that these fish cover a wide geographical range with pronounced north-south movements from Georges Bank to the Brazilian shelf, and they favor a high-use area off Cape Hatteras southwest of Bermuda for foraging.
This NOAA-funded research, which used a new approach to study one of the most important commercial tuna species in the ...
Unintended consequences: More high school math, science linked to more dropouts
2014-07-31
As U.S. high schools beef up math and science requirements for graduation, researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have found that more rigorous academics drive some students to drop out.
The research team reported in the June/July issue of the journal Educational Researcher that policies increasing the number of required high school math and science courses are linked to higher dropout rates.
"There's been a movement to make education in the United States compare more favorably to education in the rest of the world, and part of that has involved increasing ...
Is it really a concussion? Symptoms overlap with neck injuries so diagnosis is tough call
2014-07-31
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Athletes and others reporting cognitive difficulties after a head injury are usually diagnosed as having had a concussion. But is it really a concussion? A new study published by University at Buffalo medical faculty finds that many of the same symptoms are common to concussions and to injuries to the neck and/or balance system, known collectively as cervical/vestibular injuries.
The research was based on responses about symptoms from 128 patients – some of whom were professional athletes – who were being treated at UB's Concussion Management Clinic in ...
Invasive lionfish likely safe to eat after all
2014-07-31
Scientists have learned that recent fears of invasive lionfish causing fish poisoning may be unfounded. If so, current efforts to control lionfish by fishing derbies and targeted fisheries may remain the best way to control the invasion. And there's a simple way to know for sure whether a lionfish is toxic: test it after it's been cooked.
Pacific lionfish were first reported off the coast of Florida in the 1980s, and have been gaining swiftly in number ever since. They're now found in marine habitats throughout the tropical and subtropical Western Atlantic, Caribbean ...
Certain Arctic lakes store more greenhouse gases than they release
2014-07-31
New research, supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF), counters a widely-held scientific view that thawing permafrost uniformly accelerates atmospheric warming, indicating instead that certain Arctic lakes store more greenhouse gases than they emit into the atmosphere.
The study, published this week in the journal Nature, focuses on thermokarst lakes, which occur as permafrost thaws and creates surface depressions that fill with melted fresh water, converting what was previously frozen land into lakes.
The research suggests that Arctic thermokarst lakes ...
NASA's Fermi space telescope reveals new source of gamma rays
2014-07-31
Observations by NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope of several stellar eruptions, called novae, firmly establish these relatively common outbursts almost always produce gamma rays, the most energetic form of light.
"There's a saying that one is a fluke, two is a coincidence, and three is a class, and we're now at four novae and counting with Fermi," said Teddy Cheung, an astrophysicist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, and the lead author of a paper reporting the findings in the Aug. 1 edition of the journal Science.
A nova is a sudden, short-lived brightening ...
Study finds physical link to strange electronic behavior
2014-07-31
HOUSTON -- (July 31, 2014) -- Scientists have new clues this week about one of the baffling electronic properties of the iron-based high-temperature superconductor barium iron nickel arsenide. A Rice University-led team of U.S., German and Chinese physicists has published the first evidence, based on sophisticated neutron measurements, of a link between magnetic properties and the material's tendency, at sufficiently low temperatures, to become a better conductor of electricity in some directions than in others.
The odd behavior, which has been documented in a number ...
Hubble shows farthest lensing galaxy yields clues to early universe
2014-07-31
Astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have unexpectedly discovered the most distant galaxy that acts as a cosmic magnifying glass. Seen here as it looked 9.6 billion years ago, this monster elliptical galaxy breaks the previous record-holder by 200 million years.
These "lensing" galaxies are so massive that their gravity bends, magnifies, and distorts light from objects behind it, a phenomenon called gravitational lensing. Finding one in such a small area of the sky is so rare that you would normally have to survey a region hundreds of times larger to find just ...
Researchers uncover clues to flu's mechanisms
2014-07-31
HOUSTON – (July 31, 2014) – A flu virus acts like a Trojan horse as it attacks and infects host cells. Scientists at Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine have acquired a clearer view of the well-hidden mechanism involved.
Their computer simulations may lead to new strategies to stop influenza, perhaps even a one-size-fits-all vaccine.
The discovery detailed this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science shows the path taken by hemagglutinin, a glycoprotein that rides the surface of the influenza virus, as it releases fusion peptides to invade ...
UF study advances 'DNA revolution,' tells butterflies' evolutionary history
2014-07-31
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- By tracing nearly 3,000 genes to the earliest common ancestor of butterflies and moths, University of Florida scientists have created an extensive "Tree of Lepidoptera" in the first study to use large-scale, next-generation DNA sequencing.
Among the study's more surprising findings: Butterflies are more closely related to small moths than to large ones, which completely changes scientists' understanding of how butterflies evolved. The study also found that some insects once classified as moths are actually butterflies, increasing the number of butterfly ...
NYU CDUHR researchers look at prescription opioid abuse among young adults in NYC
2014-07-31
The prevalence of heroin use has been rising steadily in the U.S in recent years. According to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health, the number of individuals reporting past year heroin use almost doubled between 2007 (373,000) and 2012 (669,000). Emerging evidence suggests the increase may be linked to prescription opioid (PO) users who transition from oral and/or intranasal PO use to heroin use, with POs providing the entryway to regular opioid use, and ultimately, heroin injection. This drug-use trajectory appears to have become increasingly common over the past ...
NYU research looks to combat US Latina immigrant obesity
2014-07-31
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Latinos are the largest minority group in the United States, comprising 16.7% of the population. Approximately one-third of Latinos are obese and are 1.2 times as likely to be obese compared to non-Hispanic Whites.
NYU College of Nursing student researcher Lauren Gerchow, BSN, RN, MSN candidate, has sought to identify the factors that contribute to this problem by compiling a systematic review of qualitative studies that focused on food patterns in Latina women recently published in Nursing Research.
"The review focuses on women ...
Stanford professor finds that wildfires and other burns play bigger role in climate change
2014-07-31
It has long been known that biomass burning – burning forests to create agricultural lands, burning savannah as a ritual , slash-and-burn agriculture and wildfires – figures into both climate change and public health.
But until the release of a new study by Stanford University Civil and Environmental Engineering Professor Mark Z. Jacobson, the degree of that contribution had never been comprehensively quantified.
Jacobson's research, detailed in a paper published July 30 in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, is based on a three-dimensional computer model ...
Childhood coxsackie virus infection depletes cardiac stem cells and might compromise heart health in adults
2014-07-31
There is epidemiological evidence that links type B coxsackie virus (CVB) infection with heart disease, and research published on July 31st in PLOS Pathogens now suggests a mechanism by which early infection impairs the heart's ability to tolerate stress at later stages of life.
CVB infection is very common and affects mostly children. The symptoms range widely: over half of the infections are thought to be asymptomatic, the majority of children who get sick have only a mild fever, and a very small proportion get inflammation of the heart or brain. On the other hand, ...
Multidisciplinary study reveals big story of cultural migration
2014-07-31
Quantifying and transforming the history of culture into visual representation isn't easy. There are thousands of individual stories across millennia to consider, and some historical conditions are nearly impossible to measure.
Addressing this challenge, Dr. Maximilian Schich, associate professor of arts and technology at The University of Texas at Dallas, has brought together a team of network and complexity scientists to create and quantify a big picture of European and North American cultural history.
Schich, an art historian who works under the umbrella of the ...
Shrinking dinosaurs evolved into flying birds
2014-07-31
VIDEO:
This movie is an animated version of how birds arose from a very special lineage of evolving dinosaurs.
Click here for more information.
A new study involving scientists from the University of Southampton has revealed how massive, meat-eating, ground-dwelling dinosaurs evolved into agile flying birds: they just kept shrinking and shrinking, for over 50 million years.
Today, in the journal Science, the researchers present a detailed family tree of dinosaurs and their ...
Innovative 'genotype first' approach uncovers protective factor for heart disease
2014-07-31
Cambridge, MA. Thurs. July 31, 2014 — Extensive sequencing of DNA from thousands of individuals in Finland has unearthed scores of mutations that destroy gene function and are found at unusually high frequencies. Among these are two mutations in a gene called LPA that may reduce a person's risk of heart disease. These findings are an exciting proof-of-concept for a new "genotype first" approach to identifying rare genetic variants associated with, or protecting from, disease followed by extensive medical review of carriers. The new study by researchers from the Broad Institute, ...
A mathematical theory proposed by Alan Turing in 1952 can explain the formation of fingers
2014-07-31
Alan Turing, the British mathematician (1912-1954), is famous for a number of breakthroughs, which altered the course of the 20th century. In 1936 he published a paper, which laid the foundation of computer science, providing the first formal concept of a computer algorithm. He next played a pivotal role in the Second World War, designing the machines which cracked the German military codes, enabling the Allies to defeat the Nazis in several crucial battles. And in the late 1940's he turned his attention to artificial intelligence and proposed a challenge, now called the ...
Nanostructured metal-oxide catalyst efficiently converts CO2 to methanol
2014-07-31
UPTON, NY-Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered a new catalytic system for converting carbon dioxide (CO2) to methanol-a key commodity used to create a wide range of industrial chemicals and fuels. With significantly higher activity than other catalysts now in use, the new system could make it easier to get normally unreactive CO2 to participate in these reactions.
"Developing an effective catalyst for synthesizing methanol from CO2 could greatly expand the use of this abundant gas as an economical feedstock," ...
Refocusing research into high-temperature superconductors
2014-07-31
Below a specific transition temperature superconductors transmit electrical current nearly loss-free. For the best of the so-called high-temperature superconductors, this temperature lies around -180 °C – a temperature that can be achieved by cooling with liquid nitrogen.
The location of atomic nuclei and binding electrons in a material is determined by its crystal structure. However, electrons additionally have an electromagnetic angular momentum, referred to as spin. When many spins become coupled in a material, electromagnetic disturbances with a preferential orientation ...
Study finds benefits to burning Flint Hills prairie in fall and winter
2014-07-31
MANHATTAN — Kansas State University researchers have completed a 20-year study that looks at the consequences of burning Flint Hills prairie at different times of the year. It finds that burning outside of the current late spring time frame has no measurable negative consequences for the prairie and, in fact, may have multiple benefits.
The study was conducted by Gene Towne, research associate and the Konza Prairie Biological Station fire chief, and Joseph Craine, research assistant professor, both in the Division of Biology. They recently published the study, "Ecological ...
Fermi satellite detects gamma-rays from exploding novae
2014-07-31
TEMPE, Ariz. - The Universe is home to a variety of exotic objects and beautiful phenomena, some of which can generate almost inconceivable amounts of energy. ASU Regents' Professor Sumner Starrfield is part of a team that used the Large Area Telescope (LAT) onboard NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope satellite to discover very high energy gamma rays (the most energetic form of light) being emitted by an exploding star. The surprising discovery dispels the long-held idea that classical nova explosions are not powerful enough to produce such high-energy radiation.
In ...
NASA sees Genevieve squeezed between 3 tropical systems
2014-07-31
The resurrected Tropical Depression Genevieve appears squeezed between three other developing areas of low pressure. Satellite data from NOAA and NASA continue to show a lot of tropical activity in the Eastern and Central Pacific Oceans on July 31.
NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland has been kept busy, providing visible and infrared satellite imagery of the Eastern and Central Pacific Oceans. The project uses data from NOAA's GOES-West and GOES-East satellites to create images and animations. All four systems were captured ...
[1] ... [3444]
[3445]
[3446]
[3447]
[3448]
[3449]
[3450]
[3451]
3452
[3453]
[3454]
[3455]
[3456]
[3457]
[3458]
[3459]
[3460]
... [8830]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.