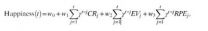A polypill strategy to improve global secondary cardiovascular prevention
2014-08-04
WASHINGTON (Aug. 4, 2014) — The polypill, a combination pill taken just once a day that includes key medications for secondary prevention of heart disease, may be an effective low-cost strategy to improve adherence to medication recommendations and reduce costs, according to researchers from Spain and New York, who reviewed research on the polypill.
The review article, A Polypill Strategy to Improve Global Secondary Cardiovascular Prevention, was published online today in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and will appear in the August 12, 2014 print issue. ...
Protective hinge process enables insulin to bind to cells
2014-08-04
CLEVELAND – August 4, 2014 – Since its landmark discovery in 1922, insulin has improved the health and extended the lives of more than 500 million people worldwide with diabetes mellitus. Yet the question of how this key hormone binds to its target cells in the body’s organs has posed an enduring scientific mystery. A global team of researchers from Cleveland, Australia, Chicago, India and Oregon has made a discovery about insulin and its structure that promises to enable design of new insulin products that will do a better job of regulating the metabolism of patients with ...
Blood-oxytocin levels in normal range in children with autism, study finds
2014-08-04
Autism does not appear to be solely caused by a deficiency of oxytocin, but the hormone's universal ability to boost social function may prove useful in treating a subset of children with the developmental disorder, according to new findings from the Stanford University School of Medicine and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital Stanford.
Low levels of oxytocin, a hormone involved in social functioning, have for years been suspected of causing autism. Prior research seeking a link has produced mixed results. Now, in the largest-ever study to test the purported connection, ...
Epidemic outbreaks caused by environment, not evolution
2014-08-04
Researchers have traced genetic changes in a bacterial pathogen over 450 years, and claim that epidemics of bacterial disease in human history may be caused by chance environmental changes rather than genetic mutations.
In a study published in PNAS, a team led by the University of Warwick analysed 149 genomes of Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi A, which is a major cause of enteric fever. Enteric fever is currently estimated at 27 million clinical cases each year, resulting in 200,000 deaths.
Lead author, Zhemin Zhou from Warwick Medical School, said: "When epidemics ...
Study traces evolutionary origins of migration in New World birds
2014-08-04
Every year, millions of birds make the journey from North America to Central and South America for the winter. But the evolutionary origins of this long-distance migration have remained opaque due to the complex geographic distributions of modern and ancient bird ranges.
Now, a team of scientists from the University of Chicago have developed a new method to reveal the ancestral ranges of New World birds, and discovered that bird migration in the Americas evolved in species that resided in North America. Their work also offers evidence that many tropical bird species descended ...
Learning how things fall apart
2014-08-04
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- Materials that are firmly bonded together with epoxy and other tough adhesives are ubiquitous in modern life — from crowns on teeth to modern composites used in construction. Yet it has proved remarkably difficult to study how these bonds fracture and fail, and how to make them more resistant to such failures.
Now researchers at MIT have found a way to study these bonding failures directly, revealing the crucial role of moisture in setting the stage for failure. Their findings are published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Science ...
Equation to predict happiness
2014-08-04
The happiness of over 18,000 people worldwide has been predicted by a mathematical equation developed by researchers at UCL, with results showing that moment-to-moment happiness reflects not just how well things are going, but whether things are going better than expected.
The new equation accurately predicts exactly how happy people will say they are from moment to moment based on recent events, such as the rewards they receive and the expectations they have during a decision-making task. Scientists found that overall wealth accumulated during the experiment was not ...
Model of viral lifecycle could help in finding a cure for hepatitis B
2014-08-04
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- A new technique for studying the lifecycle of the hepatitis B virus could help researchers develop a cure for the disease.
In a paper published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Sangeeta Bhatia of MIT and Charles Rice of Rockefeller University describe using microfabricated cell cultures to sustain hepatitis B virus in human liver cells, allowing them to study immune responses and drug treatments.
Around 400 million people worldwide are infected with the hepatitis B virus (HBV); of those, one-third will go on to develop ...
Weakness of leukemic stem cells discovered
2014-08-04
FRANKFURT. Despite improved therapy, only one out of every two adult patients survive acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). The mean survival time for this disease, which predominantly occurs in the elderly, is less than a year for patients over 65 years. It is assumed that leukaemic stem cells, which cannot be completely eliminated during treatment, are the origin of relapse. However, as has been discovered by a team of Frankfurt-based researchers, these cells do have a weakness: In the current edition of the high impact journal "Cancer Research", they report that the enzyme ...
Minuscule chips for NMR spectroscopy promise portability, parallelization
2014-08-04
Cambridge, Mass. – August 4, 2014 – A team of engineers at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), Schlumberger-Doll Research Center in Cambridge, Mass., and the University of Texas, Austin, have created a truly portable device for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
NMR spectroscopy is a technique that perturbs protons within a molecule to glean important clues about its structure. It can identify unknown substances, detect very slight variations in chemical composition, and measure how molecules interact, making it an essential tool ...
The evolution of migration
2014-08-04
Each year, millions of birds migrate thousands of miles between the locations where they breed and raise young, and the areas where they spend the winter. Each migration is a trip fraught with danger—many birds die before they reach their final destination. To scientists, long distance migration still holds many mysteries, one of which is: where did migration begin and how did it evolve? This question has long been a debated topic among scientists, but thanks to new research from Field Museum scientists, we may have an answer for one of the largest groups of migratory birds. ...
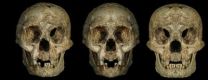
Flores bones show features of Down syndrome, not a new 'hobbit' human
2014-08-04
In October 2004, excavation of fragmentary skeletal remains from the island of Flores in Indonesia yielded what was called "the most important find in human evolution for 100 years." Its discoverers dubbed the find Homo floresiensis, a name suggesting a previously unknown species of human.
Now detailed reanalysis by an international team of researchers including Robert B. Eckhardt, professor of developmental genetics and evolution at Penn State, Maciej Henneberg, professor of anatomy and pathology at the University of Adelaide, and Kenneth Hsü, a Chinese geologist and ...
Triple therapy revs up immune system against common brain tumor
2014-08-04
A triple therapy for glioblastoma, including two types of immunotherapy and targeted radiation, has significantly prolonged the survival of mice with these brain cancers, according to a new report by scientists at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
Mice with implanted, mouse-derived glioblastoma cells lived an average of 67 days after the triple therapy, compared with mice that lasted 24 days when they received only the two immunotherapies. Half of the mice who received the triple therapy lived 100 days or more and were protected against further tumors when new cancer ...
African American professional women positive on medical research
2014-08-04
ROCHESTER, Minn. — If a research survey of African American professional women is any indication, attitudes may be changing towards participation in medical research. Mayo Clinic and The Links, Incorporated researchers teamed up to survey members of the international women's organization, and found that a majority of African American women surveyed are willing to or have taken part in medical research. The results appear in the Journal of Women's Health.
"Our findings are highly encouraging," says Sharonne Hayes, M.D., Mayo Clinic cardiologist, co-author of the study, ...
Fires in California and Oregon
2014-08-04
The Little Deer fire in California began as a lightning strike on July 31, 2014. Currently it has burned 4,700 acres and is 43% contained however there has been increased humidity over the fire the last 24 hours with shifting wind conditions. The threat of thunder storms today (08/04) and tomorrow (08/05) may cause an increase in fire activity.
The Beaver Complex is comprised of the Salt Creek Fire (20 miles northwest of Medford) and the Oregon Gulch Fire (15 miles east of Ashland), which are lightning-started fires that started on July 30-31, 2014. After it was first ...
Eiler and Bald Fires in California
2014-08-04
The Eiler wildfire which began on July 31, 2014, has almost consumed 26,000 acres. It is currently unknown as to the cause of this fire. The weather patterns currently around this fire do not bode well for a quick containment. Maximum temperatures are in the mid- to high 80's with 10-20% relative humidity. There is an unstable atmosphere at work along with thunderstorm chances which are increasingly today (08/04) through Wednesday (08/06). A Red Flag Warning in effect for dry lightning on Monday (08/04).
The Bald Fire began with a lightning strike on July 30, 2014. ...
Smoke from Canadian wildfires over Baffin Bay
2014-08-04
Canadian wildfires have been raging this summer and some of the smoke from those fires already drifted downward into the U.S. over the Great Lakes (see the image feature from July 25 below). In this image collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Aqua satellite on August 02, 2014 the large swath of smoke from these fires has taken a northward track and settled over the Bay of Baffin which borders Greenland.
To view the other Canadian fire images from July 2014:
Smoke from Canadian Fires Hovers Over Great Lakes - July 25, 2014
Smoke ...
Wildfires consume parts of eastern Russia
2014-08-04
Wildfires in far eastern Russia dot the landscape and what isn't covered by the fires is covered by the smoke that rises from these wildfires. This image taken by the Terra satellite shows the entire area covered with a blanket of heavy smoke coming off of dozens of wildfires that have broken out in the remote areas of Russia. Usually these fires are caused by lightning strikes that then consume the dry vegetation. With nothing to stop the spread, these fires take off and cover the landscape, especially during this time of year.INFORMATION:
NASA's Terra satellite collected ...
A hellacious two weeks on Jupiter's moon Io
2014-08-04
Three massive volcanic eruptions occurred on Jupiter's moon Io within a two-week period last August, leading astronomers to speculate that these presumed rare "outbursts," which can send material hundreds of miles above the surface, might be much more common than astronomers thought.
"We typically expect one huge outburst every one or two years, and they're usually not this bright," said Imke de Pater, professor and chair of astronomy at the University of California, Berkeley, and lead author of one of two papers describing the eruptions. "Here we had three extremely ...
Single-fraction RT as effective as multiple-fraction RT for palliation of bone metastases
2014-08-04
Fairfax, Va., August 4, 2014—Standardizing prescribing practices for single-fraction radiation therapy (SFRT) for palliation of bone metastases could lead to cost savings and improvement in patients' quality of life, according to a study published in the August 1, 2014 edition of the International Journal of Radiation Oncology • Biology • Physics (Red Journal), the official scientific journal of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
Bone metastases are a common manifestation of distant spread of disease, occurring most frequently with prostate, breast ...
How long does it take to make a natural fracture?
2014-08-04
Boulder, Colo., USA – How long does it take for natural Earth processes to form hydraulic fractures? Is the formation driven by sediment compaction, oil and gas generation, or something else? What role do these natural fractures play in modern hydraulic fracturing production? A new GSA BULLETIN study by András Fall and colleagues from The University of Texas at Austin, Virginia Tech, and ExxonMobil addresses these questions, and the article is open-access online.
The process of fracture formation by a natural increase in pore-fluid pressure has previously been referred ...
Bottling up sound waves
2014-08-04
There's a new wave of sound on the horizon carrying with it a broad scope of tantalizing potential applications, including advanced ultrasonic imaging and therapy, acoustic cloaking, and levitation and particle manipulation. Researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have developed a technique for generating acoustic bottles in open air that can bend the paths of sound waves along prescribed convex trajectories.
Sound waves move much like light waves. They travel on a straight path but this path - through ...
Extreme volcanism: Image captures 1 of the brightest volcanoes in the solar system
2014-08-04
During the middle of 2013, Jupiter's moon Io came alive with volcanism. Now, an image from the Gemini Observatory captures what is one of the brightest volcanoes ever seen in our solar system. The image, obtained on August 29, reveals the magnitude of the eruption that was the "grand finale" in a series of eruptions on the distant moon. Io's volcanism is caused by the tidal push-and-pull of massive Jupiter, which heats the satellite's interior – making it our Solar System's most volcanically active known body.
According to University of California Berkeley (UCB) astronomer ...
Earlier intervention for common form of heart attack linked to improved survival
2014-08-04
Changes in the treatment of the most common form of heart attack over the past decade have been associated with higher survival rates for men and women regardless of age, race and ethnicity, according to a UCLA-led analysis.
But the study also suggests that there is room for improvement in how current treatment guidelines are applied among specific patient groups.
The researchers reviewed records for 6.5 million people who were treated for heart attacks between 2002 and 2011. The analysis was among the first and largest national studies to assess the impact of the trend ...
Anorexia fueled by pride about weight loss
2014-08-04
Positive emotions – even those viewed through a distorted lens – may play an exacerbating role in fueling eating disorders like anorexia nervosa, which has a death rate 12 times higher for females between the ages of 15 and 24 than all other causes of death combined, according to a Rutgers study.
In research published in Clinical Psychological Science, Edward Selby, an assistant professor in the Department of Psychology, School of Arts and Sciences, measured over a two week period the emotional states of 118 women between the ages of 18-58 being treated for anorexia nervosa. ...
[1] ... [3437]
[3438]
[3439]
[3440]
[3441]
[3442]
[3443]
[3444]
3445
[3446]
[3447]
[3448]
[3449]
[3450]
[3451]
[3452]
[3453]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.