Offering option of initial HIV care at home increases use of ART
2014-07-19
LSTM Researchers found that offering adults in Malawi optional home initiation of care following HIV self-testing resulted in a significant increase in the proportion of adults initiating antiretroviral therapy (ART) compared with standard HIV care.
The results are part of a study that was funded by the Wellcome Trust and published in the July 23/30 issue of JAMA, which is HIV/AIDS themed and released early to coincide with the International AIDS Conference taking place in Melbourne, Australia next week.
In 2012 it was estimated that 35 million people worldwide were living ...
Hepatitis C cured in co-infected HIV patients
2014-07-19
A multicenter team of researchers report that in a phase III clinical trial, a combination drug therapy cures chronic hepatitis C in the majority of patients co-infected with both HIV and hepatitis C.
"In many settings, hepatitis C is now a leading cause of death among HIV co-infected patients," says Mark Sulkowski, M.D., medical director of the Johns Hopkins Infectious Disease Center for Viral Hepatitis and professor of medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. Approximately one-third of HIV patients in the United States have hepatitis C, with an estimated ...
Feinstein Institute researchers identify brain network
2014-07-19
Manhassett, NY – Investigators at The Feinstein Institute for Medical Research have utilized a new image-based strategy to identify and measure placebo effects in randomized clinical trials for brain disorders. The findings are published in the August issue of The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Parkinson's disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease in the US. Those who suffer from Parkinson's disease most often experience tremors, slowness of movement (bradykinesia), rigidity, and impaired balance and coordination. Patients may have difficulty walking, ...
Performance improvement program helps doctors better manage depression, reports journal of psychiatric practice
2014-07-18
A performance improvement initiative for physicians can significantly increase their use of evidence-based practices in screening for and treating depression, in the July Journal of Psychiatric Practice. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Led by Dr Michael E. Thase of the University of Pennsylvania Medical School, the researchers evaluated a performance improvement continuing medical education (PI CME) program to increase physicians' use of practices that have been shown to improve diagnosis and care for depression. ...
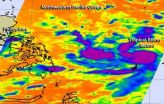
NASA sees powerful thunderstorms in Tropical Storm Matmo
2014-07-18
Strong thunderstorms reaching toward the top of the troposphere circled Tropical Storm Matmo's center and appeared in a band of thunderstorms on the storm's southwestern quadrant. Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite showed very cold temperatures that indicated the high cloud tops in the powerful storms.
Tropical cyclones consist of hundreds of thunderstorms. When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Storm Matmo on July 17 at 16:59 UTC (12:59 p.m. EDT) on July 17, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument obtained infrared data on the tropical cyclone. ...
High-dose fluticasone effective against eosinophilic esophagitis
2014-07-18
Results from a clinical trial show that high doses of the corticosteroid fluticasone propionate safely and effectively induce remission in many people with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), a chronic inflammatory disease of the esophagus characterized by high levels of white blood cells called eosinophils. However, some trial participants did not respond to fluticasone even after six months of high-dose treatments, providing evidence that certain people with EoE are steroid-resistant. By analyzing gene expression—the degree to which certain genes are turned on or off—in esophageal ...
Experts urge new discipline combining benefits of neuroscience and psychology treatments
2014-07-18
When a patient talks with a psychological therapist, what changes occur in the patient's brain that relieve mental disorders? UCLA psychology professor Michelle Craske says the honest answer is that we don't know. But, according to Craske and two colleagues, we need to find out.
Mental health disorders — such as depression, schizophrenia, post-traumatic stress disorder, obsessive–compulsive disorder and eating disorders — affect 1 in 4 people worldwide. Psychological treatments "hold the strongest evidence base for addressing many such conditions," but they need improvement, ...
Tea Party support linked to educational segregation, new study shows
2014-07-18
In January of 2009, Barack Obama assumed the U.S. presidency in the midst of the most severe recession since the great depression of the 1930s. While many Americans hoped the new administration would take an active role in providing relief for those harmed by the economic collapse, a "Tea Party" movement emerged to oppose Obama's agenda.
University of Notre Dame political sociologist Rory McVeigh, whose study, "Educational Segregation, Tea Party Organizations, and Battles over Distributive Justice," was recently published in the American Sociological Review, says "The ...
Yale researchers identify targets for immunotherapy in early-stage breast cancer
2014-07-18
July 17, 2014, New Haven, CT – Yale Cancer Center researchers used a new molecular analysis tool to accurately detect the level of an important target for immunotherapy in early-stage breast cancers. The diagnostic test, using RNAScope, measures the amount of PD-L1 (programmed death ligand 1) mRNA in routine formalin-fixed cancer tissues and is devoid of many of the technical issues that plague antibody-based detection methods that have yielded conflicting results in the past. PD-L1 is the target of several novel immune stimulatory therapies in clinical trials. The findings ...
Interleukin-10 aids survival of cells transplanted to repair cardiac tissues after MI
2014-07-18
Putnam Valley, NY. (July 18th 2014) – The long-term, positive benefits of transplanted allogenic (other-donated) smooth muscle cells (SMCs) to repair cardiac tissues after myocardial infarction (MI) have been enhanced by the addition of interleukin 10 (IL-10) to the transplanted cells, report researchers in Canada. Their study with rats modeled with MI has shown that SMCs modified with IL-10 - a small, anti-inflammatory protein - benefitted cell survival, improved heart function, and also provided protection against the host's rejection of the allogenic SMCs.
The study ...
Highly charged ions
2014-07-18
The world is mostly neutral. That is, most of the atoms in our environment are electrically neutral. The number of electrons in the outer parts of atoms equals the number of protons at the centers of atoms. As one or more electrons are plucked away from the atoms, the remaining electrons feel a much stronger positive pull from the nucleus. This enhanced pull, causing the atoms to shrink in size, ensures that those electrons are less vulnerable to the distractions of their environment, making them potentially valuable for next-generation atomic clocks, for quantum information ...
Economic development not the only influence on personal car use, study finds
2014-07-18
Although countries with high levels of economic development generally have more personal automobile travel than less-affluent nations, income is not the only factor that determines a nation's demand for cars, according to a new study.
Examining factors that may influence personal automobile use in developing nations, researchers found that government policies such as taxes that keep fuel costs high and the development of road systems can have important influence on levels of automobile travel.
Shaping the personal use of automobiles is an important issue in developing ...
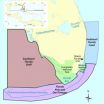
UM-led research team contributes to the management of South Florida coastal environments
2014-07-18
MIAMI – A Florida-based marine research team has developed a unique formal process and modeling framework to help manage South Florida's economically important coastal marine environments. The MARES project (Marine and Estuarine Goal Setting), led by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Cooperative Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Studies (CIMAS) based at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, successfully integrated both ecosystem science and societal benefits into a marine ecosystem support tool to ...
Scientists find new clues to brain's wiring
2014-07-18
New research provides an intriguing glimpse into the processes that establish connections between nerve cells in the brain. These connections, or synapses, allow nerve cells to transmit and process information involved in thinking and moving the body.
Reporting online in Neuron, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a group of proteins that program a common type of brain nerve cell to connect with another type of nerve cell in the brain.
The finding is an important step forward in efforts to learn how the developing brain ...
Measuring the number of protein molecules inside cells
2014-07-18
This news release is available in Portuguese. This news release is available in Portuguese.
The identification of the genes and proteins involved in a biological process, as well as the way they interact, are essential for the understanding of that process. However, often little is known about the dimensions of molecular biological structures. Knowing how many molecules make up a structure and are required for its function are essential for our understanding of biological mechanisms. Yet, quantifying molecules of infinitesimal size poses a difficult challenge. ...
Revealed: The mystery behind starling flocks
2014-07-18
The mystery behind the movements of flocking starlings could be explained by the areas of light and dark created as they fly, new research suggests.
The research, conducted by the University of Warwick and published in the journal PNAS, found that flocking starlings aim to maintain an optimum density at which they can gather data on their surroundings. This occurs when they can see light through the flock at many angles, a state known as marginal opacity. The subsequent pattern of light and dark, formed as the birds attempt to achieve the necessary density, is what provides ...
Adults with eosinophilic esophagitis should consider a diet change
2014-07-18
Bethesda, MD (July 18, 2014) — Dietary elimination is a successful method of treatment for adults with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), according to a new study1 in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association.
"By eliminating specific foods from patients' diets, symptoms improved in 71 percent of patients, and endoscopic appearance improved in 54 percent," said lead study author, W. Asher Wolf, MD, MPH, and co-author Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH, from the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, ...
Genetic variations may modify cardiovascular benefit of aspirin
2014-07-18
BOSTON – Aspirin is the gold standard for antiplatelet therapy and a daily low-dose aspirin is widely prescribed for the prevention of cardiovascular disease.
Now, a new study suggests that common genetic variation in the gene for catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) may modify the cardiovascular benefit of aspirin, and in some people, may confer slight harm. The findings, led by investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) appear online in the American Heart Association journal Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and ...
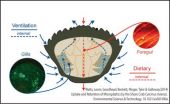
Microplastics worse for crabs and other marine life than previously thought, study shows
2014-07-18
The tiny plastic particles polluting our seas are not only orally ingested by marine creatures, but also enter their systems through their gills, according to a new study led by the University of Exeter.
Scientists also discovered that when microplastics are drawn in through this method they take over six times longer to leave the body compared with standard digestion.
Lead author Dr Andrew Watts of the University of Exeter said: "Many studies on microplastics only consider ingestion as a route of uptake into animals. The results we have just published stress other ...
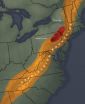
The bend in the Appalachian mountain chain is finally explained
2014-07-18
The 1500 mile Appalachian mountain chain runs along a nearly straight line from Alabama to Newfoundland—except for a curious bend in Pennsylvania and New York State. Researchers from the College of New Jersey and the University of Rochester now know what caused that bend—a dense, underground block of rigid, volcanic rock forced the chain to shift eastward as it was forming millions of years ago.
According to Cindy Ebinger, a professor of earth and environmental sciences at the University of Rochester, scientists had previously known about the volcanic rock structure under ...
Immune cell's role in intestinal movement may lead to better understanding of IBS
2014-07-18
Learning the role of immune-system cells in healthy digestive tracts and how they interact with neighboring nerve cells may lead to new treatments for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Researchers from Penn State College of Medicine, in collaboration with other scientists, have reported the role of macrophages in regulating the contractions of the colon to push digested material through the digestive tract.
The muscular lining of the intestine contains a distinct kind of macrophage, an immune system cell that helps fight infections. The role of these cells in normal colon ...
It's go time for LUX-Zeplin dark matter experiment
2014-07-18
New Haven, Conn. -- From the physics labs at Yale University to the bottom of a played-out gold mine in South Dakota, a new generation of dark matter experiments is ready to commence.
The U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science and the National Science Foundation recently gave the go-ahead to LUX-Zeplin (LZ), a key experiment in the hunt for dark matter, the invisible substance that may make up much of the universe. Daniel McKinsey, a professor of physics, leads a contingent of Yale scientists working on the project.
"We emerged from a very intense competition," ...
Improving driver safety: How to prevent streetlight glare in the new world of LED lighting
2014-07-18
WASHINGTON, July 18—Long hours of nighttime driving can cause eyestrain because while our vision adapts to the surrounding darkness, the sudden stabs of brightness from streetlamps can be irritating, distracting and even painful. Even as LED technology has transformed the lighting industry, bringing the promise of more energy-efficient road illumination, some fear that the new lights could cause even more troublesome, unsafe glare.
A team of researchers from China and the Netherlands has developed a way to evaluate the human impact of uncomfortable glare caused by LED ...
NASA sees super typhoon Rammasun eyeing landfall
2014-07-18
Imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite captured a wide-eyed Typhoon Rammasun as it was making landfall in northern Hainan Island, China early on July 18. A rainfall analysis using another NASA satellite showed the flooding potential of the storm as it left the Philippines and headed for China. Now, Rammasun is headed for a final landfall near the northeastern border of Vietnam and China.
On July 17, an analysis of Typhoon Rammasun's rainfall was conducted at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The rainfall analysis covered the storm's rainfall from ...
NASA satellite catches birth of Tropical Storm Wali near Hawaii
2014-07-18
The first tropical cyclone of the season has formed in the Central Pacific Ocean as NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead. Tropical Storm Wali formed southeast of the Big Island of Hawaii, and now that it's nearing, a Flash Flood Watch has been posted for all of the islands.
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Wali on July 17 at 19:55 UTC (3:55 p.m. EDT) just as it was being classified as Tropical Depression 1C. NOAA's Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) issued an advisory at 5 p.m. EDT (11 a.m. HST) announcing the birth of the depression near 12.7 north and 140.7 ...
[1] ... [3433]
[3434]
[3435]
[3436]
[3437]
[3438]
[3439]
[3440]
3441
[3442]
[3443]
[3444]
[3445]
[3446]
[3447]
[3448]
[3449]
... [8788]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.