Watching chemistry in motion: Chemical environments mapped using molecular vibrations
2014-08-05
Scientists have long known that a molecule's behavior depends on its environment. Taking advantage of this phenomenon, a group of researchers at the University of Chicago developed a new technique to map microscopic environments using the vibrations of molecules.
"It's a special new advance that will be broadly useful in studies of molecular and materials phenomena," said Andrei Tokmakoff, the Henry G. Gale Distinguished Service Professor in Chemistry at UChicago. He and two of his associates report their new technique in a paper published online in the journal Optics ...
Physicists eye neural fly data, find formula for Zipf's law
2014-08-05
Physicists have identified a mechanism that may help explain Zipf's law – a unique pattern of behavior found in disparate systems, including complex biological ones. The journal Physical Review Letters is publishing their mathematical models, which demonstrate how Zipf's law naturally arises when a sufficient number of units react to a hidden variable in a system.
"We've discovered a method that produces Zipf's law without fine-tuning and with very few assumptions," says Ilya Nemenman, a biophysicist at Emory University and one of the authors of the research.
The ...
'Treatments waiting to be discovered' inside new database
2014-08-05
Your genes are blueprints for proteins, and molecules called microRNA can help to determine how often these genetic blueprints are manufactured into proteins. Researchers often ask what microRNA regulates a gene related to disease. Or what gene is regulated by a microRNA found in sick patients? The answers to these questions could help doctors and researchers manipulate protein levels in the body that cause disease, especially cancer. A University of Colorado Cancer Center study recently published in the top-ranked journal Nucleic Acids Research (NAR) describes a database ...
Monthly preventative treatment with a new drug combination reduces malaria in children
2014-08-05
Preventative treatment with a monthly dose of a newer antimalarial drug can reduce the risk of malarial infection among young children, according to a study published in this week's PLOS Medicine. The study, conducted by Victor Bigira and colleagues at San Francisco General Hospital and the Makerere University College of Health Sciences in Kampala, Uganda, finds that treating young children with dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine (DP) decreased their risk of contracting malaria.
Preventative treatment of malaria is a useful strategy to protect young children in Africa, but ...
Pregnant women are often given inappropriate treatment for malaria
2014-08-05
Not all pregnant women with symptoms of malaria seek care from their formal healthcare system and if they do seek care, they may be given inappropriate treatment because healthcare providers often fail to adhere to the standard (World Health Organization-WHO) diagnostic and treatment guidelines, according to a study by UK researchers published in this week's PLOS Medicine.
The authors (led by Jenny Hill from the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine) reached these conclusions by reviewing all relevant studies that investigated the factors that affect pregnant women's ...
A campaign involving Muslim clerics has increased uptake of polio vaccination in Nigeria
2014-08-05
A coalition campaign involving imams, Islamic school teachers, traditional rulers, doctors, journalists, and polio survivors is gradually turning the tide against polio vaccine rejection in northern Nigeria, according to experts from Nigeria writing in this week's PLOS Medicine.
Sani-Gwarzo Nasir (from the Federal Ministry of Health in Nigeria) and colleagues describe how anti-polio propaganda, misconceptions, and violence against vaccinators present huge challenges to polio eradication in Nigeria but perhaps most profound is the rejection of vaccination by Muslim clerics.
However, ...
Just one simple question can identify narcissistic people
2014-08-05
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have developed and validated a new method to identify which people are narcissistic: just ask them.
In a series of 11 experiments involving more than 2,200 people of all ages, the researchers found they could reliably identify narcissistic people by asking them this exact question (including the note):
To what extent do you agree with this statement: "I am a narcissist." (Note: The word "narcissist" means egotistical, self-focused, and vain.)
Participants rated themselves on a scale of 1 (not very true of me) to 7 (very true of me).
(How ...
Salk scientists uncover new clues to repairing an injured spinal cord
2014-08-05
LA JOLLA—Frogs, dogs, whales, snails can all do it, but humans and primates can't. Regrow nerves after an injury, that is—while many animals have this ability, humans don't. But new research from the Salk Institute suggests that a small molecule may be able to convince damaged nerves to grow and effectively rewire circuits. Such a feat could eventually lead to therapies for the thousands of Americans with severe spinal cord injuries and paralysis.
"This research implies that we might be able to mimic neuronal repair processes that occur naturally in lower animals, which ...
Year-round preventive treatment reduces malaria risk in young children
2014-08-05
A year-round preventive drug treatment substantially reduces young children's risk of contracting malaria and poses no serious risk of adverse events, according to a study by researchers funded by the National Institutes of Health.
The findings demonstrate that prolonged treatment given from 6 to 24 months of age is safe and effective for young children, according to the study authors. Year-round preventive measures are badly needed in locations like Uganda, where the study took place, and where malaria rates remain high throughout the year.
Most previous studies using ...
How spiders spin silk
2014-08-05
Spider silk is an impressive material; lightweight and stretchy yet stronger than steel. But the challenge that spiders face to produce this substance is even more formidable. Silk proteins, called spidroins, must convert from a soluble form to solid fibers at ambient temperatures, with water as a solvent, and at high speed. How do spiders achieve this astounding feat? In new research publishing in the open access journal PLOS Biology on August 5, Anna Rising and Jan Johansson show how the silk formation process is regulated. The work was done at the Swedish University ...
In search for Alzheimer's drug, a major STEP forward
2014-08-05
Researchers at Yale School of Medicine have discovered a new drug compound that may help reverse the cognitive deficits of Alzheimer's disease. Their findings are publishing on August 5 in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
The compound, TC-2153, inhibits the negative effects of a protein called STriatal-Enriched tyrosine Phosphatase (STEP), which is key to regulating learning and memory. These cognitive functions are impaired in Alzheimer's.
"Decreasing STEP levels reversed the effects of Alzheimer's disease in mice," said lead author Paul Lombroso, M.D., professor ...
Pyruvate oxidation is critical determinant of pancreatic islet number and β-cell mass
2014-08-05
Researchers at the University at Buffalo, led by Dr. Mulchand Patel and also at Lawson Health Research Institute and Western Ontario, London, Canada, led by Dr. David Hill, collaboratively evaluated the role of the mitochondrial multienzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in the regulation of pancreatic β-cell development and maturation in the immediate postnatal period in mice. This study, reported in the August 2014 issue of Experimental Biology and Medicine, demonstrated that the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is not only required for insulin gene expression and ...
Butterflies change wing color in new Yale research
2014-08-05
Yale University scientists have chosen the most fleeting of mediums for their groundbreaking work on biomimicry: They've changed the color of butterfly wings.
In so doing, they produced the first structural color change in an animal by influencing evolution. The discovery may have implications for physicists and engineers trying to use evolutionary principles in the design of new materials and devices.
The research appears this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"What we did was to imagine a new target color for the wings of a butterfly, ...
Seamless gene correction of beta-thalassemia mutations in patient-specific cells
2014-08-05
August 5, 2014 – A major hurdle in gene therapy is the efficient integration of a corrected gene into a patient's genome without mutating off-target sites. In a paper published today in Genome Research, scientists have used CRISPR/Cas genome editing technology to seamlessly and efficiently correct disease-causing mutations in cells from patients with β-thalassemia.
β-thalassemia results from inherited DNA mutations in the hemoglobin beta (HBB) gene, resulting in reduced HBB expression in red blood cells and, in the most severe forms, anemia. The only established ...
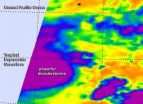
NASA sees Tropical Storm Julio as part of a heated Eastern Pacific
2014-08-05
The Eastern Pacific Ocean has been warm this springtime, and those warmer waters have contributed to the development of storms like Tropical Storm Julio and Hurricane Iselle.
"Ocean temperatures in the Eastern Tropical Pacific were heated up because of the strong Kelvin wave activity this spring. Although the initial excitement of an impending El Nino has quieted down, these warmer waters have caused an early and active hurricane season," said Bill Patzert, Climatologist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California.
"Kelvin waves" are massive ripples ...
Grizzly research offers surprising insights into diabetes-obesity link
2014-08-05
While diabetes rates are on the rise and are having serious effects on millions of people's health, researchers studying grizzly bears have now discovered a natural state of diabetes that serves a real biological purpose and is also reversible. Investigators reporting in the August 5 issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Metabolism note that grizzly bears are obese but not diabetic in the fall, become diabetic only weeks later in hibernation, and then somehow become "cured" of diabetes when they wake up in the spring. The research reveals how natural biology, through evolutionary ...
No apparent link between sleep apnea and cancer: Large study
2014-08-05
Obstructive sleep apnea, in which people stop breathing for short periods while sleeping, affects about 5% of Canadian adults aged 45 years or older and can negatively affect health. More than 1 in 5 adult Canadians have risk factors for sleep apnea such as being overweight, being male and having diabetes, chronic nasal congestion or other health conditions.
Studies have postulated that obstructive sleep apnea may be linked to cancer because of low levels of oxygen in the blood.
"There is a need for a sufficiently large cohort study with a long enough follow-up to allow ...
Common chemical in mothers may negatively affect the IQ of their unborn children
2014-08-05
(Boston) -- In some women abnormally high levels of a common and pervasive chemical may lead to adverse effects in their offspring. The study, published recently in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, is the first of its kind to shed light on the possible harmful side effects of perchlorate in mothers and their children.
Using data from the Controlled Antenatal Thyroid Study (CATS) cohort, researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) and Cardiff University studied the effect of perchlorate, an environmental contaminant found in many foods ...
Story tips from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory, August 2014
2014-08-05
To arrange for an interview with a researcher, please contact the Communications staff member identified at the end of each tip. For more information on ORNL and its research and development activities, please refer to one of our media contacts. If you have a general media-related question or comment, you can send it to news@ornl.gov.
MATERIALS – Transparent ballistic results …
Glass used for military vehicle windshields is being put to the test by an Oak Ridge National Laboratory team evaluating different formulations for mechanical strength, high pressure and shock ...
NASA sees bursts of thunderstorms in Tropical Depression Genevieve's center
2014-08-05
The AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite provided a look at what's happening under Tropical Depression Genevieve's clouds using infrared light, and it appears that thunderstorms are bubbling up again.
A false-colored infrared image created at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena California used data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite. The AIRS data showed powerful thunderstorms re-developed around Genevieve's center on August 5 at 8:35 a.m. EDT. That's an indication that there's some punch left ...
3-in-1 optical skin cancer probe
2014-08-05
WASHINGTON, D.C., August 5, 2014 – As thousands of vacationers hit the beach this summer, many of them will expose their unprotected bare limbs to direct UV sunlight, potentially putting them at risk of skin cancer later in life. To fight back, scientists can also turn to light, designing optical devices that may detect cancerous skin lesions early on, leading to better treatment outcomes and ultimately saving lives.
Researchers from the University of Texas at Austin's Cockrell School of Engineering have now developed a probe that combines into one device three unique ...
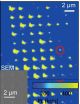
Diamond defect interior design
2014-08-05
WASHINGTON, D.C., August 5, 2014 – By carefully controlling the position of an atomic-scale diamond defect within a volume smaller than what some viruses would fill, researchers have cleared a path toward better quantum computers and nanoscale sensors. They describe their technique in a paper published in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing.
David Awschalom, a physicist at the Institute for Molecular Engineering at the University of Chicago, and his colleagues study a technologically useful diamond defect called a nitrogen vacancy (NV) center. NV ...
University of Minnesota researcher finds cooling effect in warming Arctic lakes
2014-08-05
Scientists have known for a while that warming global temperatures are causing Arctic lakes to release methane, a potent greenhouse gas that leads to even more warming. In a new study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers including U of M researcher Jacques Finlay, found that Siberian lakes have actually pulled more greenhouse gasses from the atmosphere than they have released into it since the last Ice Age, causing an overall slight cooling effect.
Permafrost, especially that in the Siberian Arctic, contains significant amounts of all organic carbon ...
UH Case Medical Center study validates new approach to high blood pressure
2014-08-05
CLEVELAND – It truly could be mind over matter after all.
University Hospitals Case Medical Center's Richard Josephson, MD, recently released trial results in a study published in Psychosomatic Medicine that discusses mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) for hypertension.
Nearly 60 million adults in the United States have high blood pressure in the pre-hypertensive range. Current treatment guidelines recommend lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise and overall weight loss.
According to the new study, these changes can be dramatically augmented by MBSR as the ...
The interaction of climate change, fire, and forests in the US
2014-08-05
A special section of the September issue of Forest Ecology and Management, available online now, assesses the interactions among fire, climate change, and forests for five major regions of the United States.
The editors of the section—Drs. Chelcy Miniat from the U.S. Forest Service, Monique Rocca from Colorado State University, and Robert Mitchell (now deceased) from the Joseph W. Jones Ecological Research Center—started the project by organizing teams of scientists from the Forest Service and universities to provide scientific input into the third National Climate ...
[1] ... [3434]
[3435]
[3436]
[3437]
[3438]
[3439]
[3440]
[3441]
3442
[3443]
[3444]
[3445]
[3446]
[3447]
[3448]
[3449]
[3450]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.