New trick for 'old' drug brings hope for pancreatic cancer patients
2014-08-04
Cancer Research UK scientists have found a new use for an old drug by showing that it shrinks a particular type of pancreatic cancer tumour and stops it spreading, according to research published in Gut*.
"It's a crucial step forward in developing new treatments for this devastating disease..." - Dr Jennifer Morton, study author
The scientists, at the Cancer Research UK Beatson Institute and the University of Glasgow, treated mice with pancreatic cancers caused by known genetic faults with the drug rapamycin**.
Previous clinical trials did not find this drug to be ...
Primary care telephone triage does not save money or reduce practice workload
2014-08-04
Demand for general practice appointments is rising rapidly, and in an attempt to deal with this, many practices have introduced systems of telephone triage. Patients are phoned by a doctor or nurse who either manages the problem on the phone, or agrees with the patient whether and how urgently they need to be seen.
A new large study, published in The Lancet on 4 August 2014 and funded by the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), has investigated the potential value of telephone triage for patients and for the NHS. It concluded that patients who receive a telephone ...
Tumor suppressor mutations alone don't explain deadly cancer
2014-08-03
Although mutations in a gene dubbed "the guardian of the genome" are widely recognized as being associated with more aggressive forms of cancer, researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have found evidence suggesting that the deleterious health effects of the mutated gene may in large part be due to other genetic abnormalities, at least in squamous cell head and neck cancers.
The study, published online August 3 in the journal Nature Genetics, shows that high mortality rates among head and neck cancer patients tend to occur only when mutations ...
Atlantic warming turbocharges Pacific trade winds
2014-08-03
New research has found rapid warming of the Atlantic Ocean, likely caused by global warming, has turbocharged Pacific Equatorial trade winds. Currently the winds are at a level never before seen on observed records, which extend back to the 1860s.
The increase in these winds has caused eastern tropical Pacific cooling, amplified the Californian drought, accelerated sea level rise three times faster than the global average in the Western Pacific and has slowed the rise of global average surface temperatures since 2001.
It may even be responsible for making El Nino events ...
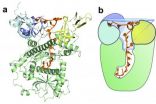
Uncovering the 3-D structure of a key neuroreceptor
2014-08-03
Neurons are the cells of our brain, spinal cord, and overall nervous system. They form complex networks to communicate with each other through electrical signals that are carried by chemicals. These chemicals bind to structures on the surface of neurons that are called neuroreceptors, opening or closing electrical pathways that allow transmission of the signal from neuron to neuron. One neuroreceptor, called 5HT3-R, is involved in conditions like chemotherapy-induced nausea, anxiety, and various neurological disorders such as schizophrenia. Despite its clinical importance, ...
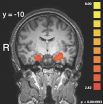
Fault trumps gruesome evidence when it comes to punishment
2014-08-03
Issues of crime and punishment, vengeance and justice date back to the dawn of human history, but it is only in the last few years that scientists have begun exploring the basic nature of the complex neural processes in the brain that underlie these fundamental behaviors.
Now a new brain imaging study – published online Aug. 3 by the journal Nature Neuroscience – has identified the brain mechanisms that underlie our judgment of how severely a person who has harmed another should be punished. Specifically, the study determined how the area of the brain that determines ...
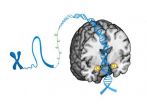
Small DNA modifications predict brain's threat response
2014-08-03
DURHAM, N.C. -- The tiny addition of a chemical mark atop a gene that is well known for its involvement in clinical depression and posttraumatic stress disorder can affect the way a person's brain responds to threats, according to a new study by Duke University researchers.
The results, which appear online August 3 in Nature Neuroscience, go beyond genetics to help explain why some individuals may be more vulnerable than others to stress and stress-related psychiatric disorders.
The study focused on the serotonin transporter, a molecule that regulates the amount of ...
Knowing what to keep and what to trash: How an enzyme distinguishes cellular messages
2014-08-03
Cold Spring Harbor, NY – Every once in a while, we are forced to sort that stack of papers on the kitchen counter. Interspersed between the expired coupons and dozens of takeout menus are important documents like your car insurance or electric bill. So it isn't an option to simply drop it all in the trash at once – you need to read through the messages to be sure that you don't lose vital information.
In the cell, proteins similarly read through messages to distinguish what needs to be saved and what needs to be discarded. But, here, the process takes on a much more ...
Atlantic origin of recent Pacific trade wind, sea level and temperature trends
2014-08-03
An Australian–US team of climate researchers has solved a puzzle that has challenged scientists for over a decade. Climate models predict that the equatorial Pacific trades should weaken with increasing greenhouse gases. Yet, since the early 1990s, satellites and climate stations reveal a rapid and unprecedented strengthening of the Pacific trade winds, accelerating sea level rise in the western Pacific and impacting both Pacific and global climate.
"The answer to the puzzle is that recent rapid Atlantic Ocean warming has affected climate in the Pacific," say the scientists. ...
Self-assembling anti-cancer molecules created in minutes
2014-08-03
Researchers have developed a simple and versatile method for making artificial anti-cancer molecules that mimic the properties of one of the body's natural defence systems.
The chemists, led by Professor Peter Scott at the University of Warwick, UK, have been able to produce molecules that have a similar structure to peptides which are naturally produced in the body to fight cancer and infection.
Published in Nature Chemistry, the molecules produced in the research have proved effective against colon cancer cells in laboratory tests, in collaboration with Roger Phillips ...
Study finds new genetic risk markers in pancreatic cancer
2014-08-03
BOSTON –– A large DNA analysis of people with and without pancreatic cancer has identified several new genetic markers that signal increased risk of developing the highly lethal disease, report scientists from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.
The markers are variations in the inherited DNA code at particular locations along chromosomes. Several of these variations in the DNA code were identified that influence an individual's risk for pancreatic cancer.
The discovery of these markers – along with four that were previously identified is important for several reasons, said ...
Rare developmental disorder linked to tumor-suppressing protein, Stanford researchers find
2014-08-03
CHARGE, which affects 1 in 10,000 babies, is an acronym whose letters stand for some of the more common symptoms of the condition: coloboma of the eye, heart defects, atresia of the choanae, retardation of growth and/or development, genital and/or urinary abnormalities, and ear abnormalities and deafness.
Originally, the researchers were examining the tumor-suppressive properties of the protein, called p53, not investigating developmental disorders. But when a mouse model developed a strange set of deficiencies, the researchers followed a trail of clues that led them ...
UMD researchers develop tool to better visualize, analyze human genomic data
2014-08-03
Scientists at the University of Maryland have developed a new, web-based tool that enables researchers to quickly and easily visualize and compare large amounts of genomic information resulting from high-throughput sequencing experiments. The free tool, called Epiviz, was described in a paper published online on August 3, 2014 in the journal Nature Methods.
Next-generation sequencing has revolutionized functional genomics. These techniques are key to understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying cell function in healthy and diseased individuals and the development ...
Making sense of scents
2014-08-03
For many animals, making sense of the clutter of sensory stimuli is often a matter or literal life or death.
Exactly how animals separate objects of interest, such as food sources or the scent of predators, from background information, however, remains largely unknown. Even the extent to which animals can make such distinctions, and how differences between scents might affect the process were largely a mystery – until now.
A new study, described in an August 3 paper in Nature Neuroscience, a team of researchers led by Venkatesh Murthy, Professor of Molecular and Cellular ...
Clues to curbing obesity found in neuronal 'sweet spot'
2014-08-02
New Haven, Conn. -- Preventing weight gain, obesity, and ultimately diabetes could be as simple as keeping a nuclear receptor from being activated in a small part of the brain, according to a new study by Yale School of Medicine researchers.
Published in the Aug. 1 issue of The Journal of Clinical Investigation (JCI), the study showed that when the researchers blocked the effects of the nuclear receptor PPARgamma in a small number of brain cells in mice, the animals ate less and became resistant to a high-fat diet.
“These animals ate fat and sugar, and did not gain ...
Pepper and halt: Spicy chemical may inhibit gut tumors
2014-08-02
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine report that dietary capsaicin – the active ingredient in chili peppers – produces chronic activation of a receptor on cells lining the intestines of mice, triggering a reaction that ultimately reduces the risk of colorectal tumors.
The findings are published in the August 1, 2014 issue of The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The receptor or ion channel, called TRPV1, was originally discovered in sensory neurons, where it acts as a sentinel for heat, acidity and spicy chemicals in the environment. ...
Study reveals one reason brain tumors are more common in men
2014-08-02
New research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis helps explain why brain tumors occur more often in males and frequently are more harmful than similar tumors in females. For example, glioblastomas, the most common malignant brain tumors, are diagnosed twice as often in males, who suffer greater cognitive impairments than females and do not survive as long.
The researchers found that retinoblastoma protein (RB), a protein known to reduce cancer risk, is significantly less active in male brain cells than in female brain cells.
The study appears Aug. ...
Understanding how neurons regulate metabolism in response to a high-fat diet
2014-08-02
The brain plays a central role in regulating appetite and whole-body metabolism. A protein known as PPARγ is important in the brain's control of food intake and body weight, but the identity of the neurons regulating this process has been unclear. A new study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation demonstrates that PPARγ activity in a type of neuron known as pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons is critical in mediating the response to high-fat diet. Sabrina Diano and colleagues at Yale University School of Medicine found that mice lacking PPARγ specifically ...
New research characterizes in-flight pediatric deaths
2014-08-01
CLEVELAND, Ohio – In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers at University Hospitals Rainbow Babies & Children's Hospital (UH Rainbow) found that lap infants may be at greater risk for death on a commercial airline flight. The study analyzed pediatric medical emergencies on flights worldwide between January 2010 and June 2013 and found 90 percent of deaths occurred in children under the age of 2.
The study was conducted in partnership with MedAire to characterize the rare event of an in-flight pediatric fatality onboard commercial airline flights worldwide. Through a ...
Best evidence yet for coronal heating theory detected by NASA sounding rocket
2014-08-01
VIDEO:
NASA's EUNIS sounding rocket mission spotted evidence to explain why the sun's atmosphere is so much hotter than its surface.
Click here for more information.
Scientists have recently gathered some of the strongest evidence to date to explain what makes the sun's outer atmosphere so much hotter than its surface. The new observations of the small-scale extremely hot temperatures are consistent with only one current theory: something called nanoflares – a constant ...
Scientists solve 2,000-year-old mystery of the binding media in China's polychrome Terracotta Army
2014-08-01
Even as he conquered rival kingdoms to create the first united Chinese empire in 221 B.C., China's First Emperor Qin Shihuang ordered the building of a glorious underground palace complex, mirroring his imperial capital near present-day Xi'an, that would last for an eternity.
To protect his underworld palaces, the First Emperor issued instructions that his imperial guard be replicated, down to the finest details, in red-brown terracotta clay, poised to do battle. Thousands of these imperial guards were initially discovered in 1974; some contained patches of pigment that ...
Advances in assisted reproduction create more options and new legal issues for LGBT couples
2014-08-01
New Rochelle, NY, August 1, 2014—Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender individuals who want to conceive a child may face the same problems as some of their heterosexual and cisgendered peers, such as reduced fertility, but in addition they often face additional physiological and legal challenges to become parents. A comprehensive review of the most recent advances in assisted reproduction options is presented in the article "LGBT Assisted Reproduction: Current Practice and Future Possibilities," published in LGBT Health, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, ...
On-chip topological light
2014-08-01
Topological transport of light is the photonic analog of topological electron flow in certain semiconductors. In the electron case, the current flows around the edge of the material but not through the bulk. It is "topological" in that even if electrons encounter impurities in the material the electrons will continue to flow without losing energy.
In the photonic equivalent, light flows not through and around a regular material but in a meta-material consisting of an array of tiny glass loops fabricated on a silicon substrate. If the loops are engineered just right, ...
Expressive writing may help breast cancer survivors
2014-08-01
Writing down fears, emotions and the benefits of a cancer diagnosis may improve health outcomes for Asian-American breast cancer survivors, according to a study conducted by a researcher at the University of Houston (UH).
"The key to developing an expressive writing intervention is the writing instruction. Otherwise, writing is just like a journal recording facts and events. Writing a journal can be therapeutic, but oftentimes we don't get the empirical evidence to determine whether it's effective or not," said Qian Lu, assistant professor and director of the Culture ...
Mapping the optimal route between two quantum states
2014-08-01
As a quantum state collapses from a quantum superposition to a classical state or a different superposition, it will follow a path known as a quantum trajectory. For each start and end state there is an optimal or "most likely" path, but it is not as easy to predict the path or track it experimentally as a straight-line between two points would be in our everyday, classical world.
In a new paper featured on the July 30 cover of Nature, scientists from the Institute for Quantum Studies at Chapman University, the University of Rochester, University of California at Berkeley, ...
[1] ... [3441]
[3442]
[3443]
[3444]
[3445]
[3446]
[3447]
[3448]
3449
[3450]
[3451]
[3452]
[3453]
[3454]
[3455]
[3456]
[3457]
... [8830]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.