Singing the same tune: Scientists develop novel ways of separating birdsong sources
2014-07-31
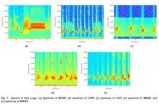
Researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles and the Chinese Academy of Sciences have pioneered a new study that could greatly improve current methods of localising birdsong data. Their findings, which ascertain the validity of using statistical algorithms to detect multiple-source signals in real time and in three-dimensional space, are of especial significance to modern warfare.
Recently published in the journal Unmanned Systems, the study demonstrates the validity of using approximate maximum likelihood (AML) algorithms to determine the direction of arrival ...
Gulf oil spill researcher: Bacteria ate some toxins, but worst remain
2014-07-31
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — A Florida State University researcher found that bacteria in the Gulf of Mexico consumed many of the toxic components of the oil released during the Deepwater Horizon spill in the months after the spill, but not the most toxic contaminants.
In two new studies conducted in a deep sea plume, Assistant Professor Olivia Mason found a species of bacteria called Colwellia likely consumed gaseous hydrocarbons and perhaps benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene compounds that were released as part of the oil spill.
But, her research also showed that bacteria ...
Hope for the overweight
2014-07-31
White, brown and beige adipocytes, or fat cells, are inherently different. Each of these cell types has different functions and each plays its own role in metabolism. In the human body, white adipose tissue is by far the most prevalent. Its primary function is energy storage. On the other hand, brown adipocytes utilize available energy to generate heat but are only found in a few places in the adult human body. Beige adipocytes, which represent a special type of brown adipocytes, appear mixed with brown adipocytes in human brown adipose tissue or develop within the white ...
Privileged strategies for direct transformations of inert aliphatic carbon-hydrogen bonds
2014-07-31
Functional group transformations are central to organic synthesis. Traditionally, the functionalities used in such transformations are highly active organic groups such as halogens, ester groups and hydroxyl groups. Carbon–hydrogen bonds are ubiquitous structural motifs in organic compounds, but they are not considered to be functional groups because (1) in general, the bond dissociation energy of a C–H bond is high, and therefore, such bonds are thermodynamically hard to break; and (2) the selective activation of one C–H bond among many similar and different C–H bonds ...
Neutron tomography technique reveals phase fractions of crystalline materials in 3-dimensions
2014-07-31
The method overcomes limitations of existing techniques which are limited to the surface or small-sized specimens, and allows a 3-D representation of the phase fractions within the sample volume. The work has just been published in the journal "Advanced Materials".
"For many engineering applications it is of major importance to characterize the bulk of materials spatially, instead of only probing selected locations. The new method provides exactly that capability, and the HZB-UTK team has demonstrated it by using samples made from stainless steel that undergo a phase ...
Vision-correcting electronic displays could let users dispense with glasses
2014-07-31
Researchers at the MIT Media Laboratory and the University of California at Berkeley have developed a new display technology that automatically corrects for vision defects — no glasses (or contact lenses) required.
The technique could lead to dashboard-mounted GPS displays that farsighted drivers can consult without putting their glasses on, or electronic readers that eliminate the need for reading glasses, among other applications.
"The first spectacles were invented in the 13th century," says Gordon Wetzstein, a research scientist at the Media Lab and one of the display's ...
Vacuum treatment may limit damage after traumatic brain injury
2014-07-31
July 31, 2014 – Controlled application of vacuum pressure is a promising approach to limiting tissue damage after traumatic brain injury (TBI), suggests an experimental study in the August issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
"Mechanical tissue resuscitation"—consisting of vacuum pressure applied over the injured area of the brain—shows promise as a safe and effective treatment for TBI, according to the research report by Dr. Louis ...
UT Dallas study reveals effect of loud noises on brain
2014-07-31
Prolonged exposure to loud noise alters how the brain processes speech, potentially increasing the difficulty in distinguishing speech sounds, according to neuroscientists at The University of Texas at Dallas.
In a paper published this week in Ear and Hearing, researchers demonstrated for the first time how noise-induced hearing loss affects the brain's recognition of speech sounds.
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) reaches all corners of the population, affecting an estimated 15 percent of Americans between the ages of 20 and 69, according to the National Institute ...
Monoamine oxidase A: Biomarker for postpartum depression
2014-07-31
This news release is available in German.
Many women suffer from baby blues after giving birth. Some even develop full-blown postpartum depression in the weeks that follow. Monoamine oxidase A, an enzyme responsible for the breakdown of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, plays an important role in this condition. In comparison to healthy women, women who experience postpartum depression present strongly elevated levels of the enzyme in their brains. This was discovered by a Canadian-German research team including Julia Sacher from the Max Planck Institute ...
Research reveals pervasive implicit hierarchies for race, religion, and age
2014-07-31
As much as social equality is advocated in the United States, a new study suggests that besides evaluating their own race and religion most favorably, people share implicit hierarchies for racial, religious, and age groups that may be different from their conscious, explicit attitudes and values.
The study findings appear in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"People from relatively low-status groups can readily report that their group does not have the most power. At the same time, most groups, even if they have less social ...
Key to aging immune system is discovered
2014-07-31
There's a good reason people over 60 are not donor candidates for bone marrow transplantation. The immune system ages and weakens with time, making the elderly prone to life-threatening infection and other maladies, and a UC San Francisco research team now has discovered a reason why.
"We have found the cellular mechanism responsible for the inability of blood-forming cells to maintain blood production over time in an old organism, and have identified molecular defects that could be restored for rejuvenation therapies," said Emmanuelle Passegué, PhD, a professor of medicine ...
Researchers at SGH and Duke-NUS a step closer to finding treatment for dengue fever
2014-07-31
There have been several news reports that the world's first dengue vaccine will be available next year. However, the latest clinical trials show that the vaccine only provides a protection of around 50 per cent for DENV-2 and DENV-1, which are commonly found in Singapore.
DENV-1 accounts for 90 per cent of infections locally as a large population lacks the immunity against this particular dengue virus serotype. Until a vaccine that can offer higher protection becomes available, it is crucial to find a suitable treatment for dengue fever, as there is presently none available ...
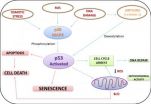
Senescence in adipose-derived stem cells and its implications in nerve regeneration
2014-07-31
Adult mesenchymal stem cells, specifically adipose-derived stem cells have self-renewal and multiple differentiation potentials and have shown to be the ideal candidate for therapeutic applications in regenerative medicine, particularly in peripheral nerve regeneration. Adipose-derived stem cells are easily harvested, although they may show the effects of aging, hence their potential in nerve repair may be limited by cellular senescence or donor age. Cellular senescence is a complex process whereby stem cells grow old as consequence of intrinsic events (e.g., DNA damage) ...
A new way to generate insulin-producing cells in Type 1 diabetes
2014-07-31
VIDEO:
Researchers discover a simple peptide that can induce new beta-cell formation in the pancreas. The findings show promise for a new approach to treating Type 1 diabetes.
Click here for more information.
La Jolla, Calif., July 31, 2014 -- A new study by researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham) has found that a peptide called caerulein can convert existing cells in the pancreas into those cells destroyed in type 1 diabetes-insulin-producing ...
Researchers uncover cause of gum disease related to type 2 diabetes
2014-07-31
Going to the dentist isn't fun for anyone, but for those with periodontal disease related to type 2 diabetes, a new research discovery may have them smiling. In a report appearing in the August 2014 issue of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology, one of the most important blood cells involved in the human immune response, B cells, are shown to promote inflammation and bone loss in type 2 diabetes-associated periodontal disease. These findings support the idea that treatments that manipulate the responses of B cells may treat or prevent this complication.
"Our study identified ...
Breakthrough in understanding of important blood protein
2014-07-31
The human body contains a unique protein that has the unusual property of destroying itself after a few hours of existence - it must therefore be continually recreated and is no stable protein. The protein, called PAI-1, affects many physiological functions, including the dissolving of coagulated blood. If you get a blood clot, it is due to the fact that the a clot has accumulated in a blood vessel, and therefore PAI-1 is extremely important – for the human body's survival in general and for helping people with a blood clot or other blood diseases in which coagulation plays ...
Common drugs adversely impair older adults' physical as well as cognitive functioning
2014-07-31
INDIANAPOLIS -- A class of medications previously linked to cognitive impairment in older adults also appears to negatively affect their physical functioning according to investigators from the Regenstrief Institute, the Indiana University Center for Aging Research, the University of East Anglia and several other United Kingdom institutions.
In a systemic review of more than a decade of studies on the effects of drugs with anticholinergic properties, they report that these drugs have a significant adverse effect on both cognitive and physical functioning, including the ...
Research finds numerous unknown jets from young stars and planetary nebulae
2014-07-31
For many years astronomers have known that young 'protostars' drive supersonic jets of gas from their north and south poles. However, this is the first time that so many of them have been detected at once.
The results come from a five year survey undertaken with the UK Infra-Red Telescope and are expected to prompt significant changes in the understanding of the planetary nebulae population in the Galaxy, as well as the properties of jets ejected from young forming stars.
By examining images of excited hydrogen molecules at infrared wavelengths, scientists have been ...
The Rim Fire 1 year later: A natural experiment in fire ecology and management
2014-07-31
The enormous conflagration known as the Rim Fire was in full fury, raging swiftly from crown to crown among mature trees, when it entered the backcountry of Yosemite National Park in California's Sierra Nevada in late August 2013. But inside the park, the battle began to turn, enacting a case study in the way management decisions and drought can combine to fuel large, severe fires.
"When the Rim Fire hit the park, it eventually encountered lands where fire had been used as a management tool, rather than immediately suppressed," said Hugh Safford, a regional ecologist ...
Congressional rift over environment influences public
2014-07-31
American citizens are increasingly divided over the issue of environmental protection and seem to be taking their cue primarily from Congress, finds new research led by a Michigan State University scholar.
The gap between conservatives who oppose environmental protection and liberals who support it has risen drastically in the past 20 years, a trend seen among lawmakers, activists and – as the study indicates – the general public as well, said sociologist Aaron M. McCright.
The findings echo a June 12 Pew Research Center poll showing that, in general, Republicans and ...
Surgeons report significant migraine relief from cosmetic eyelid surgery technique
2014-07-31
New Orleans, LA – Dr. Oren Tessler, Assistant Professor of Clinical Surgery at LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans School of Medicine, is part of a team of plastic and reconstructive surgeons who report a high success rate using a method to screen and select patients for a specific surgical migraine treatment technique. More than 90% of the patients who underwent this surgery to decompress the nerves that trigger migraines experienced relief and also got a bonus cosmetic eyelid surgery. The study, which confirms the benefit of surgical treatment for migraines and expands ...
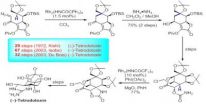
Chemists demonstrate 'bricks-and-mortar' assembly of new molecular structures
2014-07-31
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- Chemists at Indiana University Bloomington have described the self-assembly of large, symmetrical molecules in bricks-and-mortar fashion, a development with potential value for the field of organic electronic devices such as field-effect transistors and photovoltaic cells.
Their paper, "Anion-Induced Dimerization of 5-fold Symmetric Cyanostars in 3D Crystalline Solids and 2D Self-Assembled Crystals," has been published online by Chemical Communications, a journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry. It is the first collaboration by Amar Flood, the James ...
Women in military less likely to drink than civilian women
2014-07-31
Los Angeles, CA (August 1, 2014) While it is known that members of the U.S. military overall are more likely to use alcohol, a new study finds that female enlistees and female veterans are actually less likely to drink than their civilian counterparts. This study was published today in Armed Forces & Society, a SAGE journal published on behalf of the Inter-University Seminar on Armed Forces and Society.
Researchers Jay Teachman, Carter Anderson, and Lucky Tedrow studied surveys of nearly 9,000 men and women who were currently members of the U.S. military or who were military ...
U-M researchers find protein that fuels repair of treatment-resistant cancer cells
2014-07-31
ANN ARBOR—Imagine you're fighting for your life but no matter how hard you hit, your opponent won't go down.
The same can be said of highly treatment-resistant cancers, such as head and neck cancer, where during radiation and chemotherapy some cancer cells repair themselves, survive and thrive. Head and neck cancer is the sixth most common cancer in the world, but the late detection and treatment resistance result in a high mortality rate.
Now, University of Michigan researchers have found that a particular protein—TRIP13—encourages those cancer cells to repair themselves. ...
Boat noise impacts development and survival of sea hares
2014-07-31
While previous studies have shown that marine noise can affect animal movement and communication, with unknown ecological consequences, scientists from the Universities of Bristol and Exeter and the École Pratique des Hautes Études (EPHE) CRIOBE in France have demonstrated that boat noise stops embryonic development and increases larval mortality in sea hares.
Sea hares, (specifically the sea slug Stylocheilus striatus used in this study) usually hatch from their eggs to swim away and later feed on toxic alga but this study, conducted in a coral reef lagoon in French ...
[1] ... [3447]
[3448]
[3449]
[3450]
[3451]
[3452]
[3453]
[3454]
3455
[3456]
[3457]
[3458]
[3459]
[3460]
[3461]
[3462]
[3463]
... [8830]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.