NUS study shows effectiveness of common anti-malarial drug in controlling asthma
2014-08-01
Asthmatic patients may soon have a more effective way to control the condition, thanks to a new pharmacological discovery by researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS).
The team, led by Associate Professor Fred Wong from the Department of Pharmacology at the NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, together with Dr Eugene Ho Wanxing, a recent PhD graduate from the Saw Swee Hock School of Public Health at NUS, discovered that artesunate, a common herbal-based anti-malarial drug, can be used to control asthma, with better treatment outcomes than other drugs ...
Preterm children do not have an increased risk for dyscalculia
2014-08-01
Preterm children do not suffer from dyscalculia more often than healthy full term children. Dr Julia Jäkel, a developmental psychologist from Bochum, and her colleague Prof Dr Dieter Wolke from the University of Warwick, UK proved this thesis to be true in their analyses – thus refuting previous scientific studies. Unlike other studies, the researchers took the children's IQ into consideration.
Dyscalculia in preterm children often impossible to diagnose
Preterm children often have cognitive deficits; they find solving complex tasks particularly difficult. However, ...
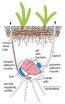
Scientists solve 2000-year-old mystery of the binding media in China's polychrome Terracotta Army
2014-08-01
Even as he conquered rival kingdoms to create the first united Chinese empire in 221 B.C., China's First Emperor Qin Shihuang ordered the building of a glorious underground palace complex, mirroring his imperial capital near present-day Xi'an, that would last for an eternity.
To protect his underworld palaces, the First Emperor issued instructions that his imperial guard be replicated, down to the finest details, in red-brown terracotta clay, poised to do battle. Thousands of these imperial guards were initially discovered in 1974; some contained patches of pigment that ...
Taking the guesswork out of cancer therapy
2014-08-01
Researchers and doctors at the Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN), Singapore General Hospital (SGH) and National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS) have co-developed the first molecular test kit that can predict treatment and survival outcomes in kidney cancer patients. This breakthrough was recently reported in European Urology, the world's top urology journal.
According to IBN Executive Director Professor Jackie Y. Ying, "By combining our expertise in molecular diagnostics and cancer research, we have developed the first genetic test to help doctors prescribe ...
Georgia Tech jailbreaks iOS 7.1.2
2014-08-01
Security researchers at the Georgia Tech Information Security Center (GTISC) have discovered a way to jailbreak current generation Apple iOS devices (e.g., iPhones and iPads) running the latest iOS software.
The jailbreak, which enables circumvention of Apple's closed platform, was discovered by analyzing previously patched vulnerabilities with incomplete fixes.
It shows that quick workarounds mitigating only a subset of a multi-step attack leave these devices vulnerable to exploitation. Patching all vulnerabilities for a modern, complex software system (i.e., Windows ...
Symbiotic survival
2014-08-01
Boulder, Colo., USA – One of the most diverse families in the ocean today -- marine bivalve mollusks known as Lucinidae (or lucinids) -- originated more than 400 million years ago in the Silurian period, with adaptations and life habits like those of its modern members. This Geology study by Steven Stanley of the University of Hawaii, published online on 25 July 2014, tracks the remarkable evolutionary expansion of the lucinids through significant symbiotic relationships.
At is origin, the Lucinidae family remained at very low diversity until the rise of mangroves and ...
Companion planets can increase old worlds' chance at life
2014-08-01
Having a companion in old age is good for people — and, it turns out, might extend the chance for life on certain Earth-sized planets in the cosmos as well.
Planets cool as they age. Over time their molten cores solidify and inner heat-generating activity dwindles, becoming less able to keep the world habitable by regulating carbon dioxide to prevent runaway heating or cooling.
But astronomers at the University of Washington and the University of Arizona have found that for certain planets about the size of our own, the gravitational pull of an outer companion planet ...
Jailed family member increases risks for kids' adult health
2014-08-01
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — New research shows that people who grew up in a household where a member was incarcerated have a 16-percent greater risk of experiencing poor health quality than adults who did not have a family member sent to prison. The finding, which accounted for other forms of childhood adversity, suggests that the nation's high rate of imprisonment may be independently imparting enduring physical and mental health difficulties in some families.
"These people were children when this happened, and it was a significant disruptive event," said Annie ...
2014 ESC/ESA Guidelines on non-cardiac surgery: Cardiovascular assessment and management
2014-08-01
The publication of the new joint ESC/ESA Guidelines on non-cardiac surgery: cardiovascular assessment and management introduces a number of recommendations in the field. Among other topics, the Guidelines include updated information on the use of clinical indices and biomarkers in risk assessment, and the use of novel anticoagulants, statins, aspirin and beta-blockers in risk mitigation.
Worldwide, non-cardiac surgery is associated with an average overall complication rate of between 7% and 11% and a mortality rate between 0.8% and 1.5%, depending on safety precautions. ...
Chemists develop MRI technique for peeking inside battery-like devices
2014-08-01
A team of chemists from New York University and the University of Cambridge has developed a method for examining the inner workings of battery-like devices called supercapacitors, which can be charged up extremely quickly and can deliver high electrical power. Their technique, based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), establishes a means for monitoring and potentially enhancing the performance of such devices.
The work, which appears in the latest issue of the journal Nature Communications, focuses on electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs), a type of so-called supercapacitor. ...
Management of anticoagulant-associated intracerebral hemorrhage
2014-08-01
Charlottesville, VA (August 1, 2014). The Journal of Neurosurgery is pleased to announce today's publication of a supplement to the August issue entitled "Race Against the Clock: Overcoming Challenges in the Management of Anticoagulant-Associated Intracerebral Hemorrhage." Authored by Peter Le Roux, MD, Charles V. Pollack, Jr., MA, MD, Melissa Milan, MD, and Alisa Schaefer, PhD, the 20-page supplement covers the current knowledge of anticoagulant-associated intracerebral hemorrhage (AAICH) and methods in use for management of the condition. Provided by Paradigm Medical ...
Scientists warn time to stop drilling in the dark
2014-08-01
The co-authors of a new study, including two Simon Fraser University research associates, cite new reasons why scientists, industry representatives and policymakers must collaborate closely on minimizing damage to the natural world from shale gas development. Viorel Popescu and Maureen Ryan, David H. Smith Conservation Research Fellows in SFU's Biological Sciences department, are among eight international co-authors of the newly published research in Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment.
Shale gas development is the extraction of natural gas from shale formations ...
Female baby boomers with asthma? You may need help
2014-08-01
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (August 1, 2014) – Women over the age of 65 face numerous barriers to good health: an increased risk for obesity, greater struggles against poverty and higher rates of asthma with worse health outcomes. An article published in the August issue of Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the scientific publication of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), outlines the challenges faced by older women in treating asthma, and offers practical solutions to improve their care.
"Allergists want older women to understand that ...
New guidelines help keep asthma out of 'yellow zone'
2014-08-01
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (August 1, 2014) – If you have asthma, you may have an asthma action plan with a "stoplight system" to help you recognize and respond to changes and understand when symptoms are getting worse and need more attention. If you're in the green zone, you're doing well, yellow means your asthma has worsened and action is needed, and red means you require urgent care. New guidelines are now available to help your allergist steer you out of the yellow zone, back into green and away from the red zone.
"Management of acute loss of asthma control in the ...
Recent use of some birth control pills may increase breast cancer risk
2014-08-01
PHILADELPHIA — Women who recently used birth control pills containing high-dose estrogen and a few other formulations had an increased risk for breast cancer, whereas women using some other formulations did not, according to data published in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Our results suggest that use of contemporary oral contraceptives [birth control pills] in the past year is associated with an increased breast cancer risk relative to never or former oral contraceptive use, and that this risk may vary by oral contraceptive ...
Light pulses control graphene's electrical behavior
2014-08-01
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- Graphene, an ultrathin form of carbon with exceptional electrical, optical, and mechanical properties, has become a focus of research on a variety of potential uses. Now researchers at MIT have found a way to control how the material conducts electricity by using extremely short light pulses, which could enable its use as a broadband light detector.
The new findings are published in the journal Physical Review Letters, in a paper by graduate student Alex Frenzel, Nuh Gedik, and three others.
The researchers found that by controlling the concentration ...
'Fracking' in the dark: Biological fallout of shale-gas production still largely unknown
2014-08-01
In the United States, natural-gas production from shale rock has increased by more than 700 percent since 2007. Yet scientists still do not fully understand the industry's effects on nature and wildlife, according to a report in the journal Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment.
As gas extraction continues to vastly outpace scientific examination, a team of eight conservation biologists from various organizations and institutions, including Princeton University, concluded that determining the environmental impact of gas-drilling sites — such as chemical contamination ...
For bats and dolphins, hearing gene prestin adapted for echolocation
2014-08-01
A little over a decade ago, prestin was found to be a key gene responsible for hearing in mammals. Prestin makes a protein found in the hair cells of the inner ear that contracts and expands rapidly to transmit signals that help the cochlea, like an antique phonograph horn, amplify sound waves to make hearing more sensitivity.
Now, in a new study published in the advanced online edition of Molecular Biology and Evolution, Peng Shi, et al., have shown that prestin has also independently evolved to play a critical role in the ultrasonic hearing range of animal sonar, ...
Scientist underlines threat of inevitable 'solar super-storms'
2014-08-01
In this month's issue of Physics World, Ashley Dale from the University of Bristol warns of the "catastrophic" and "long-lasting" impacts of "solar super-storms" and the dangers we face if the threat continues to go unnoticed.
Dale, who was a member of an international task force – dubbed SolarMAX – set up to identify the risks of a solar storm and how its impact could be minimized, explains how it is only a matter of time before an exceptionally violent solar storm is propelled towards Earth. Such a storm would wreak havoc with our communication systems and power supplies, ...
Harmful drinkers would be affected 200 times more than low risk drinkers with an MUP
2014-08-01
A new study of liver patients by the University of Southampton shows that a Minimum Unit Price (MUP) policy for alcohol is exquisitely targeted towards the heaviest drinkers with cirrhosis.
Published today in Clinical Medicine, the peer review journal for the Royal College of Physicians, the researchers studied the amount and type of alcohol drunk by 404 liver patients, and also asked patients how much they paid for alcohol. They found that patients with alcohol related cirrhosis were drinking on average the equivalent of four bottles of vodka each week, and were buying ...
Depressive symptoms and pain may affect health outcomes in dialysis patients
2014-08-01
Washington, DC (July 31, 2014) — Depressive symptoms and pain in patients on dialysis may have serious negative consequences for patients' health and increase the need for costly medical services, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (CJASN). The findings indicate that studies should evaluate the potential of anti-depressant and analgesic therapies to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs.
Depressive symptoms and pain are common in kidney failure patients receiving chronic hemodialysis, but ...
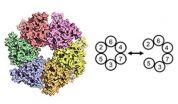
Molecular gate that could keep cancer cells locked up
2014-08-01
In a study published today in Genes & Development, Dr Christian Speck from the MRC Clinical Sciences Centre's DNA Replication group, in collaboration with Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL), New York, reveal the intricate mechanisms involved in the enzyme that governs DNA duplication during cell division. By developing a sophisticated system using synthetic, chemical and structural biology approaches, the study reveals how a key enzyme involved in duplicating genetic information embraces DNA through a gated system, which opens up at precise positions allowing for a highly ...
SwRI-led team's research shows giant asteroids battered early Earth
2014-08-01
San Antonio — July 31, 2014 — A new terrestrial bombardment model developed by an international group of scientists led by Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) indicates that Earth's surface was heavily reprocessed — or melted, mixed and buried — as a result of giant asteroid impacts more than four billion years ago.
The model, calibrated using existing lunar and terrestrial data, sheds light on the role asteroid collisions played in the geological evolution of the uppermost layers of Earth during the geologic eon call the "Hadean," or first geologic eon, approximately ...
Blood and saliva tests help predict return of HPV-linked oral cancers
2014-07-31
Physicians at Johns Hopkins have developed blood and saliva tests that help accurately predict recurrences of HPV-linked oral cancers in a substantial number of patients. The tests screen for DNA fragments of the human papillomavirus (HPV) shed from cancer cells lingering in the mouth or other parts of the body. A description of the development is published in the July 31 issue of JAMA Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery.
"There is a window of opportunity in the year after initial therapy to take an aggressive approach to spotting recurrences and intensively addressing ...
Study of twins discovers gene mutation linked to short sleep duration
2014-07-31
DARIEN, IL – Researchers who studied 100 twin pairs have identified a gene mutation that may allow the carrier to function normally on less than six hours of sleep per night. The genetic variant also appears to provide greater resistance to the effects of sleep deprivation.
Results show that a participant with p.Tyr362His – a variant of the BHLHE41 gene – had an average nightly sleep duration of only five hours, which was more than one hour shorter than the non-carrier twin, who slept for about six hours and five minutes per night. The twin with the gene mutation also ...
[1] ... [3443]
[3444]
[3445]
[3446]
[3447]
[3448]
[3449]
[3450]
3451
[3452]
[3453]
[3454]
[3455]
[3456]
[3457]
[3458]
[3459]
... [8830]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.