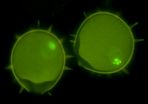
Smoking during pregnancy may raise risk for heart defects in babies
2014-05-03
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA – Women who smoke during pregnancy may be putting their newborns at risk for congenital heart defects, and the more they smoke, the higher the risk, according to a study to be presented Saturday, May 3, at the Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) annual meeting in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada.
Cigarette smoking during pregnancy has been linked to many birth defects, such as cleft lips and palates, and missing and deformed limbs. Some studies also suggest maternal smoking may be associated with heart defects.
The authors of this study ...
Study shows lower verbal test score for toddlers who play non-educational games on touch screens
2014-05-03
VANCOUVER, BC --A recent study by pediatricians from the Cohen Children's Medical Center of New York examined infants 0-3 years old that used touch-screen devices to determine if their use was of any educational benefit to infants and toddlers. The study showed that children who played non-educational games using touch-screen devices had lower verbal scores upon testing.
The results also showed that although the majority of parents cited in the study believed their children received educational benefits by using smart phones, readers and tablets, there ...
Nearly 50 percent of M.D.s believe diversion of ADHD stimulant medications among teens is a problem
2014-05-03
VANCOUVER, BC – Two recent studies by investigators at the Cohen Children's Medical Center of New York examined physicians' perceptions and knowledge of diversion of stimulant medications for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) as well as practices physicians use to prevent diversion among their patients prescribed these medications.
The results showed that while almost half of all physicians surveyed believe diversion is common among teens with ADHD, the majority never received training on the topic. Furthermore, about one-third of physicians rarely counsel ...
UN targets on health risk factors can prevent 37 million deaths by 2025
2014-05-03
Reaching globally-agreed targets for health risks such as smoking and alcohol can prevent more than 37 million deaths by 2025.
A new international study led by Imperial College London has estimated how achieving globally-agreed targets for six important health risks between 2010 and 2025 will reduce deaths caused by the big-four chronic diseases: cancers, diabetes, lung disease and cardiovascular disease (mainly heart disease and stroke).
Published in The Lancet the study finds that achieving the targets can prevent over 37 million deaths from these diseases by 2025. ...
The Lancet: Reducing just 6 risk factors could prevent 37 million deaths from chronic diseases over 15 years
2014-05-03
Reducing or curbing just six modifiable risk factors—tobacco use, harmful alcohol use, salt intake, high blood pressure and blood sugar, and obesity—to globally-agreed target levels could prevent more than 37 million premature deaths over 15 years, from the four main non-communicable diseases (NCDs; cardiovascular diseases, chronic respiratory disease, cancers, and diabetes) according to new research published in The Lancet.
Worryingly, the findings indicate that not reaching these targets would result in 38.8 million deaths in 2025 from the four main NCDs, 10.5 million ...
Leaf chewing links insect diversity in modern and ancient forests
2014-05-03
Observations of insects and their feeding marks on leaves in modern forests confirm indications from fossil leaf deposits that the diversity of chewing damage relates directly to diversity of the insect population that created it, according to an international team of researchers.
"The direct link between richness of leaf-chewing insects and their feeding damage across host plants in two tropical forests validates the underlying assumptions of many paleobiological studies that rely on damage-type richness as a means to infer changes in relative herbivore richness through ...
Salk scientists reveal circuitry of fundamental motor circuit
2014-05-02
LA JOLLA—Scientists at the Salk Institute have discovered the developmental source for a key type of neuron that allows animals to walk, a finding that could help pave the way for new therapies for spinal cord injuries or other motor impairments related to disease.
The spinal cord contains a network of neurons that are able to operate largely in an autonomous manner, thus allowing animals to carry out simple rhythmic walking movements with minimal attention—giving us the ability, for example, to walk while talking on the phone. These circuits control properties such as ...
Which came first, bi- or tricellular pollen? New research updates a classic debate
2014-05-02
With the bursting of spring, pollen is in the air. Most of the pollen that is likely tickling your nose and making your eyes water is being dispersed in a sexually immature state consisting of only two cells (a body cell and a reproductive cell) and is not yet fertile. While the majority of angiosperm species disperse their pollen in this early, bicellular, stage of sexual maturity, about 30% of flowering plants disperse their pollen in a more mature fertile stage, consisting of three cells (a body and two sperm cells). And then there are plants that do both.
So which ...
Researchers find unique fore wing folding among Sub-Saharan African Ensign wasps
2014-05-02
Researchers discovered several possibly threatened new species of ensign wasps from Sub-Saharan Africa -- the first known insects to exhibit transverse folding of the fore wing. The scientists made this discovery, in part, using a technique they developed that provides broadly accessible anatomy descriptions.
"Ensign wasps are predators of cockroach eggs, and the transverse folding exhibited by these species may enable them to protect their wings while developing inside the cramped environment of cockroach egg cases," said Andy Deans, associate professor of entomology, ...
Probing dopant distribution
2014-05-02
The icing on the cake for semiconductor nanocrystals that provide a non-damped optoelectronic effect may exist as a layer of tin that segregates near the surface.
One method of altering the electrical properties of a semiconductor is by introducing impurities called dopants. A team led by Delia Milliron, a chemist at Berkeley Lab's Molecular Foundry, a U.S Department of Energy (DOE) national nanoscience center, has demonstrated that equally important as the amount of dopant is how the dopant is distributed on the surface and throughout the material. This opens the door ...
Drinking poses greater risk for advanced liver disease in HIV/hep C patients
2014-05-02
PHILADELPHIA—Consumption of alcohol has long been associated with an increased risk of advanced liver fibrosis, but a new study published online in Clinical Infectious Diseases from researchers at Penn Medicine and other institutions shows that association is drastically heightened in people co-infected with both HIV and chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Even light ("nonhazardous") drinking—which typically poses a relatively low risk for uninfected persons—was linked to an increased risk of liver fibrosis in the co-infected group.
Reasons for this are not fully ...
Space Station research shows that hardy little space travelers could colonize Mars
2014-05-02
In the movies, humans often fear invaders from Mars. These days, scientists are more concerned about invaders to Mars, in the form of micro-organisms from Earth. Three recent scientific papers examined the risks of interplanetary exchange of organisms using research from the International Space Station. All three, Survival of Rock-Colonizing Organisms After 1.5 Years in Outer Space, Resistance of Bacterial Endospores to Outer Space for Planetary Protection Purposes and Survival of Bacillus pumilus Spores for a Prolonged Period of Time in Real Space Conditions, have appeared ...
Story tips from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory, May 2014
2014-05-02
To arrange for an interview with a researcher, please contact the Communications staff member identified at the end of each tip. For more information on ORNL and its research and development activities, please refer to one of our media contacts. If you have a general media-related question or comment, you can send it to news@ornl.gov.
DIESELS – Reducing soot . . .
Nine U.S. diesel engine manufacturers and Oak Ridge National Laboratory are using their collective horsepower to tackle the perennial industry-wide problem of efficiency-robbing soot in engines. Over time, ...
Vanderbilt study explores genetics behind Alzheimer's resiliency
2014-05-02
Autopsies have revealed that some individuals develop the cellular changes indicative of Alzheimer's disease without ever showing clinical symptoms in their lifetime.
Vanderbilt University Medical Center memory researchers have discovered a potential genetic variant in these asymptomatic individuals that may make brains more resilient against Alzheimer's.
"Most Alzheimer's research is searching for genes that predict the disease, but we're taking a different approach. We're looking for genes that predict who among those with Alzheimer's pathology will actually show ...
Researchers find way to decrease chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
2014-05-02
ATLANTA--Inhibiting enzymes that cause changes in gene expression could decrease chemotherapy resistance in ovarian cancer patients, researchers at Georgia State University and the University of Georgia say.
Dr. Susanna Greer, associate professor of biology, and research partners at the University of Georgia have identified two enzymes that suppress proteins that are important for regulating cell survival and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. Their findings are published in the journal, PLOS ONE.
Ovarian cancer is one of the deadliest gynecological cancers, with a ...
A transcription factor called SLUG helps determines type of breast cancer
2014-05-02
Findings and Significance: During breast-tissue development, a transcription factor called SLUG plays a role in regulating stem cell function and determines whether breast cells will mature into luminal or basal cells.
Studying factors, such as SLUG, that regulate stem-cell activity and breast-cell identity are important for understanding how breast tumors arise and develop into different subtypes. Ultimately, this knowledge may help the development of novel therapies targeted to specific breast-tumor subtypes.
Background: Stem cells are immature cells that can differentiate, ...
Key protein, FABP5, enhances memory and learning
2014-05-02
Case Western Reserve researchers have discovered that a protein previously implicated in disease plays such a positive role in learning and memory that it may someday contribute to cures of cognitive impairments. The findings regarding the potential virtues of fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5) — usually associated with cancer and psoriasis — appear in the May 2 edition of The Journal of Biological Chemistry.
"Overall, our data show that FABP5 enhances cognitive function and that FABP5 deficiency impairs learning and memory functions in the brain hippocampus region," ...
Better sleep predicts longer survival time for women with advanced breast cancer
2014-05-02
DARIEN, IL – A new study reports that sleep efficiency, a ratio of time asleep to time spent in bed, is predictive of survival time for women with advanced breast cancer.
Results show that higher sleep efficiency was significantly associated with lower mortality over the ensuing six years, an effect that remained after adjusting for baseline prognostic factors such as age, estrogen receptor status and treatments received. Mean survival was 68.9 months for efficient sleepers compared with 33.2 months for participants with poor sleep efficiency. Further analysis found that ...
How bacteria exploit proteins to trigger potentially lethal infections
2014-05-02
New research by scientists at the University of York sheds light on how bacteria exploit human proteins during infections.
A research team led by Professor Jennifer Potts, a British Heart Foundation Senior Research Fellow in York's Department of Biology, studied how Staphylococcus aureus, which can cause life-threatening human infections, attach to two proteins fibronectin and fibrinogen found in human blood.
The human proteins play important roles in clot formation and wound healing and the bacteria appear to exploit them during the process of infection.
Scientists ...
Element 117 discovered by Lawrence Livermore one step closer to being named
2014-05-02
Element 117, first discovered by Lawrence Livermore scientists and international collaborators in 2002, is one step closer to being named.
The existence of element 117 and its decay chain to elements 115 and 113 have been confirmed by a second international team led by scientists at GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research, an accelerator laboratory located in Darmstadt, Germany. The research will appear in an upcoming issue of the journal, Physical Review Letters.
The next step is for the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) to accept the confirmation. ...
Study shows link between sleep apnea and hospital maternal deaths
2014-05-02
Tampa, FL (May 2, 2014) -- Pregnant women with obstructive sleep apnea are more than five times as likely to die in the hospital than those without the sleep disorder, a comprehensive national study by the University of South Florida researchers found.
Among delivery-related hospital discharges, sleep apnea was also associated with an increase in severe medical conditions that are top causes of maternal death, including preeclampsia, eclampsia, an enlarged heart and pulmonary blood clots, reported the study published online this month in the journal SLEEP.
Sleep apnea ...
The Lancet: UK has one of the highest death rates for children in western Europe
2014-05-02
The UK has one of the highest rates of death for children under five in western Europe [1], according to new research published in The Lancet.
The findings come from a new study coordinated by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington, Seattle, USA. Their figures provide a comprehensive new analysis of global progress towards reducing child mortality.
Although, by international standards, the UK has very low rates of deaths in children, the figures show that within western Europe, the UK has a higher rate of deaths in children ...
Novel analyses improve identification of cancer-associated genes from microarray data
2014-05-02
Dartmouth Institute for Quantitative Biomedical Sciences (iQBS) researchers developed a new gene expression analysis approach for identifying cancer genes. The paper entitled, "How to get the most from microarray data: advice from reverse genomics," was published online March 21, 2014 in BMC Genomics. The study results challenge the current paradigm of microarray data analysis and suggest that the new method may improve identification of cancer-associated genes.
Typical microarray-based gene expression analyses compare gene expression in adjacent normal and cancerous ...
Stem cells from some infertile men form germ cells when transplanted into mice, study finds
2014-05-02
STANFORD, Calif. — Stem cells made from the skin of adult, infertile men yield primordial germ cells — cells that normally become sperm — when transplanted into the reproductive system of mice, according to researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine and Montana State University.
The infertile men in the study each had a type of genetic mutation that prevented them from making mature sperm — a condition called azoospermia. The research suggests that the men with azoospermia may have had germ cells at some point in their early lives, but lost them as they ...
The Lancet Psychiatry: Reliance on voluntary sector support for suicide bereavement 'unsustainable and inappropriate'
2014-05-02
People bereaved by the suicide of a partner and mothers losing an adult child to suicide run a significantly higher risk of suicide compared to people bereaved after sudden deaths from other causes. The psychological impact on other members of the family is also serious: children who lose a mother to suicide have an increased risk of depression, while people who lose a child to suicide have an increased likelihood of psychiatric admission for mental illness.
The findings come from a new Review, published to coincide with the launch of The Lancet Psychiatry journal, reviewing ...
[1] ... [3643]
[3644]
[3645]
[3646]
[3647]
[3648]
[3649]
[3650]
3651
[3652]
[3653]
[3654]
[3655]
[3656]
[3657]
[3658]
[3659]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.