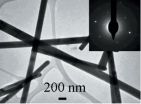
Nanosheets and nanowires
2014-04-01
Researchers in China, [J. Appl. Cryst. (2014). 47, 527-531] have found a convenient way to selectively prepare germanium sulfide nanostructures, including nanosheets and nanowires, that are more active than their bulk counterparts and could open the way to lower cost and safer optoelectronics, solar energy conversion and faster computer circuitry.
Germanium monosulfide, GeS, is emerging as one of the most important "IV–VI" semiconductor materials with potential in opto-electronics applications for telecommunications and computing, and as an absorber of light for use ...
New discovery gives hope that nerves could be repaired after spinal cord injury
2014-04-01
A new discovery suggests it could one day be possible to chemically reprogram and repair damaged nerves after spinal cord injury or brain trauma.
Researchers from Imperial College London and the Hertie Institute, University of Tuebingen have identified a possible mechanism for re-growing damaged nerve fibres in the central nervous system (CNS). This damage is currently irreparable, often leaving those who suffer spinal cord injury, stroke or brain trauma with serious impairments like loss of sensation and permanent paralysis.
Published in Nature Communications today, ...
Neuromonitoring with pulse-train stimulation for implantation of thoracic pedicle screws
2014-04-01
Charlottesville, VA (April 1, 2014). Researchers from Syracuse, New York, report a new, highly accurate, neuromonitoring method that can be used during thoracic spine surgery to prevent malpositioning of pedicle screws such that they enter the spinal canal and possibly cause postoperative neurological impairment. Findings of this prospective, blinded, and randomized study are reported and discussed in two companion papers published today online, ahead of print, in the Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine, specifically "Neuromonitoring with pulse-train stimulation for implantation ...
Child support in Tennessee paternity actions
2014-04-01
Child support in Tennessee paternity actions
Article provided by Autry L. Jones, Attorney at Law
Visit us at http://www.autryjones.com
Tennessee law recognizes that both parents have legal duties to financially support their child, so when two parents do not live together, the law allows a Tennessee court to order child support. Child support arrangements usually involve one parent -- the one with whom the child does not live (or lives less) --paying money monthly to the custodial parent to help with the child's living expenses.
While people think of child support ...
Medical marijuana bill progresses through Florida legislature
2014-04-01
Medical marijuana bill progresses through Florida legislature
Article provided by Stanley E. Peacock, P.A.
Visit us at http://www.stanpeacocklaw.com
While a handful states have already decriminalized the recreational use of marijuana, others are still debating whether to approve the drug for medical purposes, including Florida. However, if one particular piece of Florida legislation eventually becomes law, medical marijuana may become a reality in the Sunshine State.
Recently, House Bill 843 passed a Florida House Appropriations Committee by a vote of 24-0; meaning ...
Special rules for workers over age 50 who apply for disability benefits
2014-04-01
Special rules for workers over age 50 who apply for disability benefits
Article provided by Law Offices of Judith S. Leland, APLC
Visit us at http://www.disabilitylawfirm.com
According to the Social Security Administration, more than 25 percent of today's 20-year-olds will be put out of work by a disabling condition before reaching the age of 67. A disability becomes more likely as workers age and their bodies become less resistant to injury and illness.
Fortunately, for qualifying disabled workers who have paid enough into the system, compensation may be available ...
Male military spouses more likely to face divorce, but may lack support
2014-04-01
Male military spouses more likely to face divorce, but may lack support
Article provided by Anthony C. Williams & Associates, PC
Visit us at http://www.anthonywilliamslaw.com
Today, women account for 15 percent of active duty U.S. military personnel. Married female armed service members are far more likely to divorce than their male counterparts. According to the Defense Department, the overall divorce rate in the military among both men and women was 3.4 percent in fiscal year 2013. But, 7.2 percent of women in the military reported a divorce during fiscal year ...
Norman Dovichi of Notre Dame to speak at Bioanalytical Sensors Mtg, May 22-23, 2014, Cambridge, MA.
2014-04-01
Norman Dovichi, Grace-Rupley Professor at the University of Notre Dame, to give a presentation titled "Zone Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry at the zeptomole level," at the Inaugural Bioanalytical Sensors Conference, May 22 & 23, 2014 in Cambridge, MA.
Norman Dovichi received his BSc degree in Chemistry and Applied Mathematics from Northern Illinois University and his PhD in Analytical Chemistry from the University of Utah. He played a pioneering role in single molecule detection by laser-induced fluorescence. That experience led to the development of a high-throughput ...
Warriors Crowned CIHL Champions with RBC Asia Cup Victory
2014-04-01
The AsiaXPAT Kowloon Warriors have won their second CIHL championship title, with a 6-5 victory over the RBC South China Sharks in the final game of the 2013-2014 season. The Warriors, who entered the playoffs in last place but on a five-game winning streak, hoisted the RBC Asia Cup as the team became the first team to win two CIHL titles in Hong Kong's first full-contact elite ice hockey league.
With the Warriors, who also won the title in the 2011-2012 season, facing off against the Sharks, the 2012-2013 champions, it was sure to be a thrilling game at Mega Ice in ...
Calvert Holdings, Inc. Announces Executive Management Changes
2014-04-01
Calvert Holdings, Inc. announced that Michael A. Recny, Ph.D., has been appointed Chief Executive Officer and has been elected a Director of the Company. He replaces Russ McLauchlan, who will become Executive Chairman and who will also now head the newly formed Executive Committee of Calvert Holdings, which will include Dr. Recny, Allan Reiss, President of Calvert Holdings, Inc., and Charles Spainhour, DVM, Ph.D, the Company's Chief Scientific Officer. Dr. Recny will also continue to serve as President of Calvert Research, LLC, which is the investment arm of Calvert Holdings.
Of ...
National Love Our Children Day is Saturday, April 5th
2014-04-01
Love Our Children USA announces the 11th annual National Love Our Children Day. National Love Our Children Day is an initiative of Love Our Children USA, and is celebrated annually across the country on the first Saturday of every April to honor children, strengthen families and raise awareness for efforts to protect children.
National Love Our Children Day is like Mother's and Father's Day for children. This special day was created to acknowledge the value of children and to educate parents on the importance of giving them love, protection and respect, the three essential ...
Sweet Cheeks All Natural Bath & Body Launches Indiegogo Campaign
2014-04-01
Sweet Cheeks All Natural Bath & Body, purveyors of all natural bath and body products, announced they have launched an Indiegogo campaign to expand operations. https://www.indiegogo.com/projects/sweet-cheeks-all-natural/x/4182441
Sweet Cheeks All Natural explained the reason for the campaign is to raise funds because they have outgrown their current location.
Vanessa McCauley, owner, said that they have the space, they just need to raise funds to convert it to a production facility. "2013 was our tipping point. It was our ground swell year and we grew 10 times ...
"How Do I Cultivate Emotional Wellbeing?" on April 8 "Why Shamanism Now?" with Host Christina Pratt
2014-04-01
Streaming live on the Co-Creator Radio Network on Tuesday, April 8, at 11am Pacific/2pm Eastern on "Why Shamanism Now? A Practical Path to Authenticity," shaman and founder of the Last Mask Center for Shamanic Healing Christina Pratt explains to listeners that health, in shamanic terms, requires the interaction of body and spirit, mind, and emotion. There is no physical health in shamanism apart from the dynamic interaction of all four aspects of being a human. A shamanic diagnosis addresses these four aspects of the human simultaneously, while also looking back to past ...
Katana Announces Strong Presence at ARDA World 2014
2014-04-01
Katana Software, Inc., a custom development and systems integration firm providing hospitality industry software systems, Data Intelligence and Analytics Software Services will be very visible at ARDA World 2014. The American Resort Development Association (ARDA) annual convention will be held April 6-10 at the Venetian Hotel in Las Vegas.
Katana Has Two Finalists up for ARDA Awards
ARDA has honored two key Katana executives with finalist nominations in the annual awards program. COO Melissa Gordon is a finalist for Technology Project Manager and CEO Rob Woodward ...
Space Coast FPRA to Hold Media Summit at Port Canaveral on Thursday, April 24
2014-04-01
Space Coast Florida Public Relations Association (FPRA) will be holding its annual Media Summit on Thursday, April 24, at the Canaveral Port Authority Maritime Center.
The FPRA annual Media Summit provides an opportunity for the public to meet and engage with Brevard County's top media representatives. The event features presentations by multiple media representatives and encourages attendees to engage, ask questions and learn about local media outlets. The lunch presentation will feature guest speakers from Nemours Children's Health System and other Florida businesses ...
GamFed to Launch its New Website
2014-04-01
The International Gamification Confederation (GamFed) is announcing the launch of its brand new website (www.gamfed.com). Founded on January 1st 2013, GamFed is today proud to report that over 100 members across over 60 countries worldwide have joined the confederation.
Membership is open to anyone who is an individual and is involved in gamification in a professional capacity and supports the aims of the International Gamification Confederation. We also welcome companies involved in gamification who support the aims of the International Gamification Confederation. For ...
Book Marketing Announcements: The Authors Show Lineup For The Week Of March 31, 2014
2014-04-01
Don McCauley of the Free Publicity Focus Group and Danielle Hampson, Executive Producer of The Authors Show, founders of The Authors Marketing Powerhouse, have announced The Authors Show radio and broadcast schedule for the week of March 31, 2014. The new show schedule is available at the Authors Marketing Powerhouse site.
For those who hope to sell books on the Internet, the challenge can be daunting. It can be confusing difficult, time consuming and expensive. Book Marketing, branded as The Authors Marketing Powerhouse, helps authors overcome these challenges by providing ...
Liberty Stone Financial to Hold 4th Annual CTO Summit
2014-04-01
This invitation-only event convenes leading venture capitalists, executives from established and emerging technology companies, and technologists from Liberty Stone Financial's IT organization for an intensive few days of solution briefings, strategy presentations and networking.
Liberty Stone Financial's summit will provide an overview of Liberty Stone Financial's technology strategy and future needs, and the technology market overall. In addition, 16 technology executives from primarily early-stage companies will offer in-depth briefings on their solutions and services ...
Noted Author Dr. Barbara Sinor Anounces The Release Of A New Book! "The Pact: Messages From The Other Side" Is A Fascinating Mixture Of Contemporary Memoir and Past Lifetime Narratives
2014-04-01
New book by retired psychotherapist uncovers the mysterious cycles of life, birth, death, and rebirth.
Marvelous Spirit Press (an imprint of Loving Healing Press, Inc.) announces the release of The Pact: Messages from the Other Side by Barbara Sinor, Ph.D. Sinor is a retired psychotherapist living in northern California, USA. In this spiritual memoir, her sixth book, the author takes the reader on an adventure through time while weaving tales of love and determination. A vow between the author and her husband finds us tracing the steps of present and past lifetimes devoted ...
Dr. Robert Gervais M.D. Recognized as "Professional of the Year" by Capital Who's Who
2014-04-01
About Dr. Robert Gervais M.D.
Dr. Robert Gervais specializes in Diagnostic Radiology, as Chief of Radiology for Sept-Iles Regional Regional Hospital as well as through his private practice in Quebec.
Dr. Gervais received his Medical Degree from the University of Montreal, also completing both his internship and residency at this institution. Dr. Robert Gervais is a Canadian and Quebec Board Certified Diagnostic Radiologist. Dr. Gervais continues to maintain his affiliation with the American Roentgen Ray Society, the Canadian Association of Radiology, as well as the ...
Dr. Albert G. Mitsos Recognized as "Professional of the Year" by Capital Who's Who
2014-04-01
About Dr. Albert G. Mitsos M.D.
Dr. Albert G. Mitsos M.D. is a Self-Employed Professional Forensic Medical Consultant.
Dr. Albert G. Mitsos holds a B.S. in Microbiology from Louisiana State University. Having done his residency at Cook County Hospital, Dr. Mitsos earned his M.D. from the Chicago Medical School.
As a Self-Employed Medical Forensic Consultant, Dr. Mitsos assists attorneys with the formulation of cross examination questions and jury selection questions. By relating the use of science, medicine and technology in an investigation, and by studying the ...
Paula Webster-Grant Recognized as "Professional of the Year" by Capital Who's Who
2014-04-01
About Paula Webster-Grant
Paula Webster-Grant is the CEO of Phillybass'd Entertainment. Phillybass'd Entertainment, a multifaceted entertainment media consulting group, offers its clients a one-stop shop for their marketing needs. Phillybass'd Entertainment is the home of Phillybass'd Records, BGR Media, M&L Highway Publishing (BMI), Phillybass'd Music (ASCAP), G&A consulting and The Image Consulting Group.
Ms. Webster-Grant earned a Master of Business Administration Degree in Marketing and Strategic Marketing from Harrington University in London and holds ...
Dr. Cameron Stewart Recognized as "Professional of the Year" by Capital Who's Who
2014-04-01
About Dr. Cameron Stewart
Dr. Cameron Stewart is a compassionate, brilliant physician specializing in malignant hematological diseases and clinical hematology.
Dr. Stewart earned his Medical Degree from the University of Queensland in Australia, dedicating his concentration of studies to the field of Clinical Hematology.
With over thirty years experience in the healthcare industry, Dr. Cameron Stewart has gathered extensive insights and expertise in the area of Clinical Hematology. As a practicing doctor at Watkins Medical Center, Dr. Stewart daily faces the challenge ...
Study: Spinal cord injuries increasing, more likely to be caused by falls
2014-04-01
Spinal cord injuries, one of the most debilitating injuries that can afflict a person, are becoming increasingly more common across the nation, according to new research that was recently published in the Journal of Neurotrauma. The research, carried out by the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, examined the emergency room records of 43,137 adults that were treated for spinal cord injuries between 2007 and 2009.
During this period of time, the research discovered that:
- Spinal cord injuries increased among older Americans. In 2007, approximately 79 per million ...
Older couples divorcing at an unprecedented rate
2014-04-01
Older couples - those who have been married 10, 20, 30 years or more - are divorcing at a higher rate than ever before, and the so-called "gray divorce" trend shows no signs of stopping. The divorce rate for younger couples has hovered around 50 percent for years now, but the rate at which long-term marriages end has been steadily increasing. According to data compiled by the United States Bureau of Vital Statistics and gathered from the 2010 "American Community Survey," the divorce rate for couples over the age of 50 has more than doubled in the past 20 years.
Possible ...
[1] ... [3777]
[3778]
[3779]
[3780]
[3781]
[3782]
[3783]
[3784]
3785
[3786]
[3787]
[3788]
[3789]
[3790]
[3791]
[3792]
[3793]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.