Key heart-failure culprit discovered
2014-03-12
SAN DIEGO, Calif., March 12, 2014 - A team of cardiovascular researchers from Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham), the Cardiovascular Research Center at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and the University of California, San Diego have identified a small but powerful new player in the onset and progression of heart failure. Their findings, published in the journal Nature on March 12, also show how they successfully blocked the newly discovered culprit to halt the debilitating and chronic life-threatening condition in its tracks.
In the ...
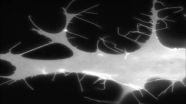
Protein key to cell motility has implications for stopping cancer metastasis
2014-03-12
VIDEO:
Aberrant filopodia are induced by co-expression of fluorescently labeled Cdc42 and non-fluorescent IRSp53. Fluorescence shows the cell shape, because Cdc42 localizes to the plasma membrane.
Click here for more information.
PHILADELPHIA - "Cell movement is the basic recipe of life, and all cells have the capacity to move," says Roberto Dominguez, PhD, professor of Physiology at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania. Motility – albeit on a cellular spatial ...
Countering the caregiver placebo effect
2014-03-12
How do you know that your pet is benefiting from its pain medication? A new clinical trial design from North Carolina State University researchers could help overcome pet owners' unconscious observation bias and determine whether the drugs they test are effective.
When animals are recruited for clinical trials, particularly for pain medications, researchers must rely on owner observation to determine whether the medication is working. Sounds simple enough, but as it turns out, human and animal behavior can affect the results.
All clinical trials have a "control" ...
'Ultracold' molecules promising for quantum computing, simulation
2014-03-12
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Researchers have created a new type of "ultracold" molecule, using lasers to cool atoms nearly to absolute zero and then gluing them together, a technology that might be applied to quantum computing, precise sensors and advanced simulations.
"It sounds counterintuitive, but you can use lasers to take away the kinetic energy, resulting in radical cooling," said Yong P. Chen, an associate professor of physics and electrical and computer engineering at Purdue University.
Physicists are using lasers to achieve such extreme cooling, reducing the temperature ...
Turing's theory of morphogenesis validated 60 years after his death
2014-03-12
PITTSBURGH—British mathematician Alan Turing's accomplishments in computer science are well known—he's the man who cracked the German Enigma code, expediting the Allies' victory in World War II. He also had a tremendous impact on biology and chemistry. In his only paper in biology, Turing proposed a theory of morphogenesis, or how identical copies of a single cell differentiate, for example, into an organism with arms and legs, a head and tail.
Now, 60 years after Turing's death, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh and Brandeis University have provided the ...
Large study identifies the exact gut bacteria involved in Crohn's disease
2014-03-12
While the causes of Crohn's disease are not well understood, recent research indicates an important role for an abnormal immune response to the microbes that live in the gut. In the largest study of its kind, researchers have now identified specific bacteria that are abnormally increased or decreased when Crohn's disease develops. The findings, which appear in the March 12 issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Host & Microbe, suggest which microbial metabolites could be targeted to treat patients with this chronic and currently incurable inflammatory bowel disease.
Twenty-eight ...
Newly diagnosed Crohn's disease patients show imbalance in intestinal microbial population
2014-03-12
A multi-institutional study led by investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the Broad Institute has identified how the intestinal microbial population of newly diagnosed Crohn's disease patients differs from that of individuals free of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In their paper in the March 12 issue of Cell Host and Microbe, the researchers report that Crohn's patients showed increased levels of harmful bacteria and reduced levels of the beneficial bacteria usually found in a healthy gastrointestinal tract.
Several studies have suggested that ...
Missing link in plant immunity identified
2014-03-12
After a 30-year search, scientists have uncovered how an enzyme critical to plants' rapid immune response against microbes is activated.
"The insights will open up new ways to improve disease resistance and stress tolerance in plants," says Professor Cyril Zipfel of The Sainsbury Laboratory in Norwich.
The enzyme, the NAPDH oxidase RBOHD, triggers a rapid generation of signalling molecules derived from oxygen that are believed to be detrimental to microbial growth. The newly-discovered way this enzyme is activated, by a protein (called BIK1) fills a gap in how plants ...
Microbes help to battle infection
2014-03-12
The human relationship with microbial life is complicated. At almost any supermarket, you can pick up both antibacterial soap and probiotic yogurt during the same shopping trip. Although there are types of bacteria that can make us sick, Caltech professor of biology and biological engineering Sarkis Mazmanian and his team are most interested in the thousands of other bacteria—many already living inside our bodies—that actually keep us healthy. His past work in mice has shown that restoring populations of beneficial bacteria can help alleviate the symptoms of inflammatory ...
Study finds increased gender variance in children with autism and ADHD
2014-03-12
Washington, DC— John F. Strang, PsyD, a pediatric neuropsychologist at Children's National Health System, and colleagues, found that children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) were more likely to exhibit gender variance, the wish to be the other gender, than children with no neurodevelopmental disorder, or a medical neurodevelopmental disorder such as epilepsy or neurofibromatosis.
The study, titled "Increased Gender Variance in Autism Spectrum Disorders and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder" was published ...
Can material rivaling graphene be mined out of rocks? Yes, if...
2014-03-12
Will one-atom-thick layers of molybdenum disulfide, a compound that occurs naturally in rocks, prove to be better than graphene for electronic applications? There are many signs that might prove to be the case. But physicists from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw have shown that the nature of the phenomena occurring in layered materials are still ill-understood and require further research.
Graphene has already been hailed as the future of electronics. Built of six-atom carbon rings arranged in a honeycomb-like structure, it forms extremely resilient ...
Transition to ICD-10 may cause information, financial losses for providers
2014-03-12
Health providers may experience information and financial loss during the mandated conversion from the current International Classification of Diseases to its new and improved version, report researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
The study, appearing in the March issue of the Journal of Oncology Practice, looked at coding ambiguity for hematology-oncology diagnoses to anticipate challenges all providers may face during the transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM.
The researchers chose to look at hematology-oncology because prior research suggested that, ...
Two definitions for chronic multisymptom illness afflicting gulf war vets should guide treatment
2014-03-12
WASHINGTON – Two existing definitions of chronic multisymptom illness (CMI) -- one by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and another from a study of Kansas Gulf War veterans -- should be used by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs to guide research and treatment of Gulf War veterans, says a new report from the Institute of Medicine. Determining which definition to use in different circumstances should be based on specific needs. Furthermore, the term "Gulf War illness" should replace "chronic multisymptom illness" to reflect the group in which the illness ...
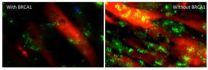
Breast cancer gene could play critical role in obesity and diabetes
2014-03-12
College Park, Md. -- The gene known to be associated with breast cancer susceptibility, BRCA 1, plays a critical role in the normal metabolic function of skeletal muscle, according to a new study led by University of Maryland School of Public Health researchers. Dr. Espen Spangenburg, associate professor of kinesiology, and his laboratory team are the first to identify that the BRCA1 protein is expressed in the skeletal muscle of both mice and humans, and that it plays a key role in fat storage, insulin response and mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle cells. The research ...
Large waist linked to poor health, even among those in healthy body mass index ranges
2014-03-12
ROCHESTER, Minn. — March 12, 2014 — Having a big belly has consequences beyond trouble squeezing into your pants. It's detrimental to your health, even if you have a healthy body mass index (BMI), a new international collaborative study led by a Mayo Clinic researcher found. Men and women with large waist circumferences were more likely to die younger, and were more likely to die from illnesses such as heart disease, respiratory problems, and cancer after accounting for body mass index, smoking, alcohol use and physical activity. The study is published in the March edition ...
Economic degrowth compatible with wellbeing if work stability is maintained
2014-03-12
Policies aimed at effectively mitigating climate change through a reduction in economic growth and consumption of fossil fuels would have a monetary impact on the economy, but also an impact on the wellbeing and happiness of individuals. Researchers at the Institute for Environmental Science and Technology at the UAB have taken advantage of the current economic crisis to analyse the impact this situation would have.
Scientists used data from a survey conducted in 2011 to measure the degree of happiness and satisfaction in a sample of 950 inhabitants from Barcelona, in ...
Boosting self-esteem prevents health problems for seniors
2014-03-12
This news release is available in French. Wednesday, March 12, 2014 — The importance of boosting self-esteem is normally associated with the trials and tribulations of adolescence. But new research from Concordia University shows that it's even more important for older adults to maintain and improve upon those confidence levels as they enter their twilight years. That's because boosting self-esteem can help buffer potential health threats typically associated with the transition into older adulthood.
A new study published in the journal Psychoneuroendocrinology, led ...
Bacterium and fungus team up to cause virulent tooth decay in toddlers
2014-03-12
Early childhood caries, a highly aggressive and painful form of tooth decay that frequently occurs in preschool children, especially from backgrounds of poverty, may result from a nefarious partnership between a bacterium and a fungus, according to a paper published ahead of print in the journal Infection and Immunity.
The resulting tooth decay can be so severe that treatment frequently requires surgery—in the operating room, says corresponding author Hyun (Michel) Koo of the University of Pennsylvania.
"Our data will certainly open the way to test agents to prevent ...
Majority of transgender patients report negative experiences in emergency departments
2014-03-12
A new study out of Western University (London, Canada) has found the majority of transgender patients have had a negative experience when it comes to receiving emergency department (ED) care. The findings, by first author Greta Bauer, PhD, is in press at the Annals of Emergency Medicine, the official publication of the American College of Emergency Physicians, and is now posted online.
The study used respondent-driven sampling, a methodology developed to specifically address the challenge of studying hard-to-reach populations. It relies on a snowball sampling, using ...
Metallurgical challenges in microelectronic 3-D IC packaging technology
2014-03-12
Mobile hand-held consumer electronic products have a rapid growing market today, witnessed by the popularity of Apple products. Most people make their first contact to internet, not by a PC, rather by a smart phone. The phone is no longer a phone, but it provides various functions for communication and for entertainment. Not only we can have recorded information such as books, images, songs, and movies from the phone or i-pad, but also we can have instant information such as traffic jam when we drive home, as well as breaking news at the last moment. It is expected that ...
Higher levels of CSF alpha-synuclein predict faster cognitive loss in Parkinson's disease
2014-03-12
Philadelphia, PA, March 11, 2014 – The course of Parkinson disease (PD) can vary from gradual deterioration to precipitous decline in motor or cognitive function. Therefore identifying predictors of progression can benefit understanding of PD disease progression and impact management. Data from 304 PD patients followed for up to 8 years indicate that patients with higher cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) alpha-synuclein levels experienced faster cognitive decline in the following months, although no associations were found between alpha-synuclein levels and motor changes. The results ...
Hasbro Children's Hospital study finds texting program good option for teen girls' health
2014-03-12
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – Megan Ranney, M.D., M.P.H., an emergency medicine attending physician at Hasbro Children's Hospital, recently led a study that found a text-message program may be an effective violence prevention tool for at-risk teen girls. The study has been published online in the Journal of Adolescent Health.
"Mobile health, or 'mHealth,' is increasingly being used as a way to improve people's health, via text-messaging or phone-based applications," said Ranney. "However, few people have studied whether teens are interested in mHealth, especially for prevention-type ...
Wishing to be another gender: Links to ADHD and autism spectrum disorders
2014-03-12
Children and teenagers with an autism spectrum disorder or those who have attention deficit and hyperactivity problems are much more likely to wish to be another gender. So says John Strang of the Children's National Medical Center in Washington, DC, USA, leader of the first study to compare the occurrence of such gender identity issues among children and adolescents with and without specific neurodevelopmental disorders. The paper is published in Springer's journal Archives of Sexual Behavior.
Children between 6 and 18 years old were part of the study. They either had ...
Lawns across America: Is the US becoming 1 shade of green?
2014-03-12
Boston and Baltimore. Miami and Minneapolis. Phoenix and Los Angeles.
Fanned across the United States and in locations from coast to prairie to desert, what do these cities have in common?
How their human residents manage that icon of America, the urban lawn, or so hypothesized a team of scientists. However, when they conducted a study comparing residential landscapes in these six cities, they discovered that lawn care practices had fewer similarities than they expected.
Ecologists Colin Polsky of Clark University in Worcester, Mass., Peter Groffman of the Cary Institute ...
Climate of Genghis Khan's ancient time extends long shadow over Asia of today
2014-03-12
Climate was very much on Genghis Khan's side as he expanded his Mongol Empire across northeastern Asia.
That link between Mongolia's climate and its human history echoes down the centuries, according to findings reported in this week's issue of the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
But climate may no longer be the boon it was during the latter, wetter part of Genghis Khan's reign. The early years were marked by drought.
Mongolia's current drought conditions could have serious consequences for the Asia region's human and other inhabitants.
The ...
[1] ... [3869]
[3870]
[3871]
[3872]
[3873]
[3874]
[3875]
[3876]
3877
[3878]
[3879]
[3880]
[3881]
[3882]
[3883]
[3884]
[3885]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.