Gestational diabetes may raise risk for heart disease in midlife
2014-03-12
Pregnant women may face an increased risk of early heart disease when they develop gestational diabetes, according to research in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Gestational diabetes, which develops only during pregnancy and usually disappears after the pregnancy, increases the risk that the mother will develop diabetes later. The condition is managed with meal planning, activity and sometimes insulin or other medications.
In the 20-year study, researchers found that a history of gestational diabetes may be a risk factor for early atherosclerosis in women ...
Nicotine withdrawal weakens brain connections tied to self-control over cigarette cravings
2014-03-12
PHILADELPHIA— People who try to quit smoking often say that kicking the habit makes the voice inside telling them to light up even louder, but why people succumb to those cravings so often has never been fully understood. Now, a new brain imaging study in this week's JAMA Psychiatry from scientists in Penn Medicine and the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Intramural Research Program shows how smokers suffering from nicotine withdrawal may have more trouble shifting from a key brain network—known as default mode, when people are in a so-called "introspective" or ...
Gestational diabetes linked to increased risk for heart disease in midlife
2014-03-12
OAKLAND, Calif. — Women who experience gestational diabetes may face an increased risk of early heart disease later in life, even if they do not develop type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome subsequent to their pregnancy, according to a Kaiser Permanente study published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
"Our research shows that just having a history of gestational diabetes elevates a woman's risk of developing early atherosclerosis before she develops type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome," said Erica P. Gunderson, PhD, MPH, study lead author and ...
MU study suggests new rehabilitation methods for amputees and stroke patients
2014-03-12
COLUMBIA, Mo. – When use of a dominant hand is lost by amputation or stroke, a patient is forced to compensate by using the nondominant hand exclusively for precision tasks like writing or drawing. Presently, the behavioral and neurological effects of chronic, forced use of the nondominant hand are largely understudied and unknown. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have shed light on ways in which a patient compensates when losing a dominant hand and suggest new and improved rehabilitation techniques for those suffering from amputation or stroke.
"Half of ...
Stem cells inside sutures could improve healing in Achilles tendon injuries
2014-03-12
Los Angeles, CA (March 12, 2014) Researchers have found that sutures embedded with stem cells led to quicker and stronger healing of Achilles tendon tears than traditional sutures, according to a new study published in the March 2014 issue of Foot & Ankle International (published by SAGE).
Achilles tendon injuries are common for professional, collegiate and recreational athletes. These injuries are often treated surgically to reattach or repair the tendon if it has been torn. Patients have to keep their legs immobilized for a while after surgery before beginning their ...
Computer model predicts vastly different ecosystem in Antarctica's Ross Sea in the coming century
2014-03-12
The Ross Sea, a major, biologically productive Antarctic ecosystem, "clearly will be extensively modified by future climate change" in the coming decades as rising temperatures and changing wind patterns create longer periods of ice-free open water, affecting the life cycles of both predators and prey, according to a paper published by researchers funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF).
To make their predictions, the researchers used information drawn from the Regional Ocean Modeling System, a computer model of sea-ice, ocean, atmosphere and ice-shelf interactions. ...
NASA sees ex-Tropical Cyclone Gillian in Australia's Gulf of Carpentaria
2014-03-12
Tropical Cyclone Gillian made landfall on the western Cape York Peninsula of Queensland, Australia, weakened and has now meandered back over water. On March 12, NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured an image of the remnants in the southern Gulf of Carpentaria.
On March 12 at 0600 UTC/2 a.m. EST, the remnants of Tropical Cyclone Gillian were located near 16.0 south and 141.1 east, about 115 nautical miles/ 132.3 miles/213 km east-northeast of Mornington Island in the Gulf of Carpentaria. According to the Joint Typhoon Warning Center or JTWC maximum sustained surface ...
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Lusi over Vanuatu
2014-03-12
Tropical Cyclone Lusi reached hurricane force as NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead early on March 12.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Cyclone Lusi that showed the storm's western quadrant affecting Vanuatu on March 12 at 02:05 UTC. In the MODIS image, Lusi had the distinct comma shape of a mature tropical cyclone, however no eye was visible. However, animated multispectral satellite imagery does show a ragged eye with tightly curved bands of thunderstorms wrapping ...
Sound trumps meaning in first language learning
2014-03-12
(Washington, DC) – A new study reveals that four-to-seven-year-old children rely on the sounds of new nouns more than on their meaning when assigning them to noun classes, even though the meaning is more predictive of noun class in the adult language. This finding reveals that children's sensitivity to their linguistic environment does not line up with objective measures of informativity, highlighting the active role that children play in selecting the data from which they learn language.
The study, "Statistical Insensitivity in the Acquisition of Tsez Noun Classes," ...
Good vibes for catalytic chemistry
2014-03-12
SALT LAKE CITY, March 12, 2014 – University of Utah chemists discovered how vibrations in chemical bonds can be used to predict chemical reactions and thus design better catalysts to speed reactions that make medicines, industrial products and new materials.
"The vibrations alone are not adequate, but combined with other classical techniques in physical organic chemistry, we are able to predict how reactions can occur," says chemistry professor Matt Sigman, senior author of the study in the Thursday, March 13, issue of the journal Nature.
"This should be applicable ...
IRX3 is likely the 'fat gene'
2014-03-12
Mutations within the gene FTO have been implicated as the strongest genetic determinant of obesity risk in humans, but the mechanism behind this link remained unknown. Now, an international team of scientists has discovered that the obesity-associated elements within FTO interact with IRX3, a distant gene on the genome that appears to be the functional obesity gene. The FTO gene itself appears to have only a peripheral effect on obesity. The study appears online March 12 in Nature.
"Our data strongly suggest that IRX3 controls body mass and regulates body composition," ...
Building new drugs just got easier
2014-03-12
LA JOLLA, CA—March 12, 2014—Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have developed a method for modifying organic molecules that significantly expands the possibilities for developing new pharmaceuticals and improving old ones.
"This is a technology that can be applied directly to many medicinally relevant compounds," said Jin-Quan Yu, a professor in TSRI's Department of Chemistry and the senior author of the new report, which appears in Nature March 13, 2014.
The innovation makes it easier to modify existing organic compounds by attaching biologically active ...
Water-rich gem points to vast 'oceans' beneath the Earth: UAlberta study
2014-03-12
A University of Alberta diamond scientist has found the first terrestrial sample of a water-rich gem that yields new evidence about the existence of large volumes of water deep beneath the Earth.
An international team of scientists led by Graham Pearson, Canada Excellence Research Chair in Arctic Resources at the U of A, has discovered the first-ever sample of a mineral called ringwoodite. Analysis of the mineral shows it contains a significant amount of water—1.5 per cent of its weight—a finding that confirms scientific theories about vast volumes of water trapped 410 ...
Quantum chaos in ultracold gas discovered
2014-03-12
The team of Francesca Ferlaino, Institute for Experimental Physics of the University of Innsbruck, Austria, has experimentally shown chaotic behavior of particles in a quantum gas. "For the first time we have been able to observe quantum chaos in the scattering behavior of ultracold atoms," says an excited Ferlaino. The physicists used random matrix theory to confirm their results, thus asserting the universal character of this statistical theory. Nobel laureate Eugene Wigner formulated random matrix theory to describe complex systems in the 1950s. Although interactions ...
Key heart-failure culprit discovered
2014-03-12
SAN DIEGO, Calif., March 12, 2014 - A team of cardiovascular researchers from Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham), the Cardiovascular Research Center at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and the University of California, San Diego have identified a small but powerful new player in the onset and progression of heart failure. Their findings, published in the journal Nature on March 12, also show how they successfully blocked the newly discovered culprit to halt the debilitating and chronic life-threatening condition in its tracks.
In the ...
Protein key to cell motility has implications for stopping cancer metastasis
2014-03-12
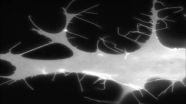
VIDEO:
Aberrant filopodia are induced by co-expression of fluorescently labeled Cdc42 and non-fluorescent IRSp53. Fluorescence shows the cell shape, because Cdc42 localizes to the plasma membrane.
Click here for more information.
PHILADELPHIA - "Cell movement is the basic recipe of life, and all cells have the capacity to move," says Roberto Dominguez, PhD, professor of Physiology at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania. Motility – albeit on a cellular spatial ...
Countering the caregiver placebo effect
2014-03-12
How do you know that your pet is benefiting from its pain medication? A new clinical trial design from North Carolina State University researchers could help overcome pet owners' unconscious observation bias and determine whether the drugs they test are effective.
When animals are recruited for clinical trials, particularly for pain medications, researchers must rely on owner observation to determine whether the medication is working. Sounds simple enough, but as it turns out, human and animal behavior can affect the results.
All clinical trials have a "control" ...
'Ultracold' molecules promising for quantum computing, simulation
2014-03-12
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Researchers have created a new type of "ultracold" molecule, using lasers to cool atoms nearly to absolute zero and then gluing them together, a technology that might be applied to quantum computing, precise sensors and advanced simulations.
"It sounds counterintuitive, but you can use lasers to take away the kinetic energy, resulting in radical cooling," said Yong P. Chen, an associate professor of physics and electrical and computer engineering at Purdue University.
Physicists are using lasers to achieve such extreme cooling, reducing the temperature ...
Turing's theory of morphogenesis validated 60 years after his death
2014-03-12
PITTSBURGH—British mathematician Alan Turing's accomplishments in computer science are well known—he's the man who cracked the German Enigma code, expediting the Allies' victory in World War II. He also had a tremendous impact on biology and chemistry. In his only paper in biology, Turing proposed a theory of morphogenesis, or how identical copies of a single cell differentiate, for example, into an organism with arms and legs, a head and tail.
Now, 60 years after Turing's death, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh and Brandeis University have provided the ...
Large study identifies the exact gut bacteria involved in Crohn's disease
2014-03-12
While the causes of Crohn's disease are not well understood, recent research indicates an important role for an abnormal immune response to the microbes that live in the gut. In the largest study of its kind, researchers have now identified specific bacteria that are abnormally increased or decreased when Crohn's disease develops. The findings, which appear in the March 12 issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Host & Microbe, suggest which microbial metabolites could be targeted to treat patients with this chronic and currently incurable inflammatory bowel disease.
Twenty-eight ...
Newly diagnosed Crohn's disease patients show imbalance in intestinal microbial population
2014-03-12
A multi-institutional study led by investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the Broad Institute has identified how the intestinal microbial population of newly diagnosed Crohn's disease patients differs from that of individuals free of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In their paper in the March 12 issue of Cell Host and Microbe, the researchers report that Crohn's patients showed increased levels of harmful bacteria and reduced levels of the beneficial bacteria usually found in a healthy gastrointestinal tract.
Several studies have suggested that ...
Missing link in plant immunity identified
2014-03-12
After a 30-year search, scientists have uncovered how an enzyme critical to plants' rapid immune response against microbes is activated.
"The insights will open up new ways to improve disease resistance and stress tolerance in plants," says Professor Cyril Zipfel of The Sainsbury Laboratory in Norwich.
The enzyme, the NAPDH oxidase RBOHD, triggers a rapid generation of signalling molecules derived from oxygen that are believed to be detrimental to microbial growth. The newly-discovered way this enzyme is activated, by a protein (called BIK1) fills a gap in how plants ...
Microbes help to battle infection
2014-03-12
The human relationship with microbial life is complicated. At almost any supermarket, you can pick up both antibacterial soap and probiotic yogurt during the same shopping trip. Although there are types of bacteria that can make us sick, Caltech professor of biology and biological engineering Sarkis Mazmanian and his team are most interested in the thousands of other bacteria—many already living inside our bodies—that actually keep us healthy. His past work in mice has shown that restoring populations of beneficial bacteria can help alleviate the symptoms of inflammatory ...
Study finds increased gender variance in children with autism and ADHD
2014-03-12
Washington, DC— John F. Strang, PsyD, a pediatric neuropsychologist at Children's National Health System, and colleagues, found that children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) were more likely to exhibit gender variance, the wish to be the other gender, than children with no neurodevelopmental disorder, or a medical neurodevelopmental disorder such as epilepsy or neurofibromatosis.
The study, titled "Increased Gender Variance in Autism Spectrum Disorders and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder" was published ...
Can material rivaling graphene be mined out of rocks? Yes, if...
2014-03-12
Will one-atom-thick layers of molybdenum disulfide, a compound that occurs naturally in rocks, prove to be better than graphene for electronic applications? There are many signs that might prove to be the case. But physicists from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw have shown that the nature of the phenomena occurring in layered materials are still ill-understood and require further research.
Graphene has already been hailed as the future of electronics. Built of six-atom carbon rings arranged in a honeycomb-like structure, it forms extremely resilient ...
[1] ... [3866]
[3867]
[3868]
[3869]
[3870]
[3871]
[3872]
[3873]
3874
[3875]
[3876]
[3877]
[3878]
[3879]
[3880]
[3881]
[3882]
... [8812]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.