Look back at US soybeans shows genetic improvement behind increased yields
2014-03-05
URBANA, Ill. – Soybean improvement through plant breeding has been critical over the years for the success of the crop. In a new study that traces the genetic changes in varieties over the last 80 years of soybean breeding, researchers concluded that increases in yield gains and an increased rate of gains over the years are largely due to the continual release of greater-yielding cultivars by breeders.
"This research in some ways looks back and informs us how soybean varieties have changed. It's useful to document these traits and changes," said Brian Diers, a University ...
Fertility prospects following ectopic pregnancy
2014-03-05
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – March 5, 2014 – Preserving a fallopian tube following an ectopic pregnancy seems like it would favor a woman's fertility prospects, right?
A new study from Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center looked at pregnancy outcomes in regards to the two surgical treatments for ectopic pregnancy -- salpingectomy, in which the affected fallopian tube is removed, or salpingotomy, in which the tube is preserved.
The aim of the study, said co-author Tamer Yalcinkaya, M.D., a reproductive endocrinologist at Wake Forest Baptist, was to assess whether salpingotomy ...
Maize and bacteria: A 1-2 punch knocks copper out of stamp sand
2014-03-05
Scientists have known for years that together, bacteria and plants can remediate contaminated sites. Ramakrishna Wusirika, of Michigan Technological University, has determined that how you add bacteria to the mix can make a big difference.
He has also shed light on the biochemical pathways that allow plants and bacteria to clean up some of the worst soils on the planet while increasing their fertility.
Wusirika, an associate professor of biological sciences, first collected stamp sands near the village of Gay, in Michigan's Upper Peninsula. For decades, copper mining ...
NASA tests new robotic refueling technologies
2014-03-05
NASA has successfully concluded a remotely controlled test of new technologies that would empower future space robots to transfer hazardous oxidizer – a type of propellant – into the tanks of satellites in space today.
Concurrently on the ground, NASA is incorporating results from this test and the Robotic Refueling Mission on the International Space Station to prepare for an upcoming ground-based test of a full-sized robotic servicer system that will perform tasks on a mock satellite client.
Collectively, these efforts are part of an ongoing and aggressive technology ...
OU study suggests non-uniform climate warming global
2014-03-05
A recent University of Oklahoma study of five decades of satellite data, model simulations and in situ observations suggests the impact of seasonal diurnal or daily warming varies between global regions affecting many ecosystem functions and services, such as food production, carbon sequestration and climate regulation. The effects of non-uniform climate warming on terrestrial ecosystems is a key challenge in carbon cycle research and for those making future predictions.
Jianyang Xia, a research associate in the OU College of Arts and Sciences, says the impact of non-uniform ...
A small step toward discovering habitable earths
2014-03-05
University of Arizona researchers snapped images of a planet outside our solar system with an Earth-based telescope using essentially the same type of imaging sensor found in digital cameras instead of an infrared detector. Although the technology still has a very long way to go, the accomplishment takes astronomers a small step closer to what will be needed to image earth-like planets around other stars
"This is an important next step in the search for exoplanets because imaging in visible light instead of infrared is what we likely have to do if we want to detect planets ...
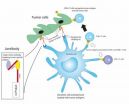
Researchers find potential target for drug to treat allergic asthma
2014-03-05
COLUMBUS, Ohio – An enzyme that helps maintain immune system function by "throwing away" a specific protein has a vital role in controlling symptoms of allergic asthma, new research in mice suggests.
The finding suggests that this enzyme, called Cbl-b, could be a target for drugs used to treat allergic asthma and other autoimmune disorders.
This new study, led by Ohio State University researchers, is the first to link Cbl-b to allergic asthma in an animal model.
The findings parallel results from a 2012 Yale study in humans, which suggested that a mutation in the ...
Pumping iron: A hydrogel actuator with mussel tone
2014-03-05
Protein from a small, tasty mollusk inspired Michigan Technological University's Bruce P. Lee to invent a new type of hydrogel actuator.
Hydrogels are soft networks of polymers with high water content, like jello. Because of their soft, gentle texture, they have the potential to interact safely with living tissues and have applications in a number of medical areas, including tissue engineering. Lee, an assistant professor of biomedical engineering, wanted to make a hydrogel that wouldn't just sit there.
"Hydrogels that can change shape on command could be used to deliver ...
Going viral to target tumors
2014-03-05
March 5, 2014, New York, NY– A Ludwig Cancer Research study suggests that the clinical efficacy of checkpoint blockade, a powerful new strategy to harness the immune response to treat cancers, might be dramatically improved if combined with oncolytic virotherapy, an investigational intervention that employs viruses to destroy tumors.
Published today in the journal Science Translational Medicine, the study evaluated a combination therapy in which the Newcastle disease virus (NDV), a bird virus not ordinarily harmful to humans, is injected directly into one of two melanoma ...
Biomarkers of cell death in Alzheimer's reverse course after symptom onset
2014-03-05
Three promising biomarkers being studied to detect Alzheimer's disease in its early stages appear to undergo a surprising shift as patients develop symptoms of dementia, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report.
Scientists use the biomarkers to assess brain changes linked to the disease in research volunteers. The levels of markers of neuronal injury increase in the spinal fluid for a decade or more before the onset of dementia, but in a new twist, the research shows for the first time that they later reverse course, decreasing as symptoms ...
An inventive new way to profile immune cells in blood
2014-03-05
ROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — When a person becomes sick or is exposed to an unwelcome substance, the body mobilizes specific proportions of different immune cells in the blood. Methods of discovering and detecting those profiles are therefore useful both clinically and in research. In a new paper in the journal Genome Biology, a team of scientists describes a new and uniquely advantageous way to detect them.
All the current means of counting immune cells in a blood sample require whole cells, said Karl Kelsey, professor of epidemiology at Brown and corresponding ...
Novel cancer vaccine holds promise against ovarian cancer, mesothelioma
2014-03-05
A novel approach to cancer immunotherapy – strategies designed to induce the immune system to attack cancer cells – may provide a new and cost-effective weapon against some of the most deadly tumors, including ovarian cancer and mesothelioma. Investigators from the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) Vaccine and Immunotherapy Center report in the Journal of Hematology & Oncology that a protein engineered to combine a molecule targeting a tumor-cell-surface antigen with another protein that stimulates several immune functions prolonged survival in animal models of both ...
Hungry for 'likes': Frequent Facebook use linked to eating disorder risk, study finds
2014-03-05
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — Frequent Facebook users might be sharing more than party pictures, vacation videos and shameless selfies — they also share a greater risk of eating disorders, according to a new study led by Florida State University researchers.
Psychology Professor Pamela K. Keel studied 960 college women and found that more time on Facebook was associated with higher levels of disordered eating. Women who placed greater importance on receiving comments and "likes" on their status updates and were more likely to untag photos of themselves and compare their own photos ...
Prenatal nicotine exposure may lead to ADHD in future generations
2014-03-05
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — Prenatal exposure to nicotine could manifest as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children born a generation later, according to a new study by Florida State University College of Medicine researchers.
Professors Pradeep G. Bhide and Jinmin Zhu have found evidence that ADHD associated with nicotine can be passed across generations. In other words, your child's ADHD might be an environmentally induced health condition inherited from your grandmother, who may have smoked cigarettes during pregnancy a long time ago. And the fact that you never ...
A single gene, doublesex, controls wing mimicry in butterflies
2014-03-05
A single gene regulates the complex wing patterns, colors and structures required for mimicry in swallowtail butterflies, report scientists from the University of Chicago, March 5 in Nature. Surprisingly, the gene described, doublesex, is already well-known for its critical role in sexual differentiation in insects.
"Conventional wisdom says that it should be multiple genes working together to control the whole wing pattern of a butterfly," said Marcus Kronforst, Neubauer Family Assistant Professor of Ecology & Evolution at the University of Chicago and senior author ...
Ultra sensitive detection of radio waves with lasers
2014-03-05
Radio waves are used for many measurements and applications, for example, in communication with mobile phones, MRI scans, scientific experiments and cosmic observations. But 'noise' in the detector of the measuring instrument limits how sensitive and precise the measurements can be. Now researchers at the Niels Bohr Institute have developed a new method where they can avoid noise by means of laser light and can therefore achieve extreme precision of measurements. The results are published in the prestigious scientific journal, Nature.
'Noise' in the detector of a measuring ...
Livestock can produce food that is better for the people and the planet
2014-03-05
With one in seven humans undernourished, and with the challenges of population growth and climate change, the need for efficient food production has never been greater. Eight strategies to cut the environmental and economic costs of keeping livestock, such as cows, goats and sheep, while boosting the quantity and quality of the food produced have been outlined by an international team of scientists.
The strategies to make ruminant - cud-chewing - livestock a more sustainable part of the food supply, led by academics at the University of Bristol's School of Veterinary ...
ALS-linked gene causes disease by changing genetic material's shape
2014-03-05
Johns Hopkins researchers say they have found one way that a recently discovered genetic mutation might cause two nasty nervous system diseases. While the affected gene may build up toxic RNA and not make enough protein, the researchers report, the root of the problem seems to be snarls of defective genetic material created at the mutation site.
The research team, led by Jiou Wang, Ph.D., an assistant professor of biochemistry and molecular biology and neuroscience at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, reports its finding March 5 on the journal Nature's ...
Study aims to define risk factors for falls in post-menopausal women
2014-03-05
ROSEMONT, Ill.–A new study appearing in the March issue of the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (JBJS) showed that women with distal radius (wrist) fractures had decreased strength compared to similar patients without fractures. This could explain why these women were more likely to fall and might sustain future fractures.
The investigators used a variety of balance and strength tests combined with patient-provided information about walking habits to evaluate the physical performance and risk of falls for post-menopausal women with and without previous wrist fractures. ...
UF researchers find drug therapy that could eventually reverse memory decline in seniors
2014-03-05
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — It may seem normal: As we age, we misplace car keys, or can't remember a name we just learned or a meal we just ordered. But University of Florida researchers say memory trouble doesn't have to be inevitable, and they've found a drug therapy that could potentially reverse this type of memory decline.
The drug can't yet be used in humans, but the researchers are pursuing compounds that could someday help the population of aging adults who don't have Alzheimer's or other dementias but still have trouble remembering day-to-day items. Their findings will ...
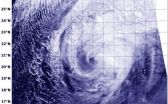
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Faxai stretching out
2014-03-05
When a tropical cyclone becomes elongated it is a sign the storm is weakening. Imagery from NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite today revealed that wind shear was stretching out Tropical Cyclone Faxai and the storm was waning.
On March 5 at 1500 UTC/10 a.m. EST, Tropical Cyclone Faxai's center was located near 22.5 south and 155.2 east, about 699 nautical miles/804.4 miles/ 1,295 km west-northwest of Wake Island. According to the Joint Typhoon Warning Center or JTWC, Faxai's maximum sustained surface winds dropped to 50 knots/57.5 mph/92.6 kph. Faxai was moving to the northeast ...
UCSB study explores cocaine and the pleasure principle
2014-03-05
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — On the other side of the cocaine high is the cocaine crash, and understanding how one follows the other can provide insight into the physiological effects of drug abuse. For decades, brain research has focused on the pleasurable effects of cocaine largely by studying the dopamine pathway. But this approach has left many questions unanswered.
So the Behavioral Pharmacology Laboratory (BPL) at UC Santa Barbara decided to take a different approach by examining the motivational systems that induce an animal to seek cocaine in the first place. Their ...
First-ever 3D image created of the structure beneath Sierra Negra volcano
2014-03-05
The Galápagos Islands are home to some of the most active volcanoes in the world, with more than 50 eruptions in the last 200 years. Yet until recently, scientists knew far more about the history of finches, tortoises, and iguanas than of the volcanoes on which these unusual fauna had evolved.
Now research out of the University of Rochester is providing a better picture of the subterranean plumbing system that feeds the Galápagos volcanoes, as well as a major difference with another Pacific Island chain—the Hawaiian Islands. The findings have been published in the Journal ...
Brain circuits multitask to detect, discriminate the outside world
2014-03-05
Imagine driving on a dark road. In the distance you see a single light. As the light approaches it splits into two headlights. That's a car, not a motorcycle, your brain tells you.
A new study found that neural circuits in the brain rapidly multitask between detecting and discriminating sensory input, such as headlights in the distance. That's different from how electronic circuits work, where one circuit performs a very specific task. The brain, the study found, is wired in way that allows a single pathway to perform multiple tasks.
"We showed that circuits in the ...
Similarity breeds proximity in memory, NYU researchers find
2014-03-05
Researchers at New York University have identified the nature of brain activity that allows us to bridge time in our memories. Their findings, which appear in the latest issue of the journal Neuron, offer new insights into the temporal nature of how we store our recollections and may offer a pathway for addressing memory-related afflictions.
"Our memories are known to be 'altered' versions of reality, and how time is altered has not been well understood," said Lila Davachi, an associate professor in NYU's Department of Psychology and Center for Neural Science and the ...
[1] ... [3905]
[3906]
[3907]
[3908]
[3909]
[3910]
[3911]
[3912]
3913
[3914]
[3915]
[3916]
[3917]
[3918]
[3919]
[3920]
[3921]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.