'Kill Bill' character inspires the name of a new parasitoid wasp species
2013-03-20
Parasitoid wasps of the family Braconidae are known for their deadly reproductive habits. Most of the representatives of this group have their eggs developing in other insects and their larvae, eventually killing the respective host, or in some cases immobilizing it or causing its sterility. Three new species of the parasitoid wasp genus Cystomastacoides, recently described in the Journal of Hymenoptera Research, reflect this fatal behavior.
Two of the new species were discovered in Papua New Guinea, while the third one comes from Thailand. The Thai species, Cystomastacoides ...
Max Planck Florida Institute study points to major discovery for Alzheimer's disease
2013-03-20
FLORIDA, March 19, 2013 – The Journal of Neuroscience has published a study led by researchers at the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience, the first and only U.S. extension of the prestigious Max Planck Society, that may hold a stunning breakthrough in the fight to treat Alzheimer's disease. The study potentially identifies a cause of Alzheimer's disease—based on a newly-discovered signaling pathway in cellular models of Alzheimer's disease—and opens the door for new treatments by successfully blocking this pathway. The Institute, which recently opened in December ...
First of its kind study in Canada looks at who is taking aspirin to prevent heart attack or stroke
2013-03-20
A new study out of the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry shows a large population of healthy people are taking Aspirin to prevent cardiovascular disease, despite the fact that new literature shows it isn't as beneficial as once thought.
Olga Szafran and Mike Kolber, in the Department of Family Medicine at the University of Alberta, surveyed patients over the age of 50 at two clinics in Alberta. They found that more than 40 per cent of people who don't suffer from cardiovascular disease are popping pills daily to prevent a heart attack or stroke – a practice called primary ...
More career options may explain why fewer women pursue jobs in science and math
2013-03-20
Women may be less likely to pursue careers in science and math because they have more career choices, not because they have less ability, according to a new study published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Although the gender gap in mathematics has narrowed in recent decades, with more females enrolling and performing well in math classes, females are still less likely to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) than their male peers.
Researchers tend to agree that differences in math ...
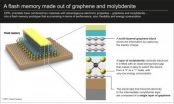
Fantastic flash memory combines graphene and molybdenite
2013-03-20
After the molybdenite chip, we now have molybdenite flash memory, a significant step forward in the use of this new material in electronics applications. The news is even more impressive because scientists from EPFL's Laboratory of Nanometer Electronics and Structures (LANES) came up with a truly original idea: they combined the advantages of this semiconducting material with those of another amazing material – graphene. The results of their research have recently been published in the journal ACS Nano.
Two years ago, the LANES team revealed the promising electronic ...
Are survivors of childhood leukemia and lymphoma at greater risk of chronic fatigue as adults?
2013-03-20
New Rochelle, NY, Mar 19, 2013—Chronic fatigue, a persistent lack of energy that does not improve with rest, is at least three times more prevalent among adult survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoma experienced during childhood or adolescence than in the general adult population, according to an article in Journal of Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology (JAYAO), (http://www.liebertpub.com/JAYAO) a multidisciplinary peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. (http://www.liebertpub.com) JAYAO is the Official Journal of the Society for ...
Biennial mammograms best after 50, even for women with dense breasts
2013-03-20
Screening for breast cancer every two years appears just as beneficial as yearly mammograms for women ages 50 to 74, with significantly fewer "false positives" – even for women whose breasts are dense or who use hormone therapy for menopause.
That is the finding of a new national study involving more than 900,000 women.
The study was published on March 18 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The same team of researchers from UC San Francisco and Seattle-based Group Health Research Institute recently reported similar results for older women ages 66 to 89 years old.
By contrast, ...
Record simulations conducted on Lawrence Livermore supercomputer
2013-03-20
LIVERMORE, Calif. -- Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory have performed record simulations using all 1,572,864 cores of Sequoia, the largest supercomputer in the world. Sequoia, based on IBM BlueGene/Q architecture, is the first machine to exceed one million computational cores. It also is No. 2 on the list of the world's fastest supercomputers, operating at 16.3 petaflops (16.3 quadrillion floating point operations per second).
The simulations are the largest particle-in-cell (PIC) code simulations by number of cores ever performed. PIC simulations ...
To make health systems more effective, physicians say time is now for clinician-led innovation
2013-03-20
(Boston) –Physician experts in health system issues propose a timely alternative process for harnessing and supporting physician-led innovations to rapidly address front-line health care delivery problems and improve health. Published as a Viewpoint article in the March 20th issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), the authors propose health systems adopt a strategy widely accepted in U.S. industries of "user-led" innovation.
User-led innovation is predicated on the idea that important enhancements to products and services are often made by users ...
University of Maryland researchers identify fish protein that may inhibit cancer metastasis
2013-03-20
BALTIMORE – March 19, 2013. Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine have identified a peptide, or protein, derived from Pacific cod that may inhibit prostate cancer and possibly other cancers from spreading, according to preclinical research published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
"The use of natural dietary products with anti-tumor activity is an important and emerging field of research," says senior author Hafiz Ahmed, Ph.D., assistant professor of biochemistry and molecular biology at the University of Maryland ...
Transportation study reveals potential for deep cuts to petroleum use and carbon emissions
2013-03-20
The U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and Argonne National Laboratory (ANL) today announced the release of the Transportation Energy Futures (TEF) study, an assessment of avenues to reach deep cuts in petroleum use and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the transportation sector.
"Transportation is an engine of our economic strength, but it also represents a key challenge for the future of U.S. energy use," NREL Senior Analyst Austin Brown said. "Transportation accounts for 71 percent of total U.S. petroleum consumption and 33 ...
Highlights from the March GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy special issue on colorectal cancer
2013-03-20
OAK BROOK, Ill. – March 19, 2013 – In recognition of National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month, GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy has published a special issue for March on colorectal cancer. The issue includes a practical guide for approaching and managing serrated colon polyps, one of the most common types of polyps, and a study on reducing postpolypectomy bleeding with prophylactic clip closure. GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy is the monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE).
"The cutting edge of serrated ...
Nurses can play key role in reducing deaths from world's most common diseases
2013-03-20
Nurses and midwives can play a critical role in lessening people's risk of cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory disease and diabetes, according to a groundbreaking new report issued by the World Health Organization and co-authored by a UCLA nursing professor.
These four non-communicable disease types account for a combined 60 percent of all deaths worldwide.
"The global burden of non-communicable diseases is already high and continues to grow in all regions of the world," said Linda Sarna, a professor at the UCLA School of Nursing and co-author ...
US company identified as manufacture of lead paint in Africa
2013-03-20
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (March 19, 2013) - House paint containing dangerous
concentrations of lead is being sold in Cameroon by an American company – and the
company is refusing to remove the paint from store shelves.
"There is an immediate need for regulations to restrict the lead content of paint in
Cameroon to protect public health," said Perry Gottesfeld, Executive Director of
Occupational Knowledge International (OK International) and co-author of a new
research study about this lead hazard.
"The levels of lead are extraordinarily high, and these products have been ...
Study could aid development of new drugs to treat gout
2013-03-20
MAYWOOD, Ill. – Findings from a Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine study could lead to the development of new drugs to treat gout.
The study, led by Liang Qiao, MD, and his colleagues and collaborators, was published March 19 in the journal Nature Communications.
Gout is caused by a buildup of uric acid around joints, typically the big toe, knee or ankles. The immune system revs up to attack uric acid salt crystals, and this immune response causes painful inflammation.
The innate immune response is mainly activated by calcium that enters a macrophage ...
Mayo Clinic researchers develop test to gauge severity of concussions
2013-03-20
SAN DIEGO — Neurologists at Mayo Clinic in Arizona have taken a promising step toward identifying a test that helps support the diagnosis of concussion. Their research has shown that autonomic reflex testing, which measures involuntary changes in heart rate and blood pressure, consistently appear to demonstrate significant changes in those with concussion. They presented the findings at the American Academy of Neurology annual meeting in San Diego this week.
Right now doctors rely primarily on self-reporting of symptoms to make a diagnosis of concussion. In addition, ...
Fewer women pursue jobs in science because they have more career options
2013-03-20
PITTSBURGH—Women may be less likely to pursue careers in science—not because they have less ability—but because they have more career choices, according to a University of Pittsburgh study published today in Psychological Science.
Although the gender gap in mathematics has narrowed in recent decades between males and females, women are still less likely to pursue STEM careers than their male counterparts. Together with colleagues at the University of Michigan, the Pitt research team investigated whether differences in overall patterns of math and verbal ability might ...
IUPUI stem cell research could expand clinical use of regenerative human cells
2013-03-20
Research led by a biology professor in the School of Science at Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis (IUPUI) has uncovered a method to produce retinal cells from regenerative human stem cells without the use of animal products, proteins or other foreign substances, which historically have limited the application of stem cells to treat disease and other human developmental disorders.
The study of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) has been pursued vigorously since they were first discovered in 2007 due to their ability to be manipulated into specific ...
Alloy developed at Sandia National Laboratories has potential for electronics in wells
2013-03-20
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — An alloy that may improve high-temperature electronics in oil and geothermal wells was really a solution in search of a problem.
Sandia National Laboratories first investigated the gold-silver-germanium alloy about 15 years ago as a possible bonding material in a new neutron tube product. But a design change forced Sandia to shelve the material, said Paul Vianco, who has worked in soldering and brazing technology at Sandia for 26 years.
Then a few years ago, researchers working on other projects with applications inside a well, referred to as downhole, ...
Los Alamos science sleuth on the trail of a Martian mystery
2013-03-20
THE WOODLANDS, Texas, March 19, 2013 — When it comes to examining the surface of rocks on Mars with a high-powered laser, five is a magic number for Los Alamos National Laboratory postdoctoral researcher Nina Lanza.
During a poster session today at the 44th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference at The Woodlands, Texas, Lanza described how the laser-shooting ChemCam instrument aboard the Curiosity rover currently searching the surface of Mars for signs of habitability has shown what appears to be a common feature on the surface of some very different Martian rocks ...
Are accountable care organizations 'improving population health'?
2013-03-20
NEW YORK (March 19, 2013) -- Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs), a key feature of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), aim to control health care costs, enhance quality in health care and improve population health. But what does "improving population health" really mean? This is the question asked in a new viewpoint article by Weill Cornell Medical College researchers published in the March 20 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA). The authors argue a clear definition is crucial in order to formulate effective health care and social service policy.
Section ...
NASA's LRO sees GRAIL's explosive farewell
2013-03-20
VIDEO:
On Dec. 17, 2012, NASA's twin GRAIL spacecraft were deliberately crashed into the lunar surface traveling at nearly 4,000 mph. Another NASA spacecraft, Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, observed the impact using...
Click here for more information.
Many spacecraft just fade away, drifting silently through space after their mission is over, but not GRAIL. NASA's twin GRAIL (Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory) spacecraft went out in a blaze of glory Dec. 17, 2012, ...
Practice makes perfect with Webb telescope mirror placement
2013-03-20
VIDEO:
Engineers at the Goddard Space Flight Center test the robotic-like fixture that will place the primary mirror segments of the Webb Telescope onto the telescopes back plane.
Click here for more information.
NASA engineers and scientists have been making practice runs to ensure the placement of primary mirror segments on the James Webb Space Telescope go perfectly when the flight equipment is ready. NASA issued a video and photos showing the practice run in the giant ...
Abnormal stress response seen in toddlers exposed to meth in womb
2013-03-20
PISCATAWAY, NJ – Some 2-year-olds whose moms used methamphetamine during pregnancy may have an abnormal response to stressful situations, according to a study in the May issue of the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
Researchers saw the altered response in toddlers who were exposed to meth in the womb and who currently had signs of strife in their lives—such as a mom who drank heavily or had depression or other mental health symptoms. Specifically, the children's levels of the stress hormone cortisol did not rise as they should have during a tense situation (a ...
Atypical brain circuits may cause slower gaze shifting in infants who later develop autism
2013-03-20
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Infants at 7 months of age who go on to develop autism are slower to reorient their gaze and attention from one object to another when compared to 7-month-olds who do not develop autism, and this behavioral pattern is in part explained by atypical brain circuits.
Those are the findings of a new study led by University of North Carolina School of Medicine researchers and published online March 20 by the American Journal of Psychiatry.
"These findings suggest that 7-month-olds who go on to develop autism show subtle, yet overt, behavioral differences ...
[1] ... [5021]
[5022]
[5023]
[5024]
[5025]
[5026]
[5027]
[5028]
5029
[5030]
[5031]
[5032]
[5033]
[5034]
[5035]
[5036]
[5037]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.