Havoc in biology's most-used human cell line
2013-03-12
HeLa cells are the world's most commonly used human cell lines, and have served as a standard for understanding many fundamental biological processes. In a study published today in G3: Genes, Genomes and Genetics online, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in Heidelberg, announce they have successfully sequenced the genome of a HeLa cell line. It provides a high-resolution genomic reference that reveals the striking differences between the HeLa genome and that of normal human cells. The study could improve the way HeLa cells are used to model human biology.
The ...
Watery research theme to flow through new Tokmakoff lab
2013-03-12
Once Andrei Tokmakoff gets his new laser laboratory operational later this year, he will use the world's shortest infrared light pulses to pluck molecular bonds like a stringed musical instrument.
Tokmakoff, the Henry G. Gale Distinguished Service Professor of Chemistry, arrived at the University of Chicago in January to tackle new problems in biology with the aid of ultrafast vibrational spectroscopy methods that he has developed.
"He does very sophisticated spectroscopy, in particular vibrational spectroscopy," said Richard Jordan, professor and chairman of chemistry. ...
Anemia drugs does not improve health of anemic heart failure patients
2013-03-12
Researchers from Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Sweden, have found that a commonly used drug to treat anemia in heart failure patients does not improve patients' health, nor does it reduce their risk of death from heart failure. Results of the international study were presented at the American College of Cardiology's annual meeting in San Francisco on March 10 and published simultaneously online by The New England Journal of Medicine.
Initiated in 2006, the RED-HF (Reduction of Events With Darbepoetin Alfa in Heart Failure) trial involved 2,278 anemic ...
Heat-stressed cows spend more time standing
2013-03-12
Des Moines, IA – A new study by researchers at the University of Arizona and Northwest Missouri State University shows that standing and lying behavior can predict heat stress in cows.
In a presentation at the 2013 ADSA Midwest Branch / ASAS Midwestern Section Meeting, Dr. Jamison Allen explained that predicting heat stress is vital for keeping cows healthy and productive. Cows will pant, eat less and produce less milk when their core body temperature increases.
Allen said cows prefer standing to lying on hot days. Cows stand to allow more of their surface area to disperse ...
Ruptured aneurysm has lasting impact on quality of life
2013-03-12
Philadelphia, Pa. (March 12, 2013) – Ten years after stroke caused by a ruptured aneurysm of the brain, surviving patients have persistent difficulties in several areas affecting quality of life, reports a study in the March issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The long-term impact of ruptured aneurysms causing subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) highlights the need for "survivorship care plans" comparable to those made for long-term cancer ...
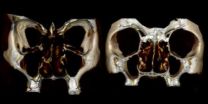
The nose's unheralded neighbor
2013-03-12
Pity the poor maxillary sinuses. Those bulbous pouches on either side of the human nose are known more for trapping mucus and causing sinus infections than anything else. They were thought to be an evolutionary relic of our distant past, with little known present value.
Yet researchers led by the University of Iowa believe the unheralded maxillary sinuses play a fortuitous, integral role in the shape and function of the human nose, even today. After studying faces of African and European origin, the team has concluded that the maxillary sinuses act as a cushion of sorts, ...
Tickling the brain with magnetic stimulation improves memory in schizophrenia
2013-03-12
Philadelphia, PA, March 12, 2013 – Cognitive impairments are disabling for individuals with schizophrenia, and no satisfactory treatments currently exist. These impairments affect a wide range of cognition, including memory, attention, verbal and motor skills, and IQ. They appear in the earliest stages of the disease and disrupt or even prevent normal day-to-day functioning.
Scientists are exploring a variety of strategies to reduce these impairments including "exercising the brain" with specially designed computer games and medications that might improve the function ...
Antibiotic-resistant strain of E. coli increasing among older adults and residents of nursing homes
2013-03-12
Antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli (E. coli) continues to proliferate, driven largely by expansion of a strain of E. coli know as sequence type ST131. A new study points to hospitals and long-term care facilities (LTCF) as settings in which this antibiotic-resistant strain is increasingly found. The study is published in the April issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
E. coli is the most common gram-negative pathogen, causing both gastrointestinal disease and extraintestinal infections ...
Infants prefer individuals who punish those not like themselves, Yale researchers find
2013-03-12
Infants as young as nine months old prefer individuals who punish those who are not like them, and this seemingly innate mean streak grows stronger in the next five months of life, a study by researchers at Yale University has found.
Babies, like adults, prefer individuals who like the same things they do. A new study reports that they want individuals who share their tastes to be treated well by others, but want those whose tastes differ from their own to be treated badly. The study of 200 nine- and 14-month-old infants was published online in Psychological Science, ...
New distance record for 400 Gb/s data transmission
2013-03-12
As network carriers debate the next Ethernet standard—and whether transmission speeds of 400 gigabit per second or 1 terabit per second should be the norm—engineers are working on new measures to squeeze next-generation performance out of current-generation systems.
To that end, a team from AT&T has devised a new patent pending technique enabling tuning of the modulation spectral efficiency, which allows, for the first time, 400 Gb/s signals to be sent over today's 100 gigahertz-grid optical networks over ultra-long distances. Spectral efficiency is the information rate ...
Job burnout can severely compromise heart health
2013-03-12
Americans work longer hours, take fewer vacation days, and retire later than employees in other industrialized countries around the globe. With such demanding careers, it's no surprise that many experience job burnout — physical, cognitive, and emotional exhaustion that results from stress at work. Researchers have found that burnout is also associated with obesity, insomnia, and anxiety.
Now Dr. Sharon Toker of Tel Aviv University's Faculty of Management and her fellow researchers — Profs. Samuel Melamed, Shlomo Berliner, David Zeltser and Itzhak Shpira of TAU's Sackler ...
Ultra-high-speed optical communications link sets new power efficiency record
2013-03-12
Ultrafast supercomputers that operate at speeds 100 times faster than current systems are now one step closer to reality. A team of IBM researchers working on a U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA)-funded program have found a way to transmit massive amounts of data with unprecedentedly low power consumption.
The team will describe their prototype optical link, which shatters the previous power efficiency record by half at the Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exposition/National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference (OFC/NFOEC) in Anaheim, Calif. ...
New automated process simplifies alignment and splicing of multicore optical fibers
2013-03-12
New multicore optical fibers have many times the signal-carrying capacity of traditional single-core fibers, but their use in telecommunications has been severely restricted because of the challenge in splicing them together-- picture trying to match up and connect two separate boxes of spaghetti so that all of the noodles in each box are perfectly aligned. Now, a new splicing technique offers an automated way to do just that, with minimal losses in signal quality across the spliced sections. The method will be described at the Optical Fiber Communication Conference and ...
Penn study: Financial incentives affect prostate cancer treatment patterns
2013-03-12
Philadelphia - According to a new study by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, prostate cancer patients of urologists who own expensive radiation equipment are more likely to receive radiation treatment in lieu of surgery than patients treated by urologists without an ownership stake in the equipment. The study, now available online in the Journal of Urology, found that integrated prostate cancer centers (IPCCs), where urology and radiation oncology practices are combined, use expensive radiation-based treatments at higher rates ...
Mystery of 'zombie worm' development unveiled
2013-03-12
How do bone-eating worms reproduce? A new study by Norio Miyamoto and colleagues from the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology sheds light on this question through a detailed observation of the postembryonic development and sexual maturation of Osedax worms, also known as "zombie worms." These worms typically inhabit vertebrate bones on the seafloor. The study is published online in Springer's journal Naturwissenschaften - The Science of Nature.
Osedax is Latin for "bone-devourer," which refers to how the worms bore into the bones of whale carcasses to ...
Neural 'synchrony' may be key to understanding how the human brain perceives
2013-03-12
Despite many remarkable discoveries in the field of neuroscience during the past several decades, researchers have not been able to fully crack the brain's "neural code." The neural code details how the brain's roughly 100 billion neurons turn raw sensory inputs into information we can use to see, hear and feel things in our environment.
In a perspective article published in the journal Nature Neuroscience on Feb. 25, 2013, biomedical engineering professor Garrett Stanley detailed research progress toward "reading and writing the neural code." This encompasses the ability ...
4 dinosaur egg species identified in Lleida
2013-03-12
A study headed by the Miquel Crusafont Catalan Palaeontology Institute has for the first time documented detailed records of dinosaur egg fossils in the Coll de Nargó archaeological site in Lleida, Spain. Up until now, only one type of dinosaur egg had been documented in the region.
The archaeological site in Coll de Nargó containing dinosaur eggs lies some 8 kilometres to the west of the town that bears the same name in the province of Lleida. This region is home to different types of geological formations, including the Areniscas de Arén Formation and the Tremp Formation, ...
Does expressing anger on online rant-sites make you feel better or worse?
2013-03-12
New Rochelle, NY, March 12, 2013—Little is known about the value and emotional consequences of expressing anger on the Internet. Rant-sites provide an outlet for anonymous, angry outbursts. How people feel after reading and writing rants and the effects of this behavior is explored in an article in Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, (http://www.liebertpub.com/cyber) a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers (http://www.liebertpub.com). The article is available online on the Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking (http://www.liebertpub.com/cyber) ...
Young pigs prefer traditional soybean diet
2013-03-12
Des Moines, IA – Pigs aren't known for being picky, but new research shows they avoid bitter tastes when they can.
In a new study of nursery pig diets, researchers from the University of Alberta offered pigs different amounts of soybean meal, napus canola meal and juncea canola meal. They found that pigs ate more soybean meal when given a choice.
Napus canola meal and juncea canola meal come from rapeseed and mustard greens, respectively. Canola meals are less expensive than soybean meal. If producers can replace soybean meal in swine diets, they could produce pork ...
Updated 'stereo EEG' workflow simplifies planning of epilepsy surgery
2013-03-12
Philadelphia, Pa. (March 12, 2013) – For patients with "drug-resistant" epilepsy requiring surgery, an updated stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG) technique provides a more efficient process for obtaining critical data for surgical planning, according to a study in the March issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
"SEEG is a safe and accurate procedure for invasive assessment of the epileptogenic zone," according to the new report by Dr. ...
Some bacteria may protect against disease caused by stomach infection
2013-03-12
Half of the world's human population is infected with the stomach bacteria called Helicobacter pylori, yet it causes disease in only about 10 percent of those infected. Other bacteria living in the stomach may be a key factor in whether or not H. pylori causes disease, according to a new study led by scientists at the University of California, Santa Cruz.
"People tend to think of the stomach as a relatively sterile environment, but it's actually populated with microbes," said Karen Ottemann, professor and chair of microbiology and environmental toxicology at UC Santa ...
Nearly a third of antibiotic prescriptions for dialysis patients inappropriate
2013-03-12
Patients who receive hemodialysis are at a significant risk of developing infections, a leading cause of hospitalization and death in this patient population. A new study highlights the need to improve antibiotic use in outpatient dialysis facilities as data shows nearly a third of antibiotic prescriptions are deemed inappropriate. The study is published in the April issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
The United States Renal Data System reported that from 1993 to 2010, the number of ...
Computer model may help athletes and soldiers avoid brain damage and concussions
2013-03-12
Concussions can occur in sports and in combat, but health experts do not know precisely which jolts, collisions and awkward head movements during these activities pose the greatest risks to the brain. To find out, Johns Hopkins engineers have developed a powerful new computer-based process that helps identify the dangerous conditions that lead to concussion-related brain injuries. This approach could lead to new medical treatment options and some sports rule changes to reduce brain trauma among players.
The research comes at a time when greater attention is being paid ...
BUSM study reveals therapeutic targets to alter inflammation, type 2 diabetes
2013-03-12
New research from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) reveals that B cells regulate obesity-associated inflammation and type 2 diabetes through two specific mechanisms. The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academies of Sciences, indicates the importance of continuing to explore B cells as a therapeutic target to treat these diseases. Barbara Nikolajczyk, PhD, associate professor of microbiology at BUSM, is the study's senior author.
The incidence of diabetes continues to rise at alarming rates. According to the National Institute of Diabetes ...
Sri Lankan snake study reveals new species, rich biodiversity in island country
2013-03-12
WASHINGTON Alex Pyron's expertise is in family trees. Who is related to whom, who begat whom, how did they get where they are now. But not for humans: reptiles.
In 2011, his fieldwork in Sri Lanka studying snake diversity on the island led him to confirm the identity of 60 known species of snakes. With Sri Lankan collaborators, Ruchira Somaweera, an author on snakes and expert on amphibians and reptiles, and Dushantha Kandambi, a local naturalist and snake expert, the team collected 60 species of snakes and of those, Dr. Pyron used DNA sequencing technology on 40 of them. ...
[1] ... [5041]
[5042]
[5043]
[5044]
[5045]
[5046]
[5047]
[5048]
5049
[5050]
[5051]
[5052]
[5053]
[5054]
[5055]
[5056]
[5057]
... [8800]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.