Cities can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 70 percent, says U of T researcher
2013-02-13
TORONTO, ON – Cities around the world can significantly reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by implementing aggressive but practical policy changes, says a new study by University of Toronto Civil Engineering Professor Chris Kennedy and World Bank climate change specialist Lorraine Sugar, one of Kennedy's former students.
Kennedy and Sugar make the claim in 'A low carbon infrastructure plan for Toronto, Canada,' published in the latest issue of The Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering. The paper aims to show how cities can make a positive difference using realistic, ...
Stanford scientist uncovers the reproductive workings of a harvester ant dynasty
2013-02-13
Ants are just about everywhere you look, and yet it's largely unknown how they manage to be so ubiquitous. Scientists have understood the carnal mechanism of ant reproduction, but until now have known little of how successful the daughters of a colony are when they attempt to found new colonies.
For the first time, Stanford biologists have been able to identify specific parent ants and their own children in wild ant colonies, making it possible to study reproduction trends.
And in a remarkable display of longevity, an original queen ant was found to be producing new ...
Major clinical trial finds no link between genetic risk factors and 2 top wet AMD treatments
2013-02-13
SAN FRANCISCO – February 12, 2013 – New findings from a landmark clinical trial show that although certain gene variants may predict whether a person is likely to develop age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a potentially blinding eye disease that afflicts more than nine million Americans, these genes do not predict how patients will respond to Lucentis™ and Avastin™, the two medications most widely used to treat the "wet" form of AMD. This new data from the Comparison of AMD Treatment Trials (CATT), published online in Ophthalmology, the journal of the American Academy ...
Explosive breakthrough in research on molecular recognition
2013-02-13
Edmonton—Ever wonder how sometimes people still get through security with explosives on their person? Research done in the University of Alberta's Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering has revealed a new way to better detect these molecules associated with explosive mixtures.
A team of researchers including post-doctoral fellows Seonghwan Kim, Dongkyu Lee and Xuchen Liu, with research associate Charles Van Neste, visiting professor, Sangmin Jeon from the Pohang University of Science and Technology (South Korea), and Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering ...
Lower autism risk with folic acid supplements in pregnancy
2013-02-13
Women who took folic acid supplements in early pregnancy almost halved the risk of having a child with autism. Beginning to take folic acid supplements later in pregnancy did not reduce the risk. This is shown in new findings from the ABC Study and Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study published in the Journal of The American Medical Association (JAMA).
Women who took folic acid supplements from four weeks before conception to eight weeks into pregnancy had a 40 per cent lower risk of giving birth to children with childhood autism (classic autism). Use of folic acid ...
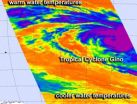
NASA sees Cyclone Gino wind up to wind down later
2013-02-13
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Cyclone Gino as the storm continues to wind up in the southern Indian Ocean, consolidating and strengthening. Infrared data shows the storm has strengthened but it is headed for cooler waters which will weaken it in coming days.
On Feb. 12 at 0841 UTC, NASA Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard the Aqua satellite captured infrared imagery of Cyclone Gino that showed the storm developed a large area of very cold, high cloud top temperatures around its center indicating powerful thunderstorms. Cloud top temperatures ...
NASA provides satellite views of nor'easter lifespan
2013-02-13
NASA and NOAA satellites have provided animations and images of the coupling of two low pressure areas that created the now historic winter-time nor'easter that brought more than two feet of snow to portions of the New England states on Feb. 8 and 9, 2013. NASA released an animation of NOAA satellite imagery that shows the lifetime of the historic nor'easter.
The nor'easter dropped between 2 and 3 feet of snowfall over the U.S. Northeast and left more than 650,000 without power in eight states, according to the Associated Press. Several governors established travel bans ...
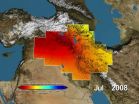
NASA satellites find freshwater losses in Middle East
2013-02-13
A new study using data from a pair of gravity-measuring NASA satellites finds that large parts of the arid Middle East region lost freshwater reserves rapidly during the past decade.
Scientists at the University of California, Irvine; NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.; and the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colo., found during a seven-year period beginning in 2003 that parts of Turkey, Syria, Iraq and Iran along the Tigris and Euphrates river basins lost 117 million acre feet (144 cubic kilometers) of total stored freshwater. That ...
Gaps in mental health infrastructure for youth identified in many US communities
2013-02-13
ATLANTA- Mental health facilities that provide outpatient specialty services for youth are a critical element of the mental health care infrastructure, especially for youth who are uninsured or publically insured.
In a Viewpoint article in the February 13 issue of JAMA, Janet Cummings, PhD, assistant professor of health policy and management at Emory's Rollins School of Public Health, presents data from the 2008 National Survey of Mental Health Treatment Facilities and examines the extent to which gaps exist in the mental health treatment system for youth.
Based ...
In some dystonia cases, deep brain therapy benefits may linger after device turned off
2013-02-13
LOS ANGELES (Feb. 12, 2013) – Two patients freed from severe to disabling effects of dystonia through deep brain stimulation therapy continued to have symptom relief for months after their devices accidentally were fully or partly turned off, according to a report published online Feb. 11 in the journal Movement Disorders.
"Current thought is that symptoms will worsen within hours or days of device shut-off, but these two young men continued to have clinical benefit despite interruption of DBS therapy for several months. To our knowledge, these two cases represent the ...
Novel test streamlines testing for Huntington Disease
2013-02-13
Philadelphia, PA, February 13, 2013 – A new test may help to streamline genetic testing for Huntington Disease (HD) by generating accurate results, avoiding unnecessary additional testing, and improving turnaround time. The test, which uses chimeric or triplet repeat primed PCR (TP PCR) methodology, yielded results that were 100% concordant with standard genotyping methods in an analysis of 246 samples. The high sensitivity and specificity of the test could reduce the number of false negative results and facilitate both diagnosis and prognosis by correctly sizing the genetic ...
Scientists should advance management of behavioral norms
2013-02-13
Researchers should study how people's social and personal norms are influenced by behavior and use their insights to help governments promote pro-environmental actions, a distinguished group of scholars writes in the March issue of BioScience. The authors maintain that effective policies induce not only short-term changes in behavior but also long-term changes in norms. More effective management of social norms will be necessary, they write, to persuade the public to accept the inconvenience and expense of many environmental policies.
The interdisciplinary group, led by ...
Colorado DUI checkpoints lead to over 1,300 arrests in one weekend
2013-02-13
Colorado DUI checkpoints lead to over 1,300 arrests in one weekend
Article provided by James L. Finegan, P.C.
Visit us at http://www.fineganduilaw.com
The Colorado Department of Transportation (CDOT) reports that over 26,000 people in the state are arrested for driving under the influence, or DUI, every year. These arrests are not just from enforcement officers pulling over obviously impaired drivers or issuing tickets after an accident, but also the result of officers testing drivers at DUI checkpoints.
The state uses these checkpoints throughout the year, often ...
Slips, trips and falls: Serious hazard for nursing home residents
2013-02-13
Slips, trips and falls: Serious hazard for nursing home residents
Article provided by Ginsberg & Katsorhis, P.C.
Visit us at http://www.gkf-law.com
When we must place a loved one in the care of a nursing home, we must rely on the facility to protect the physical safety of the resident from a wide range of potential hazards. Falls are one of the most common risks to a resident's safety in these environments.
In fact, recent research from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration has revealed that nursing homes are also especially hazardous for the ...
Despite Increased Regulation, Truck Accident Fatalities Increase
2013-02-13
Despite Increased Regulation, Truck Accident Fatalities Increase
Article provided by Gelber & O'Connell, LLC
Visit us at http://www.gelberoconnell.com
When you are driving down the road, there is always a chance that you could be involved in an accident. Regardless of how safely you drive, other motorists may not do the same, making an accident inevitable. Perhaps you console yourself by thinking that if such an accident occurred, it would likely be a fender-bender with little damage and few injuries.
However, if the other vehicle in the crash happens to ...
Criminal records need not haunt an ex-offender forever
2013-02-13
Criminal records need not haunt an ex-offender forever
Article provided by Knight & Cerritell LLC
Visit us at http://www.kclawyers.net/
A Connecticut resident who makes an unfortunate mistake leading to a criminal conviction can feel the consequences years later, even after serving whatever sentence and probation has been required.
Problems for ex-offenders
Across the nation, more than 10,000 people are released from America's prisons each week, according to the U.S. Department of Justice. Within three years after release, about two-thirds of them will ...
Swim Live with the Queen of Shark Tank
2013-02-13
The Small Businesses Do It Better live show platform includes an instant chat window where viewers interact with each other and the host, Carissa Dunphy. Throughout live programs, including this special episode with Barbara Corcoran, Carissa Dunphy fields questions from the audience, keeping the conversation dynamic, relevant and in absolute real-time.
"Watching a live streaming interview with the exceptional Barbara Corcoran is rare," says Carissa Dunphy, host of Small Businesses Do It Better. "Having the opportunity to ask her a question is almost inconceivable. ...
America's Most Visible Restaurant Expert Witness, Howard Cannon, Announces the Restaurant Expert Witness YouTube Channel
2013-02-13
Howard Cannon, Restaurant Expert Witness, and CEO says: "Each year our office receives thousands of calls requesting information about the services we provide. In response to those inquiries, and in an effort to help educate others about our restaurant litigation support and expert witness services, we developed a series of free videos that are available on our YouTube channel." http://www.youtube.com/restaurantexpertwtns
Mr. Cannon's videos have already received thousands of views - one of the highlights being his recent appearance on Anderson Cooper. Cannon ...
The Reparations of Bill Clinton at the Teflon Hall of Fame
2013-02-13
From David Letterman and Stephen Colbert to Tina Fey and John Stewart, there's no end in sight to Prime-Time comedy firing satirical darts in the face of Conservatives. Inspired by the lack of return fire at Liberals, author JC Shannon has taken it upon himself to prove that being blue doesn't make you immune from laughter.
In his new book, 'The Reparations of Bill Clinton', Shannon takes readers to his 'Teflon Hall of Fame' to meet a band of real-life characters worthy of wit.
Synopsis:
At the height of the Monica sex scandal, President Bill Clinton is taken to ...
Hot Stone Pedicures are Now Available in American Fork Utah By LA Nails 1
2013-02-13
Locals can now have hot stone pedicures in American Fork. Being the first salon that offers hot stone pedicures in American Fork, Utah. LA Nails 1 now provides nail services just like the pedicures at top luxury resorts. For those who are looking for first-class services and require experienced nail professionals who can work on nails, LA Nails 1 can be a great choice.
A hot stone pedicure is much like a normal pedicure with the addition of heated or hot stones that are applied to the foot and leg to give additional soothing and relaxation. Technicians are trained to ...
"Hear My Roar" Fashion Show and Benefit Event - Woman to Woman
2013-02-13
"Hear My Roar" Fashion Show and Benefit Event - March 9, 2013
On Saturday, March 9th, 2013 the Woman to Woman Ministries will host a Fashion Show and Benefit Event, at Best Western Airport Inn, 6815 West Kellogg Drive, Wichita, Kansas, from 1:00 pm to 5:00 pm. This event will honor and pay special tribute to children in our community. Admission is a $10 donation, with limited scholarships available.
Special guest will include: Ms. Sloane Lewis, Miss Kansas' Outstanding Teen and the Sunflower Princess mentoring programs. As a state ambassador for the state ...
Summertime Entertainment's Dorothy of Oz Film Garners Nomination in "The Earnies" Social Media Awards
2013-02-13
Totally Toto Tuesday, a Facebook campaign created to help rescue Cairn terriers from animal shelters across the country and promote Summertime Entertainment's upcoming 3D animated feature film Dorothy of Oz, has been nominated for "The Earnies," PR Newswire's community-chosen awards program that honors excellence in earned media through social-media channels.
Competing in the category of "Best Connection to Twitter, LinkedIn or Facebook Audience," the highly effective campaign on the Dorothy of Oz Facebook page features a photo of a Cairn terrier, ...
Young Entrepreneur Council Announces the Newest Addition to Their Elite Membership Roster: Andrew Loos
2013-02-13
Attack! Marketing is pleased to announce the appointment of their Co-Founder/CXO, Andrew Loos as a member of the Young Entrepreneur Council. YEC is an invite-only nonprofit organization comprised of innovators from every market sector and industry. Membership recognizes individuals who have demonstrated outstanding professional achievement and is considered one of the highest honors for young entrepreneurs.
"We see Andrew as a real thought leader within the marketing industry right now and feel his contribution to the YEC community is going to be invaluable. He ...
Now Available New Release Non Fiction- Celibacy's Child
2013-02-13
Celibacy's Child by Lisa B. Overton is an emotionally rigged, true story of a women's life starting from the first day she was brought into this world up to the present. This moving story details her experience growing up as the child of a Catholic priest and an ex-nun who entered into a 30+ year clandestine love affair.
The author, Lisa B. Overton tells the poignant story of her childhood and how she survived loneliness, shame and hypocrisy in her parents' painful and secretive shadow and how she eventually forgave them both.. It was on her mother's death bed that Lisa ...
Space Age Gizmos Fast Gaining Popularity as an Online Electronics Gadget Store
2013-02-13
Space Age Gizmos is an online company that sells all kinds of electronic products. However, it mainly specializes in car audio and video systems, marine electronics, gaming accessories and retro gaming systems, portable audio systems and headphones. The company stocks merchandise from leading brands in the electronics industry, such as Jensen, Hyperkin, JVC, Kenwood, Pioneer and Boss, to name a few. Most of their customers buy car amplifiers and car subwoofers, with headphones and car audio CD players also making quick sales.
The website http://www.spaceagegizmos.com/ ...
[1] ... [5224]
[5225]
[5226]
[5227]
[5228]
[5229]
[5230]
[5231]
5232
[5233]
[5234]
[5235]
[5236]
[5237]
[5238]
[5239]
[5240]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.