Immunity for surrendered guns in South Brunswick? There's a catch
2013-02-09
Gun crime has received increased attention in recent weeks. Communities across the nation, including many in New Jersey, have been highlighting programs that allow area residents to turn in unwanted firearms to local authorities.
"Project Safe Surrender," a public awareness program aimed at getting weapons off the streets, is the latest initiative launched by police in South Brunswick. Under the terms of the program, individuals can turn into unwanted guns to the police, and in return receive immunity from weapons charges. However, the offer of immunity is ...
Distracted driving leading cause of auto accidents
2013-02-09
Even though the dangers of distracted driving are widely-publicized, it seems that the message has not sunk in to every driver. According to the Transportation Safety Group at the National Safety Council, driver distraction is the leading cause of motor vehicle accidents. The Group found distraction is a factor in about 80 percent of car accidents. Before picking up the phone while behind the wheel, Illinois drivers should consider the dangers of distracted driving and the state's laws about distracted driving.
Dangers of distracted driving
The U.S. Department of ...
Distracted driving dangers -- and what Nevada is doing about it
2013-02-09
Texting or talking to a client who has a question that can't wait until the morning. Putting on makeup or getting in a quick shave before a job interview. Eating breakfast or drinking your morning coffee on the go. Setting your GPS as you set off on a long weekend. Even disciplining squabbling siblings in the back seat. Sound familiar? That's because many people do all of these things while behind the wheel -- and more -- without thinking twice. More important, they often believe that they are still in control of their vehicle at the time and that accidents only happen ...
V2 Cigs Announces Irresistible Offer for Valentine's Day
2013-02-09
Ranked number one according to a consumer-based review conducted by EcigaretteReviewed.com and a myriad of other websites, V2 Cigs has put forth its stellar product the 'V2 Couples Kit' on an exclusive Valentine's Day discount. Customers can further obtain an additional discount by using the special coupon code brought to them by E Cigarette Reviewed.
In light of the upcoming Valentine's Day, the formerly priced $124.95 V2 Couples Kit can now be purchased at $79.96 with the V2 Cigs coupon. Inclusive in the kit are 4 V2 Batteries, 2 Wall Adaptors, 2 NEW Smart Chargers, ...
For the Second Quarter in a Row Visitor Numbers to Bridesandlovers.com Has Doubled Affirming its Position as One of the Largest and Fastest Growing Russian Brides Sites Online
2013-02-09
The newly rebranded Bridesandlovers.com has once again achieved a major milestone, for the second quater in a row visitor numbers to the site has doubled affirming its position as one of the largest and fastest growing Russian brides sites online.
A special page has been created for men searching for Ukrainian brides, http://www.bridesandlovers.com/marry_ukrainian_brides.php
Bridesandlovers.com operate In an increasingly competitive dating niche, the site distinguishes itself with a diverse international membership database made up of Russian women living in Russia ...
Hotter Comfort Concept Introduces 32 New Ladies Styles for Spring 2013
2013-02-09
Hotter Comfort Concept has launched its new collection for spring 2013 with 32 new ladies styles.
Shoe fans will be delighted with the new collection; each and every style has been designed with style seeking customers in mind and comes in the latest on-trend seasonal shades.
The new range features styles for every shoe-loving customer and covers all their wardrobe dilemmas. Hotter's signature collection has shoes for summer days, work shoes, designs for glamorous evenings out with friends, casual styles for everyday wear and the active collection features shoes ...
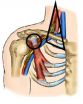
Surgeons find better ways to treat nerve compression disorder that can sideline athletes
2013-02-08
Two new studies from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis suggest ways to improve surgical treatment for a debilitating condition caused by compressed nerves in the neck and shoulder.
The condition, neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome, causes pain, numbness or tingling in the shoulder, arm or hand and is perhaps best known for affecting baseball pitchers and other elite athletes. Patients often describe pain and tension in the neck and upper back, numbness and tingling in the fingers, headaches and perceived muscle weakness in the affected limb.
Treatment ...
Few pregnant women treated for sexually transmitted infections
2013-02-08
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- Many pregnant women with sexually transmitted infections aren't getting the treatment they need when they visit emergency rooms, according to a new Michigan State University study that highlights a wholly preventable risk to unborn children and raises questions about current medical guidelines.
About half of the 735 women with gonorrhea or chlamydia who visited the ERs at three hospitals in Grand Rapids, Mich. from 2008 through 2010 did not get treatment there, despite the availability of effective and relatively inexpensive antibiotics. Of the ...
Surveillance system can identify and track emerging infectious diseases
2013-02-08
A team of researchers have developed a method to identify the cause of infectious disease outbreaks based on online reports about the symptoms, the season, and the ratio of cases to fatalities. Using data from the Internet outbreak reporting system ProMED-mail, the researchers applied this method to more than 100 outbreaks of encephalitis in South Asia, recently identified as an emerging infectious disease "hotspot," to determine which of 10 infectious diseases was causing symptoms of encephalitis, and whether Nipah -- a serious emerging infection -- could be reliably differentiated ...
Researchers explore quantum entanglement
2013-02-08
Albert Einstein called quantum entanglement—two particles in different locations, even on other sides of the universe, influencing each other—"spooky action at a distance."
Einstein made the comment while criticizing quantum mechanics as incomplete—the phenomenon of quantum entanglement seems to be at odds with Einstein's theory of relativity.
"Eighty years after Einstein, quantum physics is still so mysterious that there are many different interpretations of its physical meaning. All the interpretations agree on what is going to be observed in any given experiment, ...
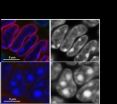
A*STAR scientists' groundbreaking discovery of nucleus structure crucial to understanding diseases
2013-02-08
1. Scientists from Singapore and Germany have identified that the proteins lamin A (Lmna) and lamin B receptor (Lbr) are essential for holding silent genes in their correct position at the edge of the nucleus, in the form of heterochromatin . A deviation from their normal position will cause the genes to malfunction, leading to heart failure, vascular disease and muscle wasting.
2. For hundreds of years before this discovery, scientists were puzzled by why heterochromatin clustered at the edge of the nucleus and how it was relevant to normal cell function. This recent ...
Rooting out recurrent breast cancer
2013-02-08
Due to chemotherapy resistance and a high rate of relapse, triple negative cancers are among the most difficult breast cancers to treat. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers led by Carlos Arteaga at Vanderbilt University identified a protein, TGF-β, that is highly expressed in triple negative breast cancer cells after chemotherapy. In a mouse model of breast cancer, TGF-β both diverted cells down a path to becoming cancerous and allowed for cancer to come back after treatment. Importantly, loss of TGF-β prevented tumor recurrence ...
New insight into RASopathy-associated lymphatic defects
2013-02-08
The RAS pathway is a cellular signaling pathway that regulates growth and development in humans. RASopathies are a group of diseases characterized by defects in RAS signaling. Many patients with RASopathies present with defects in the lymphatic system, which removes excess fluid from tissues, absorbs fats from the digestive system, and transports immune cells. To determine how alterations in the RAS pathway affect development of the lymphatic system, researchers at Yale University generated transgenic mice that expressed mutations associated with a RASopathy known as Noonan ...
Targeting T cells in rheumatoid arthritis
2013-02-08
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder in which immune cells attack the joints, causing inflammation, swelling, and erosion. Specific sets of immune cells, known as T cells, are responsible for inducing disease. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers led by Harvey Cantor at Harvard University analyzed the contributions of different subsets of T cells to an RA-like condition in mice. Cantor and colleagues identified a subset of regulatory T cells (CD8+ Tregs) that can remove pathogenic T cell subsets and inhibit disease progression. ...
JCI early table of contents for Feb. 8, 2013
2013-02-08
Rooting out recurrent breast cancer
Due to chemotherapy resistance and a high rate of relapse, triple negative cancers are among the most difficult breast cancers to treat. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers led by Carlos Arteaga at Vanderbilt University identified a protein, TGF-β, that is highly expressed in triple negative breast cancer cells after chemotherapy. In a mouse model of breast cancer, TGF-β both diverted cells down a path to becoming cancerous and allowed for cancer to come back after treatment. Importantly, loss ...
Comparing mechanical clot removal and standard medical therapy for severe stroke
2013-02-08
WASHINGTON – Results of the first randomized controlled study to evaluate a procedure that removes blood clots in the brain from patients experiencing severe strokes will be presented at the International Stroke Conference in Honolulu, Hawaii on Feb. 8. The study also evaluates if imaging techniques were helpful in identifying patients who potentially would benefit most from clot removal.
In addition to the presentation, the full study, led by Chelsea Kidwell, M.D., professor of neurology and director of the Stroke Center at Georgetown University Medical Center, will ...
Yeast we can! New report answers questions on microbiology and beer
2013-02-08
WASHINGTON, DC – February 5, 2013 – What do microbes have to do with beer? Everything! Because the master ingredient in beer is yeast – a microbe – and every step in the brewing process helps the yeast do its job better. A new freely-available report; FAQ: If the Yeast Ain't Happy, Ain't Nobody Happy: The Microbiology of Beer explores the synergy between microbiology and brewing beer.
"Every time someone brews a batch of beer, in a very real sense he or she is doing a microbiology experiment. If you brew beer at home, you're a microbiologist.' says Dr. Charles Bamforth ...
Genetics Society of America's Genetics journal highlights for February 2013
2013-02-08
Bethesda, MD—February 8, 2013 – Listed below are the selected highlights for the February 2013 issue of the Genetics Society of America's journal, Genetics. The February issue is available online at www.genetics.org/content/current. Please credit Genetics, Vol. 193, February 2013, Copyright © 2013.
Please feel free to forward to colleagues who may be interested in these articles on population and evolutionary genetics; gene expression; genome and systems biology; and methods, technology and resources.
ISSUE HIGHLIGHTS
Population and Evolutionary Genetics
Patterns ...
Combining plasma screening methods better identifies diagnostic and therapeutic targets
2013-02-08
BETHESDA, MD — February 8, 2013 — For the first time, scientists have combined genomic and proteomic analysis of blood plasma to enhance identification of genetically regulated protein traits. This could be applied to any large association study of civilization diseases where blood plasma has been collected, vastly improving a clinician's ability to identify disease susceptibility in individuals and populations. This advance is published in the February 2013 issue of the journal Genetics.
"We hope that combining genome-wide with proteome-wide screening of blood plasma ...
Putting our heads together: Canines may hold clues to human skull development
2013-02-08
BETHESDA, MD – February 8, 2013 -- Man's best friend may touch our hearts with their empathy, companionship, playfulness and loyalty, and they may also lead us to a deeper understanding of our heads.
In the article, "The Genetics of Canine Skull Shape Variation," in the February issue of the Genetics Society of America's journal, Genetics, Jeffrey J. Schoenebeck, PhD, and Elaine A. Ostrander, PhD, researchers at the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), the National Institutes of Health (NIH), review progress in defining the genes and pathways that determine ...
Physicians' belief about obesity causes impacts advice and care
2013-02-08
How physicians view the causes of obesity may impact the advice they give their patients. The findings are from a new study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health who compared the relationship between primary care physicians' beliefs about the causes of obesity with the frequency of nutritional counseling. They found that physicians who believed over consumption of food to be a major contributor to obesity were significantly more likely to counsel their patients to modify nutritional habits. The results are featured in the February 2013 ...
New strategy prevents rheumatoid arthritis in mice
2013-02-08
BOSTON—Dana-Farber Cancer Institute scientists have demonstrated a new strategy for treating autoimmune disease that successfully blocked the development of rheumatoid arthritis in a mouse model. They say it holds promise for improved treatment of arthritis and other autoimmune disorders in people.
The scientists report in the Journal of Clinical Investigation that infusing a highly specific type of cell that regulates immune responses into arthritis-prone mice shut down the cascade of inflammation that damages tissues and joints.
The method worked best when the infusions ...
New brain-test app
2013-02-08
Two years ago, researcher Josef Bless was listening to music on his phone when he suddenly had an idea.
"I noticed that the sounds of the different instruments were distributed differently between the ears, and it struck me that this was very similar to the tests we routinely use in our laboratory to measure brain function. In dichotic listening, each ear is presented with a different syllable at the same time (one to the left and one to the right ear) and the listener has to say which syllable seems clearest. The test indicates which side of the brain is most active during ...
Implants make light work of fixing broken bones
2013-02-08
Artificial bone, created using stem cells and a new lightweight plastic, could soon be used to heal shattered limbs.
The use of bone stem cells combined with a degradable rigid material that inserts into broken bones and encourages real bone to re-grow has been developed at the Universities of Edinburgh and Southampton.
Researchers have developed the material with a honeycomb scaffold structure that allows blood to flow through it, enabling stem cells from the patient's bone marrow to attach to the material and grow new bone. Over time, the plastic slowly degrades as ...
New insight on relationship between parents, preschoolers and obesity
2013-02-08
PULLMAN, Wash. - While sugary drinks, lack of exercise and genetics contribute to a growing number of overweight American children, new research from Washington State University reveals how a mom's eating habits and behavior at the dinner table can influence her preschooler's obesity risk.
The findings come from WSU alumna Halley Morrison's undergraduate honors thesis, which recently was published in the journal Appetite.
As a biology major and student fitness instructor, Morrison knew she wanted to focus on health and the human body. She learned about the childhood ...
[1] ... [5244]
[5245]
[5246]
[5247]
[5248]
[5249]
[5250]
[5251]
5252
[5253]
[5254]
[5255]
[5256]
[5257]
[5258]
[5259]
[5260]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.