Drug abuse impairs sexual performance in men even after rehabilitation
2013-01-17
Researchers at the University of Granada, Spain, and Santo Tomas University in Colombia have found that drug abuse negatively affects sexual performance in men even after years of abstinence. This finding contradicts other studies reporting that men spontaneously recovered their normal sexual performance at three weeks after quitting substance abuse.
The results of this study have been published in the prestigious Journal of Sexual Medicine, the official journal of the International Society for Sexual Medicine. The authors of this paper are Pablo Vallejo Medina –a professor ...
Trading wetlands no longer a deal with the devil
2013-01-17
URBANA – If Faust had been in the business of trading wetlands rather than selling his soul, the devil might be portrayed by the current guidelines for wetland restoration. Research from the University of Illinois recommends a new framework that could make Faustian bargains over wetland restoration sites result in more environmentally positive outcomes.
U of I ecologist Jeffrey Matthews explained that under the current policies if a wetland is scheduled for development and a negative impact is unavoidable, the next option is to offset, or compensate, for the destruction ...
UNC researchers use luminescent mice to track cancer and aging in real-time
2013-01-17
Chapel Hill, NC – In a study published in the January 18 issue of Cell, researchers from the University of North Carolina Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center have developed a new method to visualize aging and tumor growth in mice using a gene closely linked to these processes.
Researchers have long known that the gene, p16INK4a (p16), plays a role in aging and cancer suppression by activating an important tumor defense mechanism called 'cellular senescence'. The UNC team led by Norman Sharpless, MD, Wellcome Distinguished Professor of Cancer Research and Deputy Cancer ...
How are middle-aged women affected by burnout?
2013-01-17
New Rochelle, NY, January 17, 2013—Emotional exhaustion and physical and cognitive fatigue are signs of burnout, often caused by prolonged exposure to stress. Burnout can cause negative health effects including poor sleep, depression, anxiety, and cardiovascular and immune disorders. The findings of a 9-year study of burnout in middle-aged working women are reported in an article in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://www.liebertpub.com/jwh.
In ...
Researchers create method for more sensitive electrochemical sensors
2013-01-17
Graphene and related materials hold promise for the future of electrochemical sensors — detectors that measure the concentration of oxygen, toxic gases, and other substances — but many applications require greater sensitivity at lower detection ranges than scientists have been able to achieve.
A Northwestern University research team and partners in India have recently developed a new method for amplifying signals in graphene oxide-based electrochemical sensors through a process called "magneto-electrochemical immunoassay." The findings could open up a new class of technologies ...
Guided care provides better quality of care for chronically ill older adults
2013-01-17
Patients who received Guided Care, a comprehensive form of primary care for older adults with chronic health problems, rated the quality of their care much higher than patients in regular primary care, and used less home care, according to a study by researchers at Johns Hopkins University. In an article published online by the Journal of General Internal Medicine, researchers found that in a 32-month randomized controlled trial, Guided Care patients rated the quality of their care significantly higher than those in normal care, and were 66 percent more likely to rate their ...
New key to organism complexity identified
2013-01-17
The enormously diverse complexity seen amongst individual species within the animal kingdom evolved from a surprisingly small gene pool. For example, mice effectively serve as medical research models because humans and mice share 80-percent of the same protein-coding genes. The key to morphological and behavioral complexity, a growing body of scientific evidence suggests, is the regulation of gene expression by a family of DNA-binding proteins called "transcription factors." Now, a team of researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory ...
Hearing-loss-prevention drugs closer to reality thanks to new UF test
2013-01-17
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — A new way to test anti-hearing-loss drugs in people could help land those medicines on pharmacy shelves sooner. University of Florida researchers have figured out the longstanding problem of how to safely create temporary, reversible hearing loss in order to see how well the drugs work. The findings are described in the November/December 2012 issue of the journal Ear & Hearing.
"There's a real need for drug solutions to hearing loss," said lead investigator Colleen Le Prell, Ph.D., an associate professor in the department of speech, language, and hearing ...
The new age of proteomics: An integrative vision of the cellular world
2013-01-17
The enormous complexity of biological processes requires the use of highperformance technologies —also known as 'omics'—, that are capable of carrying out complete integrated analyses of the thousands of molecules that cells are made up of, and of studying their role in illnesses. In the post-genomic age we find ourselves in, the comprehensive study of cellular proteins —prote-omics— acquires a new dimension, as proteins are the molecular executors of genes and, therefore, the most important pieces of the puzzle if we wish to understand more completely how cells work.
The ...
Implicit race bias increases the differences in the neural representations of black and white faces
2013-01-17
Racial stereotypes have been shown to have subtle and unintended consequences on how we treat members of different race groups. According to new research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, race bias also increases differences in the brain's representations of faces.
Psychological scientists Tobias Brosch of the University of Geneva in Switzerland and Eyal Bar-David and Elizabeth Phelps of New York University examined activity in the brain while participants looked at pictures of White and Black faces. Afterwards, ...
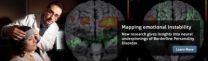
New insights into the 'borderline personality' brain
2013-01-17
New work by University of Toronto Scarborough researchers gives the best description yet of the neural circuits that underlie a severe mental illness called Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD), and could lead to better treatments and diagnosis.
The work shows that brain regions that process negative emotions (for example, anger and sadness) are overactive in people with BPD, while brain regions that would normally help damp down negative emotions are underactive.
People with BPD tend to have unstable and turbulent emotions which can lead to chaotic relationships with ...
Lack of key enzyme in the metabolism of folic acid leads to birth defects
2013-01-17
AUSTIN, Texas — Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have discovered that the lack of a critical enzyme in the folic acid metabolic pathway leads to neural tube birth defects in developing embryos.
It has been known for several decades that folic acid supplementation dramatically reduces the incidence of neural tube defects, such as spina bifida and anencephaly, which are among the most common birth defects. In some populations, folic acid supplementation has decreased neural tube defects by as much as 70 percent.
However, scientists still do not fully ...
New UAlberta research shows commonly prescribed medications could have adverse effects
2013-01-17
A research team with the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry at the University of Alberta reported findings that significantly improve understanding of how widely used drugs in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) affect the heart health of treated patients.
The research shows that medications often prescribed for PAH could block the function of an important hormone in the heart, decreasing the strength of contraction of the right heart chambers, a potentially important and yet unrecognized adverse effect.
PAH is a disease that affects the blood vessels of the lungs, causing ...
Novel technique reveals dynamics of telomere DNA structure
2013-01-17
Biomedical researchers studying aging and cancer are intensely interested in telomeres, the protective caps on the ends of chromosomes. In a new study, scientists at UC Santa Cruz used a novel technique to reveal structural and mechanical properties of telomeres that could help guide the development of new anti-cancer drugs.
Telomeres are long, repetitive DNA sequences at the ends of chromosomes that serve a protective function analogous to that of the plastic tips on shoelaces. As cells divide, their telomeres get progressively shorter, until eventually the cells stop ...
Diabetic fruit flies support buzz about dietary sugar dangers
2013-01-17
LA JOLLA, Calif., January 15, 2013 – Regularly consuming sucrose—the type of sugar found in many sweetened beverages—increases a person's risk of heart disease. In a study published January 10 in the journal PLOS Genetics, researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute and Mount Sinai School of Medicine used fruit flies, a well-established model for human health and disease, to determine exactly how sucrose affects heart function. In addition, the researchers discovered that blocking this cellular mechanism prevents sucrose-related heart problems.
"Our study ...
NFL players may be at higher risk for depression as they age
2013-01-17
SAN DIEGO – National Football League (NFL) players may be at increased risk of depression as they age due to brain damage resulting from concussions, according to two studies released today that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 65th Annual Meeting in San Diego, March 16 to 23, 2013.
"The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that about 1.6 to 3.8 million sports concussions occur each year. While it is known that sports concussions can cause immediate disturbances in mood and thinking, few studies have investigated the long-term ...
Shorter woman, taller man: Preferences for partner height translate into actual partner choices
2013-01-17
Finding Mr. or Ms. Right is a complicated process, and choosing a mate may involve compromising on less important factors like their height. However, research published January 16 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Gert Stulp and colleagues from the University of Groningen, Netherlands suggests that despite the many other factors involved, people's preferences for a partner's height are reflected in real couples in the UK.
Given the average heights of men and women in typical Western populations, two out of every hundred couples should comprise a woman who is taller ...
Warmest spring on record causes earliest flowering ever observed in eastern U.S.
2013-01-17
Exceptionally warm spring weather in 2010 and 2012 resulted in the earliest flowering times known in 161 years of recorded history at two sites in the eastern US, according to research published January 16 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Elizabeth Ellwood of Boston University and colleagues.
Many plants need a long winter break to undergo physiological changes that make them bloom in the spring. According to several previous studies, this blooming is occurring earlier than before due to warmer springs caused by climate change. The consequences of such early flowering ...
Earliest sea cow ancestors originated in Africa, lived in fresh water
2013-01-17
A new fossil discovered in Tunisia represents the oldest known ancestor of modern-day sea cows, supporting the African origins of these marine mammals. The find is described in research published January 16 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Julien Benoit and colleagues from the University of Science and Technology in Montpellier, France.
Some fossils of sea cow ancestors have been found in Jamaica, but the Tunisian fossil is more primitive and pre-dates these, revealing an older ancestor for sea cows that emerged at the same time as other modern mammals. Unlike ...
'Shell-shocked' crabs can feel pain
2013-01-17
The latest study by Professor Bob Elwood and Barry Magee from Queen's School of Biological Sciences looked at the reactions of common shore crabs to small electrical shocks, and their behaviour after experiencing those shocks. The research has been published in the Journal of Experimental Biology.
Professor Elwood's previous research showed that prawns and hermit crabs respond in a way consistent with pain. This latest study provides further evidence of this.
Professor Elwood said: "The experiment was carefully designed to distinguish between pain and a reflex phenomenon ...
New study sheds light on the origin of the European Jewish population
2013-01-17
Despite being one of the most genetically analysed groups, the origin of European Jews has remained obscure. However, a new study published online today (Thursday) in the journal Genome Biology and Evolution by Dr Eran Elhaik, a geneticist at the Johns Hopkins School of Public Health, argues that the European Jewish genome is a mosaic of Caucasus, European, and Semitic ancestries, setting to rest previous contradictory reports of Jewish ancestry. Elhaik's findings strongly support the Khazarian Hypothesis, as opposed to the Rhineland Hypothesis, of European Jewish origins. ...
Seeing beyond cameras: Predicting where people move in CCTV blind spots
2013-01-17
A new model from Queen Mary, University of London could be a useful security tool in tracking people in large, busy venues such as airport terminals and shopping centres.
The research fuses information gathered from multiple Close-Circuit Television (CCTV) network cameras and geographical maps for the first time, and could be useful in locating people in blind-spots where the CCTV cannot see, known as invisible areas.
Co-author Professor Andrea Cavallaro and director of Queen Mary's Centre for Intelligent Sensing, based in the School of Electronic Engineering and ...
Study suggests lung cancer mortality highest in black persons living in most segregated counties
2013-01-17
CHICAGO – Lung cancer mortality appears to be higher in black persons and highest in blacks living in the most segregated counties in the United States, regardless of socioeconomic status, according to a report published in the January issue of JAMA Surgery, a JAMA Network publication.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in the United States and blacks are disproportionately affected with the highest incidence and mortality rates.
Awori J. Hayanga, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues examined the relationship between race ...
Smartphone applications assessing melanoma risk appear to be highly variable
2013-01-17
CHICAGO – Performance of smartphone applications in assessing melanoma risk is highly variable and 3 of 4 applications incorrectly classified 30 percent or more of melanomas as unconcerning, according to a report published Online First by JAMA Dermatology, a JAMA Network publication.
To measure the performance of smartphone applications that evaluate photographs of skin lesions and provide the user with feedback about the likelihood of malignancy, Joel A. Wolf, B.A., and colleagues at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, tested the sensitivity, specificity, and ...
UAlberta medical researchers find DNA marker that predicts breast cancer recurrence
2013-01-17
Medical researchers at the University of Alberta tested the DNA of more than 300 women in Alberta and discovered a 'genetic marker' method to help accurately profile which women were more apt to have their breast cancer return years later.
Sambasivarao Damaraju, a professor with the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, and at the Cross Cancer Institute just published his team's findings in the peer-reviewed journal, PLoS One. Using a simple blood test, Damaraju and his team, which included his PhD student Yadav Sapkota, scanned the entire human genome of 369 women who had ...
[1] ... [5352]
[5353]
[5354]
[5355]
[5356]
[5357]
[5358]
[5359]
5360
[5361]
[5362]
[5363]
[5364]
[5365]
[5366]
[5367]
[5368]
... [8825]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.