In Honor of Sandy Hook Victims, SafeSchools to Provide Free 'Aftermath of Tragedy' Resources to All Schools
2012-12-19
SafeSchools, LLC, the leader in web-based safety and compliance solutions for schools, today announced that they would provide complimentary access to their 'Managing the Aftermath of Tragedy' courses to every school district in the U.S. and Canada.
"As news of the shootings at Sandy Hook Elementary School reached our offices on Friday, our hearts were broken once again by another senseless school shooting," said Brian Taylor, President and Chief Executive Officer, SafeSchools. "We know that every school district grieves with the Newtown community and ...
Purines fend off surgery-related damage
2012-12-18
Anesthesia is quite safe these days. But sometimes putting a patient under to fix one problem, such as heart damage, can harm a different organ, such as a kidney.
Now a group of researchers led by Holger Eltzschig, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology at the University Colorado School of Medicine, has found a group of molecules that fend off damage during anesthesia.
"This is a promising discovery," says Eltzschig, who practices at University of Colorado Hospital. "It suggests a new way to promote healing."
In an article published Dec. 12 in the New England Journal ...
Evidence on abortion figures overestimated in Mexico fuels scientific debate in medical journal
2012-12-18
This press release is available in Spanish.
A detailed letter entitled “Methodological flaws in the estimation of abortion in Latin America: Author’s reply to Singh and Bankole” was published today in Ginecología y Obstetricia de México (Ginecol Obstet Mex), a Mexican peer-reviewed journal specialized in Obstetrics and Gynecology. The letter is a reply by researchers from the Institute of Molecular Epidemiology (MELISA) to researchers from the Alan Guttmacher Institute (AGI) regarding methodological flaws that led to a significant overestimation of induced abortions ...
Hass Avocado Board study published in Food & Function journal
2012-12-18
IRVINE, Calif. (December 18, 2012) – The Hass Avocado Board (HAB) is supporting research to improve understanding of the unique, positive benefits of consuming fresh avocados to human health and nutrition. Clinical studies are currently underway to investigate the relationship between avocado consumption and risk factors for cardiovascular disease, avocados' potential positive role in weight management and diabetes, and avocados' ability to enhance nutrient absorption. In November 2012, the first study supported by the HAB and conducted by researchers at the University ...
Survival of the females
2012-12-18
Because of the process involved in the formation of sperm cells, there should be an equal chance that a mammalian egg will be fertilized by "male" sperm, carrying a Y chromosome, as by a "female" sperm, carrying an X chromosome. The symmetry of the system ensures that roughly the same number of males and females are born, which is clearly helpful for the species' long-term survival.
Surprisingly, though, many mammals do not produce equal numbers of male and female offspring. The discrepancy could theoretically be explained by differential fertilization efficiencies ...
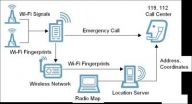
KAIST announces a major breakthrough in high-precision indoor positioning
2012-12-18
Daejeon, Republic of Korea, December 18th, 2012—Cell phones are becoming ever smarter, savvy enough to tell police officers where to go to find a missing person or recommend a rescue team where they should search for survivors when fire erupts in tall buildings. Although still in its nascent stages, indoor positioning system will soon be an available feature on mobile phones.
People widely rely on the Global Positioning System (GPS) for location information, but GPS does not work well in indoor spaces or urban canyons with streets cutting through dense blocks of high-rise ...
Silent stroke can cause Parkinson's disease
2012-12-18
Scientists at The University of Manchester have for the first time identified why a patient who appears outwardly healthy may develop Parkinson's disease.
Whilst conditions such as a severe stroke have been linked to the disease, for many sufferers the tremors and other symptoms of Parkinson's disease can appear to come out of the blue. Researchers at the university's Faculty of Life Sciences have now discovered that a small stroke, also known as a silent stroke, can cause Parkinson's disease. Their findings have been published in the journal "Brain Behaviour and Immunity".
Unlike ...
Prehistoric ghosts revealing new details
2012-12-18
Scientists at The University of Manchester have used synchrotron-based imaging techniques to identify previously unseen anatomy preserved in fossils.
Their work on a 50 million year old lizard skin identified the presence of teeth (invisible to visible light), demonstrating for the first time that this fossil animal was more than just a skin moult. This was only possible using some of the brightest light in the universe, x-rays generated by a synchrotron.
Dr Phil Manning, Dr Nick Edwards, Dr Roy Wogelius and colleagues from the Palaeontology Research group used Synchrotron ...
Research finds crisis in Syria has Mesopotamian precedent
2012-12-18
Research carried out at the University of Sheffield has revealed intriguing parallels between modern day and Bronze-Age Syria as the Mesopotamian region underwent urban decline, government collapse, and drought.
Dr Ellery Frahm from the University of Sheffield's Department of Archaeology made the discoveries by studying stone tools of obsidian, razor-sharp volcanic glass, crafted in the region about 4,200 years ago.
Dr Frahm used artefacts unearthed from the archaeological site of Tell Mozan, known as Urkesh in antiquity, to trace what happened to trade and social networks ...
pH measurements: How to see the real face of electrochemistry and corrosion?
2012-12-18
For several decades antimony electrodes have been used to measure the acidity/basicity – and so to determine the pH value. Unfortunately, they allow for measuring pH changes of solutions only at a certain distance from electrodes or corroding metals. Researchers at the Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences developed a method for producing antimony microelectrodes that allow for measuring pH changes just over the metal surface, at which chemical reactions take place.
Changes in solution acidity/basicity provide important information on the nature ...
Patients with diabetes may not receive best treatment to lower heart disease risk
2012-12-18
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — For some people with diabetes, there may be such a thing as too much care.
Traditional treatment to reduce risks of heart disease among patients with diabetes has focused on lowering all patients' blood cholesterol to a specific, standard level. But this practice may prompt the over-use of high-dose medications for patients who don't need them, according to new research from the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) and the University of Michigan Health System.
The study encourages a more individualized approach to treatment that adjusts treatment ...
Way to make one-way flu vaccine discovered by Georgia State researcher
2012-12-18
A new process to make a one-time, universal influenza vaccine has been discovered by a researcher at Georgia State University's Center for Inflammation, Immunity and Infection and his partners.
Associate Professor Sang-Moo Kang and his collaborators have found a way to make the one-time vaccine by using recombinant genetic engineering technology that does not use a seasonal virus.
Instead, the new vaccine uses a virus' small fragment that does not vary among the different strains of flu viruses.
By using the fragment and generating particles mimicking a virus in ...
Southampton researchers find a glitch' in pulsar 'glitch' theory
2012-12-18
Researchers from the University of Southampton have called in to question a 40 year-old theory explaining the periodic speeding up or 'glitching' of pulsars.
A pulsar is a highly magnetised rotating neutron star formed from the remains of a supernova. It emits a rotating beam of electromagnetic radiation, which can be detected by powerful telescopes when it sweeps past the Earth, rather like observing the beam of a lighthouse from a ship at sea.
Pulsars rotate at extremely stable speeds, but occasionally they speed up in brief events described as 'glitches' or 'spin-ups'. ...
Women earn more if they work in different occupations than men
2012-12-18
Women earn less money than men the more the sexes share the same occupations, a large-scale survey of 20 industrialised countries has found.
Researchers from the universities of Cambridge, UK, and Lakehead, Canada, found that the more women and men keep to different trades and professions, the more equal is the overall pay average for the two sexes in a country.
The researchers attribute the surprising results to the fact that when there are few men in an occupation, women have more chance to get to the top and earn more. But where there are more equal numbers of ...
Visions of snowflakes: An American Chemical Society holiday video
2012-12-18
WASHINGTON, Dec. 18, 2012 — For everyone with holiday visions of snowflakes dancing in their heads, the American Chemical Society, the world's largest scientific society, today issued a video explaining how dust, water, cold and air currents collaborate to form these symbols of the season. It's all there in an episode of Bytesize Science, the award-winning video series produced by the ACS Office of Public Affairs at www.BytesizeScience.com.
The video tracks formation of snowflakes from their origins in bits of dust in clouds that become droplets of water falling to Earth. ...
Mistaking OCD for ADHD has serious consequences
2012-12-18
On the surface, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) appear very similar, with impaired attention, memory, or behavioral control. But Prof. Reuven Dar of Tel Aviv University's School of Psychological Sciences argues that these two neuropsychological disorders have very different roots — and there are enormous consequences if they are mistaken for each other.
Prof. Dar and fellow researcher Dr. Amitai Abramovitch, who completed his PhD under Prof. Dar's supervision, have determined that despite appearances, OCD and ACHD ...
Spread of cancer cells may be slowed by targeting of protein
2012-12-18
HERSHEY, Pa.--The spread of cancer cells may be slowed by targeting the protein km23-1, according to researchers at Penn State College of Medicine.
A motor protein that transports cargo within the cell, km23-1 is also involved in the movement or migration of cells. Migration is necessary for cancer to spread, so understanding this cell movement is important for development of better cancer treatments.
Kathleen Mulder, Ph.D., professor, biochemistry and molecular biology, looked for partner proteins that bind to and cooperate with km23-1 during cell movement, which ...
UNC researchers discover how hepatitis C virus reprograms human liver cells
2012-12-18
Chapel Hill, NC – CHAPEL HILL – Hepatitis C virus has evolved to invade and hijack the basic machinery of the human liver cell to ensure its survival and spread. Researchers at the University of North have discovered how hepatitis C binds with and repurposes a basic component of cellular metabolism known as a microRNA to help protect and replicate the virus.
In a paper published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Dec. 17, researchers in the laboratory of Stanley M. Lemon, MD, professor of medicine and microbiology and immunology and member of ...
Long-terms benefits follow brain surgery for certain forms of epilepsy
2012-12-18
DETROIT – Brain surgery for certain difficult forms of epilepsy often reduces or eliminates seizures for more than 15 years after the procedure, according to new research by neurologists at Henry Ford Hospital.
Drugs are not effective in controlling seizures in 30 out of 100 people with epilepsy, and resective surgery is the most common alternative treatment. During resective surgery, the portion of the brain responsible for the seizures is removed, usually reducing their frequency and sometimes eliminating them.
"Our study shows that a significant number of patients ...
Long-term survival after less-invasive repair of abdominal aneurysm same as with 'open' procedure
2012-12-18
Despite earlier signs that a less-invasive surgery is safer and better than "open" operations to repair potentially lethal abdominal aortic aneurysms, a study led by a Johns Hopkins professor shows survival rates after four years are similar for both procedures.
In an extended follow-up of patients in the OVER (Open Versus Endovascular Repair) Trial, researchers found that, contrary to expectations, the two procedures carried about the same long-time survival after four years, even though survival was higher in the endovascular group at the two-year mark. Moreover, among ...
Reproductive Health Matters announces publication of its themed issue
2012-12-18
Amsterdam, December 18, 2012 - Sexual and reproductive morbidities are not a priority in health policy. They do not feature among donors favourite health initiatives and remain outside the global health agenda. In many parts of the world practice is stubbornly failing to catch up with national policies, leaving shortfalls in every area of care. This, despite the enormous impact such morbidities have on the lives of women, men and their families, is something that is illustrated in a number of papers published in the latest issue of Reproductive Health Matters (RHM) which ...
Evidence insufficient to recommend routine antibiotics for joint replacement patients
2012-12-18
Rosemont, Ill. - The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), and the American Dental Association (ADA) found that there is insufficient evidence to recommend the routine use of antibiotics for patients with orthopaedic implants to prevent infections prior to having dental procedures because there is no direct evidence that routine dental procedures cause prosthetic joint infections.
The AAOS and ADA's recommendations are based on a collaborative evidence-based clinical practice guideline that focuses on the possible linkage between orthopaedic implant infection ...
Study of pipestone artifacts overturns a century-old assumption
2012-12-18
CHAMPAIGN, lll. — In the early 1900s, an archaeologist, William Mills, dug up a treasure-trove of carved stone pipes that had been buried almost 2,000 years earlier. Mills was the first to dig the Native American site, called Tremper Mound, in southern Ohio. And when he inspected the pipes, he made a reasonable – but untested – assumption. The pipes looked as if they had been carved from local stone, and so he said they were. That assumption, first published in 1916, has been repeated in scientific publications to this day. But according to a new analysis, Mills was wrong.
In ...
Researchers use liquid metal to create wires that stretch 8 times their original length
2012-12-18
Researchers from North Carolina State University have created conductive wires that can be stretched up to eight times their original length while still functioning. The wires can be used for everything from headphones to phone chargers, and hold potential for use in electronic textiles.
To make the wires, researchers start with a thin tube made of an extremely elastic polymer and then fill the tube with a liquid metal alloy of gallium and indium, which is an efficient conductor of electricity.
"Previous efforts to create stretchable wires focus on embedding metals ...
Reappraisal defuses strong emotional responses to Israel-Palestine conflict
2012-12-18
Reappraisal is a widely-used cognitive strategy that can help people to regulate their reactions to emotionally charged events. Now, new research suggests that reappraisal may even be effective in changing people's emotional responses in the context of one of the most intractable conflicts worldwide: the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
"Negative intergroup emotions play a crucial role in decisions that perpetuate intractable conflicts," observes lead researcher Eran Halperin of the New School of Psychology at the Interdisciplinary Center in Israel.
With this in mind, ...
[1] ... [5471]
[5472]
[5473]
[5474]
[5475]
[5476]
[5477]
[5478]
5479
[5480]
[5481]
[5482]
[5483]
[5484]
[5485]
[5486]
[5487]
... [8825]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.