NASA sees 'hot towers' in intensifying Typhoon Bopha
2012-12-01
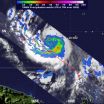
Bopha intensified into a typhoon today, Nov. 30, as it continues to affect the islands in Micronesia in the western North Pacific Ocean. NASA's TRMM satellite captured rainfall data of Bopha and noticed "Hot Tower" thunderstorms as it was intensifying from a tropical storm into a typhoon.
When NASA and the Japanese Space Agency's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over Bopha twice on Nov. 29, and the later data showed that the area of heaviest rainfall had expanded and was still south of the center of circulation. The heaviest rainfall was occurring ...
Emerging vector-borne diseases create new public health challenge
2012-12-01
Human activities are advancing the spread of vector-borne, zoonotic diseases such as West Nile virus, Lyme disease and dengue fever, report scientists publishing a series of papers today in the journal The Lancet.
Vector-borne zoonotic diseases result from disease-causing agents or pathogens that naturally infect wildlife, and are transmitted to humans by carriers such as mosquitoes and ticks. In short, they're diseases transmitted between animals and humans.
Widespread land-use change, globalization of trade and travel, and social upheaval are driving the emergence ...
ORNL develops lignin-based thermoplastic conversion process
2012-12-01
Turning lignin, a plant's structural "glue" and a byproduct of the paper and pulp industry, into something considerably more valuable is driving a research effort headed by Amit Naskar of Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
In a cover article published in Green Chemistry, the research team describes a process that ultimately transforms the lignin byproduct into a thermoplastic – a polymer that becomes pliable above a specific temperature. Researchers accomplished this by reconstructing larger lignin molecules either through a chemical reaction with formaldehyde or by washing ...
Preventing 'Cyber Pearl Harbor'
2012-12-01
Cyber attacks that have long caused major work disruption and theft of private information are becoming more sophisticated with prolonged attacks perpetrated by organized groups. In September 2012, Bank of America, Citibank, the New York Stock Exchange, and other financial institutions were targets of attacks for more than five weeks. Defense Secretary Leon E. Panetta warned that the United States was facing the possibility of a "cyber-Pearl Harbor" and was increasingly vulnerable to foreign computer hackers who could disrupt the government, utility, transportation, and ...
NASA's TRMM satellite video reveals 2012 hurricane season rainfall
2012-12-01
The 2012 Atlantic Hurricane season was a busy one as there were 19 tropical cyclones. A new NASA animation using data from the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM shows rainfall from tropical cyclones in the western Atlantic, as measured from space.
The TRMM satellite has now been making highly accurate measurements of rainfall from space for fifteen years since it launched in Nov. 1997. TRMM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japanese space agency, JAXA.
TRMM can be used to calibrate rainfall estimates from other satellites. Those rainfall ...
In schizophrenia patients, auditory cues sound bigger problems
2012-12-01
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and the VA San Diego Healthcare System have found that deficiencies in the neural processing of simple auditory tones can evolve into a cascade of dysfunctional information processing across wide swaths of the brain in patients with schizophrenia.
The findings are published in the current online edition of the journal Neuroimage.
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by disturbed thought processes and difficulty in discerning real from unreal perceptions. Common symptoms include auditory ...
Steroid injection linked with significant bone loss in postmenopausal women treated for back pain
2012-12-01
DETROIT – Postmenopausal women suffered significant bone density loss in their hip after they were treated with an epidural steroid injection for back pain relief, according to a Henry Ford Hospital study
Bone density loss after six months was six times greater when compared to the typical bone density loss seen in a year in a postmenopausal woman who doesn't receive steroid injection, researchers say.
Shlomo Mandel, M.D., a Henry Ford orthopedic physician and the study's lead author, says physicians should exercise caution prescribing an epidural steroid for select ...
Lung cancer patients with pockets of resistance prolong disease control by 'weeding the garden'
2012-12-01
The central skill of cancer is its ability to mutate – that's how it became cancerous in the first place. Once it's started down that path, it's not so difficult for a cancer cell to mutate again and again. This means that different tumors within a single patient or even different areas within the same cancerous deposit may develop different genetic characteristics. This heterogeneity helps cancer escape control by new, targeted cancer therapy drugs.
Two of these targeted drugs are crizotinib and erlotinib – they do wonders for the patients whose cancers depend on the ...
Extended sleep reduces pain sensitivity
2012-12-01
DARIEN, IL – A new study suggests that extending nightly sleep in mildly sleepy, healthy adults increases daytime alertness and reduces pain sensitivity.
"Our results suggest the importance of adequate sleep in various chronic pain conditions or in preparation for elective surgical procedures," said Timothy Roehrs, PhD, the study's principal investigator and lead author. "We were surprised by the magnitude of the reduction in pain sensitivity, when compared to the reduction produced by taking codeine."
The study, appearing in the December issue of the journal SLEEP, ...
Long-term research reveals how climate change is playing out in real ecosystems
2012-12-01
NORTH WOODSTOCK, N.H., December 1, 2012—Around the world, the effects of global climate change are increasingly evident and difficult to ignore. However, evaluations of the local effects of climate change are often confounded by natural and human induced factors that overshadow the effects of changes in climate on ecosystems. In the December issue of the journal BioScience, a group of scientists writing on long-term studies of watershed and natural elevation gradients at the Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest in New Hampshire and in the surrounding region report a number ...
X-ray analysis deciphers master regulator important for skin cancer
2012-12-01
This press release is available in German.
With the X-ray vision of DESY's light source DORIS, a research team from Hamburg and Iceland has uncovered the molecular structure of a master regulator central to the most deadly form of skin cancer, melanoma. The results, published in the scientific journal "Genes & Development", throw new light on the workings of the so-called Microphthalmia-associated Transcription Factor MITF, that is not only connected to skin cancer, but also to a variety of hereditary diseases where the production of the skin pigment melanin is disturbed, ...
How To Discuss Estate Planning With Aging Loved Ones
2012-12-01
How to discuss estate planning with aging loved ones
Dealing with the discussion of inheritance while a loved one is in their old age can sometimes be a challenging and uncomfortable experience. However, there are many reasons why discussing a person's will can be beneficial for all family members in the long run, and conversations about estate plans should not be avoided simply because they might feel awkward.
Elderly family members will have differing responses to the subject of their own estate planning, but there are a number of approaches that you can take to ...
Seventeen-Year-Old Wisconsin Offenders Face Harsh Punishments
2012-12-01
Seventeen-Year-Old Wisconsin Offenders Face Harsh Punishments
Wisconsin is one of 13 states with laws classifying 17-year-olds as adults in their criminal justice systems, producing harsher penalties for minor offenders. Many people are surprised to learn that all 17-year-olds are prosecuted as adults in Wisconsin, because for all other purposes they are not considered adults. Seventeen-year-olds cannot vote, or enter into contracts. Yet they are prosecuted in criminal court -- and that means the court records are open to anyone, including future employers or colleges.
Treating ...
Former NFL Players Take Advantage of California's Workers' Comp Law
2012-12-01
Former NFL Players Take Advantage of California's Workers' Comp Law
The purpose of workers' compensation benefits is to ensure that both replacement wages and medical care are available to those who are injured on the job. And while most people might be familiar with construction workers, teachers and truck drivers filing for benefits, a new group of workers are beginning to take advantage of the system: former players in the National Football League.
Workers' Comp Claims: an Alternative to Concussion Lawsuits?
The NFL is currently facing a great number of lawsuits ...
CCRA Unveils a New Travel Agent Blog Featuring a "Wednesday Rewards" Contest for Agents to Win Prizes
2012-12-01
This month CCRA Travel Solutions - a leading provider of business-related solutions for the travel professional -- is pleased to unveil a new travel agent blog (http://ccratravelagentblog.com) that will feature travel tips and industry insight; travel agent success stories and advice; the latest CCRA agent offerings, and much more. The new blog will also feature a "Wednesday Rewards" contest offering regular opportunities for travel agents to win prizes courtesy of CCRA and its suppliers. This blog was created to become the "go to" place for travel agents ...
Advanced Pension Strategies Expands Financial Services To Greater Los Angeles Area
2012-12-01
Advanced Pension Strategies (http://www.AdvancedPensions.com), a United States based insurance and financial services company is excited to expand into new marketplaces. Initially the company was formed in Los Angeles and has expanded at a rapid pace calling for new locations throughout Southern California. The new business radius covers cities in the Valley all the way to San Diego and out to Riverside. In addition to the office in the City of Los Angeles, Advanced Pension Strategies will also have a presence in Westlake Village, Pasadena and Torrance.
The expanded ...
Occidental Vacation Club Receives RCI Gold Crown Ratings
2012-12-01
Occidental Vacation Club, a division of Occidental Hotels and Resorts (Madrid), has been awarded the coveted RCI Gold Crown rating for 10 of its resorts. The term Gold Crown resort is reserved for the highest standard vacation / timeshare resorts within the Resort Condominiums International (RCI) exchange network. In most cases the RCI Gold Crown Resorts provide the owner the highest trading power within the RCI exchange network. In addition to other ranking qualities, the final Gold Crown designation is achieved only through actual Guest Comments with point ratings that ...
Brookfield to Release Final Phase of Homes at Award-Winning Rockrose Community in Carlsbad this Weekend
2012-12-01
Prospective buyers will get their last chance to own a new eco-savvy home at Rockrose at The Foothills when Brookfield Homes releases the final phase of homes in the Carlsbad community on Saturday, Dec. 1.
The final six homes will be priced from $612,900.
"We've seen increasing interest in the new home market and already have a few families anticipating the release of these final homes at Rockrose," said Debby King, director of marketing for Brookfield Homes. "Our residents have told us they love the community with its resort-like Swim Club; the community's ...
Hotels Take Control of Online Reputation with Opinionmeter's TouchPoint for Hotels
2012-12-01
Most unhappy hotel guests simply want a venue to let management know they are disappointed. If hotel management provides an outlet for the guest to communicate, they will be less likely to search online for a website to complain or post guest reviews. Opinionmeter's new in-room survey system is providing hotels the opportunity to take control of their online reputation and react in real-time to customer complaints.
Here is how TouchPoint for Hotels in-room survey system works:
• Hotel management decides to take control of their online reputation by intervening before ...
Travelers Glow On-The-Go with Newly Launched Sonya Dakar Skincare Jet Set Kits
2012-12-01
Leading luxury brand, Sonya Dakar Skincare, launches five new Jet Set travel kits just in time for holiday travel. Each Jet Set kit includes three of Sonya Dakar Skincare's bestselling products in travel-friendly sizes, available in their Ultraluxe for anti-aging, Clear, Maintenance, and Irritation lines. Complete with a convenient satin carrying case, these FAA approved Jet Set travel kits ensure a smooth landing for every skin type.
"Climate changes, low humidity, and stress are all factors that make skin increasingly vulnerable during travel. However, packing ...
Tax Defense Network PR Explains Tax Debt Resolution
2012-12-01
Tax Defense Network PR has been making efforts to inform taxpayers about how they can resolve their tax debt in the simplest manner possible. Being in the tax industry since 1997, Tax Defense Network is aware of the many problems that taxpayers face while getting their tax debt resolved. Through its PR, Tax Defense Network shares their expertise in tax debt cases, such as Tax Defense Network Explains How to Deal with a Back Tax Debt.
Before a taxpayer applies for an IRS tax debt payment plan, taxpayers must fully understand their case. In tax debt cases where taxpayers ...
Chicago Born Singer-Songwriter And Producer Sijay Creates a Modern Take on Neo Soul with Latest Album Detroit Club
2012-12-01
The epitome of a triple threat, Sijay is a producer, songwriter and mixer. Every note he sings, and every word he writes is meaningful; combining beautifully crafted tones with a rich timbre that eludes even the most experienced singers. His album "Detroit Club" released Tuesday, November 20 by World Stage International Records; will open his audience up to a musical mind shaped as a complex instrument that has been resting in a rich marinade of Neo Soul, R&B, and Jazz.
In celebration of his new album "Detroit Club" and the upcoming holidays, ...
Danforth Center Scientist Elected 2012 Fellow
2012-12-01
Dr. Tom Brutnell director of the Enterprise Rent-A-Car Institute for Renewable Fuels at the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center has been named a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). The election of AAAS Fellows by their peers has been a tradition for more than 130 years and is an honor bestowed upon distinguished persons who are members of the Association. Fellows are recognized for meritorious efforts to advance science or its applications.
Brutnell is being honored for his distinguished contributions to the understanding of C4 ...
Near Field Communications (NFC), Moving Beyond Payments
2012-12-01
NFC and Marketing: Bridging the Gap, an essential Whitepaper for mobile marketers
Vancouver, Wednesday, November 28, 2012: The Whitepaper, a first of its kind in Canada, provides in-depth research, analysis, and case studies on one of the most talked about aspects of mobile marketing: Near Field Communications (NFC). The document is a collaborative project between Gauge Mobile, Newad and Astral Out-Of-Home, and has been made available completely free of charge to the public at http://www.scanvee.com/nfc-white-paper.
"We found that there wasn't a lot of publicly ...
Robert C. Wiegand Named Managing Shareholder and Chief Operating Officer of Godwin Lewis PC
2012-12-01
Texas trial and appellate law firm Godwin Lewis PC is pleased to announce changes to the firm's Executive Committee, effective Dec. 1, 2012.
Robert C. Wiegand has been named the firm's Managing Shareholder, in addition to his existing responsibilities as Chief Operating Officer.
Houston-based Shareholder R. Alan York will assume the responsibilities of firm President. Mr. York previously served as Secretary/Treasurer. Jenny L Martinez will assume the responsibilities of Secretary/Treasurer. Marilea W. Lewis, who became a named shareholder on Nov. 19, will assume ...
[1] ... [5555]
[5556]
[5557]
[5558]
[5559]
[5560]
[5561]
[5562]
5563
[5564]
[5565]
[5566]
[5567]
[5568]
[5569]
[5570]
[5571]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.