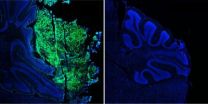
For brain tumors, origins matter
2012-11-14
Cancers arise when a normal cell acquires a mutation in a gene that regulates cellular growth or survival. But the particular cell this mutation happens in—the cell of origin—can have an enormous impact on the behavior of the tumor, and on the strategies used to treat it.
Robert Wechsler-Reya, Ph.D., professor and program director at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute, and his team study medulloblastoma, the most common malignant brain cancer in children. A few years ago, they made an important discovery: medulloblastoma can originate from one of two cell types: ...
Stem cell finding could advance immunotherapy for lung cancer
2012-11-14
CINCINNATI—A University of Cincinnati (UC) Cancer Institute lung cancer research team reports that lung cancer stem cells can be isolated—and then grown—in a preclinical model, offering a new avenue for investigating immunotherapy treatment options that specifically target stem cells.
John C. Morris, MD, and his colleagues report their findings in the Nov. 13, 2012, issue of PLOS One, a peer-reviewed online publication that features original research from all disciplines within science and medicine.
Stem cells are unique cells that can divide and differentiate into ...
New type of bacterial protection found within cells
2012-11-14
Irvine, Calif., Nov. 13, 2012 — UC Irvine biologists have discovered that fats within cells store a class of proteins with potent antibacterial activity, revealing a previously unknown type of immune system response that targets and kills bacterial infections.
Steven Gross, UCI professor of developmental & cell biology, and colleagues identified this novel intercellular role of histone proteins in fruit flies, and it could herald a new approach to fighting bacterial growth within cells. The study appears today in eLife, a new peer-reviewed, open-access journal supported ...
Uranium exposure linked to increased lupus rate
2012-11-14
CINCINNATI—People living near a former uranium ore processing facility in Ohio are experiencing a higher than average rate of lupus, according a new study conducted by scientists at the University of Cincinnati and Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center.
Lupus is a chronic inflammatory disease that can affect the skin, joints, kidneys, lungs, nervous system and other organs of the body. The underlying causes of lupus are unknown, but it is usually more common in women of child-bearing age.
For this new study, a collaborative team of UC and Cincinnati Children's ...
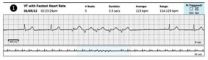
Less of a shock
2012-11-14
Implantable defibrillators currently on the market apply between 600 and 900 volts to the heart, almost 10 times the voltage from an electric outlet, says Ajit H. Janardhan, MD, PhD, a cardiac electrophysiology fellow at the Washington University's School of Medicine.
After being shocked, he says, some patients get post-traumatic stress disorder. Patients may even go so far as to ask their physicians to remove the defibrillator, even though they understand that the device has saved their lives.
The huge shocks are not only unbearably painful, they damage the heart muscle ...
The road to language learning is iconic
2012-11-14
Languages are highly complex systems and yet most children seem to acquire language easily, even in the absence of formal instruction. New research on young children's use of British Sign Language (BSL) sheds light on one of the mechanisms - iconicity - that may endow children with this amazing ability.
For spoken and written language, the arbitrary relationship between a word's form – how it sounds or how it looks on paper – and its meaning is a particularly challenging feature of language acquisition. But one of the first things people notice about sign languages is ...
State of Nuevo León first to benefit from improved nationwide air quality information system
2012-11-14
This press release is available in Spanish and French.
Monterrey, 13 November 2012—Today, the Nuevo León state ministry of sustainable development, with support from the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), launched a revamped air quality information management system in Monterrey, Mexico, using AirNow-International.
This CEC initiative, developed in coordination with Canadian, Mexican and US government agencies, is laying the foundation for improved ways to inform citizens around the country about air quality in their communities with real-time data that ...
NASA sees sun emit a mid-level flare
2012-11-14
On Nov. 13, 2012, the sun emitted a mid-level solar flare, peaking at 9:04 p.m. EST.
Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where Global Positioning System (GPS) and communications signals travel. This disrupts the radio signals for as long as the flare is ongoing, anywhere from minutes to hours.
This flare is classified as an M6 flare. M-class flares are the weakest flares ...
Hinode to support ground-based eclipse observations
2012-11-14
On Nov. 13, 2012, certain parts of Earth will experience a total solar eclipse, which, like all eclipses, will only be visible when you are aligned in a straight line with the moon and the sun. In this case the eclipse will only be seen from a narrow corridor in the southern hemisphere that is mostly over the ocean but also cuts across the northern tip of Australia. The JAXA/NASA Hinode mission will experience a partial eclipse of the sun near the same time as the observers in Australia. Hinode will coordinate its observations with those from the ground, before, during, ...
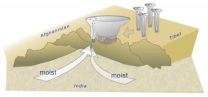
Roots of deadly 2010 India flood identified; Findings could improve warnings
2012-11-14
On the night of Aug. 5, 2010, as residents slept, water began rushing through Leh, an Indian town in a high desert valley in the Himalayas.
Average total rainfall in the area for August is about a half-inch. During this 24-hour period more than 8 inches fell, causing severe damage and leaving 193 dead, hundreds missing and thousands homeless.
"Flash flooding events don't happen often but when they do they are some of the scariest, most dangerous and quickest natural disasters that can happen," said Kristen Rasmussen, a University of Washington graduate student in ...
Increasing efficiency of wireless networks
2012-11-14
RIVERSIDE, Calif. (www.ucr.edu) — Two professors at the University of California, Riverside Bourns College of Engineering have developed a new method that doubles the efficiency of wireless networks and could have a large impact on the mobile Internet and wireless industries.
Efficiency of wireless networks is key because there is a limited amount of spectrum to transmit voice, text and Internet services, such as streaming video and music. And when spectrum does become available it can fetch billions of dollars at auction.
The "spectrum crunch" is quickly being accelerated ...
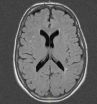
Migraine-associated brain changes not related to impaired cognition
2012-11-14
Women with migraines did not appear to experience a decline in cognitive ability over time compared to those who didn't have them, according to a nine-year follow up study funded by the National Institutes of Health.
The study also showed that women with migraine had a higher likelihood of having brain changes that appeared as bright spots on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a type of imaging commonly used to evaluate tissues of the body.
"The fact that there is no evidence of cognitive loss among these women is good news," said Linda Porter, Ph.D., pain health science ...
First-of-its-kind program improves outcomes for seniors admitted for trauma
2012-11-14
TORONTO, Nov. 13, 2012—A first-of-its-kind program at St. Michael's Hospital lowers risk of delirium in elderly patients admitted for trauma and decreases the likelihood they will be discharged to a long-term care facility.
The Geriatric Trauma Consultation Service is a program where every patient over 60 admitted to the trauma service is seen by a member of the geriatric team within 72 hours.
This is a big change from previous practice, where only 4 per cent of elderly patients admitted to trauma were seen by a geriatric team member during their stay in hospital.
"Older ...
Scientists question the designation of some emerging diseases
2012-11-14
The Ebola, Marburg and Lassa viruses are commonly referred to as emerging diseases, but leading scientists say these life-threatening viruses have been around for centuries.
In a perspective in the Nov. 9 issue of the journal Science, researchers including a professor at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) say it would be more appropriate to refer to these viruses as emerging diagnoses.
"The infectious agents were identified around the middle of the 20th century but that does not mean that they were new," said Joseph McCormick, M.D., ...
Ancient foot massage technique may ease cancer symptoms
2012-11-14
EAST LANSING, Mich. — A study led by a Michigan State University researcher offers the strongest evidence yet that reflexology – a type of specialized foot massage practiced since the age of pharaohs – can help cancer patients manage their symptoms and perform daily tasks.
Funded by the National Cancer Institute and published in the latest issue of Oncology Nursing Forum, it is the first large-scale, randomized study of reflexology as a complement to standard cancer treatment, according to lead author Gwen Wyatt, a professor in the College of Nursing.
"It's always been ...
PCBs, other pollutants may play role in pregnancy delay
2012-11-14
Couples with high levels of PCBs and similar environmental pollutants take longer to achieve pregnancy in comparison to other couples with lower levels of the pollutants, according to a preliminary study by researchers at the National Institutes of Health and other institutions.
PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls) are chemicals that have been used as coolants and lubricants in electrical equipment. They are part of a category of chemicals known as persistent organochlorine pollutants and include industrial chemicals and chemical byproducts as well as pesticides. In many ...
Timing of first menstrual cycle may be predictor of cardiovascular disease risk in women
2012-11-14
Chevy Chase, MD—Age at onset of menarche (first menstrual cycle) is associated with increased body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, and overall obesity in adulthood, according to a recent study accepted for publication in The Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM).
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in women in the United States. When compared to men, women may manifest their clinical disease later in life, rendering standard risk prediction algorithms less reliable in women. The current study uses a life ...
Diabetic patients have higher prevalence of hearing impairment
2012-11-14
Chevy Chase, MD –– Patients with diabetes have a significantly higher prevalence of hearing impairment than patients without diabetes, according to a recent study accepted for publication in The Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM). Study authors note that the finding is likely to be independent of the effect of aging or a noisy environment.
The number of those with impaired hearing more than doubled in the period from 1995 to 2004. Epidemiologically, several health problems in relation to hearing impairment have been reported such ...
BPA shown to disrupt thyroid function in pregnant animals and offspring
2012-11-14
Chevy Chase, MD –– In utero exposure to bisphenol A (BPA) can be associated with decreased thyroid function in newborn sheep, according to a recent study accepted for publication in Endocrinology, a journal of The Endocrine Society. Hypothyroidism is characterized by poor mental and physical performance in human adults and in children can result in cognitive impairment and failure to grow normally.
BPA, a major molecule used in the plastic industry, has been shown to be an endocrine disruptor that could exert deleterious effects on human health. Most investigations have ...
Climate change increases stress, need for restoration on grazed public lands
2012-11-14
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Eight researchers in a new report have suggested that climate change is causing additional stress to many western rangelands, and as a result land managers should consider a significant reduction, or in some places elimination of livestock and other large animals from public lands.
A growing degradation of grazing lands could be mitigated if large areas of Bureau of Land Management and USDA Forest Service lands became free of use by livestock and "feral ungulates" such as wild horses and burros, and high populations of deer and elk were reduced, the ...
Jeff Brown Joins Petey Silveira on New Pathway to Healing Radio Show
2012-11-14
A former criminal lawyer and psychotherapist, Jeff Brown is the author of "Soulshaping: A Journey of Self-Creation," published by North Atlantic Books. Endorsed by authors Elizabeth Lesser and Ram Dass, "Soulshaping" is Brown's autobiography — an inner travelogue of his journey from archetypal male warrior to a more surrendered path.
A frequent inspiration writer for ABC's 'Good Morning America' website, he is also the author of the new quotes book 'Ascending with both feet on the Ground' and the co-producer of the just released spiritual documentary ...
League of Women Voters of Northern Valley in New Jersey to Present Forum on Human Trafficking
2012-11-14
The League of Women Voters of Northern Valley (LWVNV) will present the forum, STOP Human Trafficking Now, a panel discussion on prevention, awareness and advocacy. The forum will take place on Monday, November 19, 7:30 p.m., at the Tenafly Middle School auditorium, located at 10 Sunset Lane in Tenafly, New Jersey.
Co-sponsors of the forum are the Northern New Jersey National Organization for Women, National Organization for Women of New Jersey, and the National Council of Jewish Women Bergen County Section. The event is free and open to the public.
The program will ...
Happy Nails Wins Three Consecutive Talk of the Town Awards for Customer Satisfaction
2012-11-14
With a jump during the past three years to a 4.5-star rating for customer satisfaction, Happy Nails has earned its third straight CMUS Talk of the Town Customer Satisfaction Award in the Beauty & Spas — Nail Salons category.
The Talk of the Town Awards, presented by Talk of the Town News, Customer Care News magazine and Celebration Media U.S. (CMUS), honors companies and professionals that provide excellent customer service as reported by their customers through no-cost, user-review websites, blogs, social networks, business rating services, and other honors and ...
CELI Opens Up a Variety of Services
2012-11-14
Cleverlearn English Language Institute Inc., (CELI) a fast growing international school for English language, takes pride in announcing its growing population and its wide-range services not just in the academe but in accommodation services and other areas as well. With the continuing development of information technology and e-commerce, the company enables to continue establishing a quality of service to their clients most especially to foreign students. The enrichment of technology day by day provides business solutions, makes the business easier and saves a lot of time ...
Summertime Entertainment Releases New Stills of "Dorothy of Oz"
2012-11-14
Summertime Entertainment recently released several new images from its upcoming film "Dorothy of Oz," starring "Glee's" Lea Michele who voices Dorothy Gale. The beloved character is called back to Oz to save Lion, Scarecrow, Tin Man, Glinda, and the other quirky inhabitants of Oz from a new foe.
The new images reveal a few unseen moments from the film including: the Jester (Martin Short) with Glinda (Bernadette Peters) before Dorothy arrives; Dorothy (Lea Michele), Wiser the Owl (Oliver Platt) and Marshal Mallow (Hugh Dancy) in a Candy County courthouse; ...
[1] ... [5635]
[5636]
[5637]
[5638]
[5639]
[5640]
[5641]
[5642]
5643
[5644]
[5645]
[5646]
[5647]
[5648]
[5649]
[5650]
[5651]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.