Screening history, stage at diagnosis, and mortality in screen-detected breast cancer
2025-04-15
About The Study: In this cohort study of older women with screen-detected estrogen receptor–positive or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative breast cancer, prior screening mammography was associated with earlier stage at breast cancer diagnosis and lower breast cancer mortality. These findings support the potential for routine screening to improve breast cancer outcomes. As with all observational studies, this study is limited by the potential effects of other differences between the screening and nonscreening groups.
Corresponding Author: To contact the ...
Pitt researchers release Phage images with unprecedented detail
2025-04-15
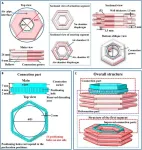
Researchers at Pitt have produced the most detailed image to date of a bacteriophage–phage for short–that has allowed them to see for the first time the structural makeup of the part of the phage that directly attaches to its target Mycobacterium cell.
“Now you've got like a spec sheet for going in and designing phages so that they’ll bind to different kinds of cells,” said Graham Hatfull, the Eberly Family Professor of Biotechnology in the Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences.
That’s important because of what a phage, which is a kind of virus, does after it binds to a bacterial cell: it pierces a hole in the cell membrane and injects ...
Sound wave research for breast cancer receives $5.5 million
2025-04-15
University of Virginia researcher Natasha D. Sheybani, PhD, has received $5.5 million from the federal Department of Defense to support her cutting-edge efforts to use focused sound waves to improve our immune system’s ability to battle breast cancer.
Sheybani, the research director of UVA’s Focused Ultrasound Cancer Immunotherapy Center, was the only scientist in the nation selected to receive a Breast Cancer Research Program Era of Hope Scholar Award in the latest funding round; she is UVA’s first recipient of the award. She will use the grant to advance her research into the potential of focused ultrasound to improve the safety, ...
Gene variant linked to benign prostate hyperplasia risk in Lebanese men
2025-04-15
“Our results indicate a strong association between certain genotypes of the SNP -765 G>C of the PTGS2 gene and BPH.”
BUFFALO, NY – April 15, 2025 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget, Volume 16, on April 4, 2025, titled “Association between two single nucleotide polymorphisms of the Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthase 1 and 2 genes and cell proliferative prostatic diseases in Lebanon.”
The team of researchers led by first author Brock J. Sheehan and corresponding author Ruhul H. Kuddus, from Utah Valley University, discovered that a specific genetic variation ...
Teoxane announces new study reinforcing the biocompatibility, safety and efficacy of RHA®4 in dynamic facial support
2025-04-15
Teoxane reinforces its commitment to scientific innovation with the publication of a new study in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery – Global Open, providing robust preclinical and clinical evidence on the safety, biocompatibility, and performance of RHA®4* in midface augmentation.
The study confirms that RHA®4[1], a resilient hyaluronic acid filler designed for dynamic facial areas[2],[3], integrates harmoniously within subcutaneous adipose tissue, preserving its natural biomechanics while delivering effective volume restoration. ...
Study identifies U.S. hotspots for drinking water quality violations and lack of access to safe, clean water
2025-04-15
Herndon, VA, March 25, 2025 -- About two million people in the United States lack access to running water or indoor plumbing in their homes. Another 30 million people live where drinking water systems violate safety rules. Water privatization -- the transfer of public water systems ownership and/or management to private companies -- has been proposed as a potential solution to provide more Americans with safe, clean drinking water. But opponents argue that private companies may prioritize profits over public needs.
To investigate how ...
Busted! Researchers revolutionize fraud detection with machine learning
2025-04-15
Fraud is widespread in the United States and increasingly driven by technology. For example, 93% of credit card fraud now involves remote account access, not physical theft. In 2023, fraud losses surpassed $10 billion for the first time. The financial toll is staggering: credit card fraud costs $5 billion annually, affecting 60% of U.S. cardholders, while identity theft resulted in $16.4 billion in losses in 2021. Medicare fraud costs $60 billion each year, and government losses range from $233 billion to $521 billion annually, with improper payments totaling $2.7 trillion since 2003.
Machine learning plays a critical ...
Earthworm-inspired multimodal pneumatic continuous soft robot enhanced by winding transmission
2025-04-15
A research paper by scientists at Tianjin University presented an earthworm-inspired multimodal pneumatic continuous soft robot enhanced by wire-winding transmission.
The research paper, published on Mar. 19, 2025 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, proposes an earthworm-inspired multimodal pneumatic continuous soft robot to simultaneously achieve multimodal motion and good motion performance. Using the derived overlapped continuous control law (DOCCL) and wire-winding transmission, the robot can achieve a maximum planar crawling speed that surpasses that of other robots of the same type by an order of magnitude.
With ...
Coastal heritage threatened by climate change
2025-04-15
Humans have always lived by coasts and waterways, and thus these locations are rich with archeological sites. Natural and cultural resource management are conducted separately, despite the fact that climate change, sea level rise, and extreme weather threaten them both. Jayur Mehta and colleagues argue a synergy of both approaches is required to protect coastal archaeological landscapes. The authors used LiDAR digital elevation models, site location data, and NOAA sea level rise models to define ...
A tale of two hummingbird bills
2025-04-15
There are two species of streamertail hummingbirds on the island of Jamaica, West Indies—one with red-billed males (Trochilus polytmus) and the other with black-billed males (T. scitulus). This is a puzzling situation, as many evolutionary biologists have argued that avian speciation is unlikely to occur on small oceanic islands. Caroline Duffie Judy and colleagues investigated the hybrid zone that separates the two species, which is as narrow as 3.2 km. The authors analyzed 186 Trochilus specimens from 12 ...
Corn leads to improved performance in lithium-sulfur batteries
2025-04-15
PULLMAN, Wash.­­ -- Researchers at Washington State University have demonstrated a way to use corn protein to improve the performance of lithium-sulfur batteries, a finding that holds promise for expanding the use of the high-energy, lighter-weight batteries in electric vehicles, renewable energy storage and other applications.
Lithium-sulfur batteries are lighter for the same amount of energy and more environmentally friendly than commonly used lithium-ion batteries, but their commercial adoption has been limited by technological hurdles that shorten their lifespan.
The WSU team’s research, published in the Journal of Power Sources, ...
SynGAP Research Fund (SRF), dba Cure SYNGAP1, announces Board of Trustees Update 2025
2025-04-15
Mill Valley, CA – April 15, 2025 – SynGAP Research Fund (SRF), dba Cure SYNGAP1, the leading patient advocacy group dedicated to improving the lives of those affected by SYNGAP1-related disorders (SRD), today announced the appointment of Jaime Aranda, Steve Gore, Heather Mestemaker, and Brian Smith to its Board of Trustees, effective April 15, 2025. They will succeed outgoing Trustees Emily Barnes, Sydney Stelmaszek, and Stella Tavilla, whose terms conclude on April 14, 2025. Additionally, a seat previously held by Pavel Gerovich, who stepped ...
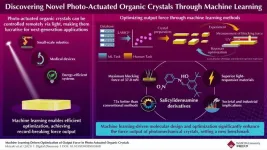
Machine learning unlocks superior performance in light-driven organic crystals
2025-04-15
Materials that convert external stimuli into mechanical motion, known as actuators, play a crucial role in robotics, medical devices, and other advanced applications. Among them, photomechanical crystals deform in response to light, making them promising for lightweight and remotely controllable actuation. Their performance depends on factors such as molecular structures, crystal properties, and experimental conditions.
A key performance indicator of these materials is the blocking force—the maximum force exerted when deformation is completely ...
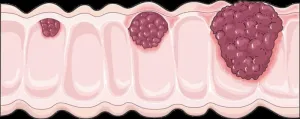
Exploring the mutational landscape of colorectal cancer
2025-04-15
Colorectal cancer (CRC), a type of cancer that affects the large intestine and rectum, is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. The mutational landscape of CRC is well characterized, revealing key pathogenic genetic abnormalities that drive carcinogenesis (cancer development) and disease progression. Moreover, a step-wise colorectal carcinogenesis model has been proposed wherein normal epithelial cells transition to adenoma (non-cancerous tumor) and then to carcinoma (cancerous tumor) as they sequentially acquire genetic mutations.
Mutations ...
Researchers have mapped the hidden control system of vision
2025-04-15
Vision is one of the most complex functions of our brain and requires a seamless interaction between many different brain structures to decode shapes, colours, depths, and movements and turn them into a meaningful whole. Just like other brain functions, vision also depends on a balanced and controlled interaction between the chemical signals that "activate" and "brake" activity in the eye's cells – much like the accelerator and brake of a car. In research, the "brake" is known as GABA, which stands for gamma-aminobutyric ...
Key to the high aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer identified
2025-04-15
Barcelona, 15th April 2025. – Pancreatic cancer is one of the most aggressive cancers and has one of the lowest survival rates—only 10% after five years. One of the factors contributing to its aggressiveness is its tumor microenvironment, known as the stroma, which makes up the majority of the tumor mass and consists of a network of proteins and different non-tumor cells. Among these, fibroblasts play a key role, helping tumor cells to grow and increasing their resistance to drugs. Now, a study led by researchers from the Hospital del Mar Research Institute, IIBB-CSIC-IDIBAPS, ...
How proactive salmon conservation in the North Pacific can deliver global benefits
2025-04-15
April 15, 2025 | Portland, Oregon—A new study in the journal Fisheries shows how a salmon-focused ecosystem protection strategy in the North Pacific can deliver meaningful results in the global drive to protect biodiversity.
The approach, called the stronghold strategy, aims to proactively protect the world’s greatest remaining “strongholds”—a select group of salmon, steelhead, and trout systems that collectively comprise 119 distinct watersheds. According to Wild Salmon Center President & CEO Guido Rahr—lead author of the peer-reviewed study—salmonids center the strategy because they are both iconic and globally recognized ...
Blocking chemokine receptor increases effectiveness of glucocorticoids in multiple myeloma treatment
2025-04-15
Researchers at the VIB-UGent Center for Medical Biotechnology have discovered a promising strategy to improve treatment responses in multiple myeloma patients by blocking a protein that plays a key role in drug resistance. The study, published in Pharmacological Research, offers a potential new strategy to improve outcomes for patients whose disease has become less responsive to standard therapies.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a type of blood cancer that affects the bone marrow. Patients are often treated with dexamethasone, a synthetic glucocorticoid frequently used in the clinic to regulate immune responses and slow cancer growth. However, as the disease progresses, many patients develop ...
Amount of sunlight reaching Earth’s surface varies over decades, researchers report
2025-04-15
The sun may rise every morning, but the amount of sunlight reaching the Earth’s surface can substantially vary over decades, according to a perspectives article led by an international research team. The article, published on March 15 in Advances in Atmospheric Science, suggests that stages of “dimming” and “brightening” correspond with increased air pollution and implementation of clean energy solutions, respectively.
“The amount of sunlight — which is solar ...
Heart valve abnormality is associated with malignant arrhythmias
2025-04-15
People with a certain heart valve abnormality are at increased risk of severe heart rhythm disorders, even after successful valve surgery. This is according to a new study from Karolinska Institutet and Karolinska University Hospital in Sweden published in the European Heart Journal. The condition is more common in women and younger patients with valve disorder and can, in the worst case, lead to sudden cardiac arrest.
Mitral annular disjunction, MAD, is a heart abnormality in which the mitral valve attachment ‘slides’. In recent years, the condition has ...
Explainable AI for ship navigation raises trust, decreases human error
2025-04-15
The Titanic sunk 113 years ago on April 14-15, after hitting an iceberg, with human error likely causing the ship to stray into those dangerous waters. Today, autonomous systems built on artificial intelligence can help ships avoid such accidents, but could such a system explain to the captain why it was maneuvering a certain way?
That’s the idea behind explainable AI, which should help human actors trust autonomous systems more. Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Engineering have developed an explainable AI model for ships that quantifies the collision risk for all vessels ...
Study reveals erasing inequality could prevent hundreds of adverse births annually in major UK city
2025-04-15
In Birmingham, 43% of the population live in the most deprived 10% of neighborhoods in England. It is well known that deprivation can lead to adverse pregnancy outcomes, including low birth weight, premature birth, stillbirths, and neonatal mortality.
Now, researchers there examined the association between demographic, socioeconomic, and lifestyle factors and the risk of adverse birth outcomes in Birmingham and neighboring Solihull, an area much less affected by deprivation.
“Within the study population, there were significant differences in the odds of adverse birth outcomes and the risk factors of adverse birth outcomes by ethnicity ...
No “uncanny valley” effect in science-telling AI avatars
2025-04-15
If you’re among the 1.5 billion people worldwide using TikTok, you may have come across exceptional “testimonials” like Nikola Tesla or Marie Curie delivering short science-related messages that have garnered millions of views. This is just one of many examples where AI-generated avatars are used to communicate science — a strategy that might also have its drawbacks.
The generation of images and animations through artificial intelligence is a rapidly growing field, constantly improving in quality. Yet many avatars, though realistic, still present minor flaws — glitches, delays, inconsistent ...
New UNCG research shows southern shrews shrink in winter
2025-04-15
Newly published research from UNC Greensboro biology professor Dr. Bryan McLean and colleagues shows that the masked shrew, a small, mole-like mammal found in the Appalachian Mountains, shrinks its body and braincase to conserve energy during winter months. The study, published in the May 2025 issue of The American Naturalist, found that the masked shrew (Sorex cinereus) reduces its body mass by 13 percent in the colder months; the creature then grows larger in spring when conditions improve. In addition to a shrinking body, the team also found seasonal changes in the height of the creature’s ...
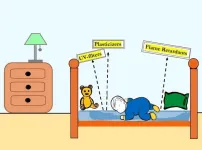
Children exposed to brain-harming chemicals while sleeping
2025-04-15
Babies and young children may breathe and absorb plasticizers called phthalates, flame retardants, and other harmful chemicals from their mattresses while they sleep, according to a pair of peer-reviewed studies published today from the University of Toronto in Environmental Science & Technology and Environmental Science & Technology Letters. These chemicals are linked to neurological and reproductive problems, asthma, hormone disruption, and cancer.
"Sleep is vital for brain development, ...
[1] ... [569]
[570]
[571]
[572]
[573]
[574]
[575]
[576]
577
[578]
[579]
[580]
[581]
[582]
[583]
[584]
[585]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.