USC scientists find a gut-brain link that may affect behavior in children with autism
2025-04-14
A new USC study suggests that gut imbalances in children with autism may create an imbalance of metabolites in the digestive system — ultimately disrupting neurotransmitter production and influencing behavioral symptoms.
The research, published today in Nature Communications, adds to a growing body of science implicating the “gut-brain” axis in autism. The discovery raises the possibility of new treatment avenues. It’s an example of how research at USC, and other universities, drives ...
Pioneering research reveals Arctic matter pathways poised for major shifts amidst climate change
2025-04-14
A new study has shed unprecedented light on the highly variable and climate-sensitive routes that substances from Siberian rivers use to travel across the Arctic Ocean. The findings raise fresh concerns about the increasing spread of pollutants and the potential consequences for fragile polar ecosystems as climate change accelerates.
The international research, published today in Nature Communications and led by the University of Bristol, in the UK, provides the clearest ever picture of how the underlying transport system, known as the Transpolar Draft, operates. It also uncovers the various factors controlling this major Arctic surface current, ...
Scientists may have solved a puzzling space rock mystery
2025-04-14
An international team of researchers may have answered one of space science’s long-running questions – and it could change our understanding of how life began.
Carbon-rich asteroids are abundant in space yet make up less than 5 per cent of meteorites found on Earth.
An international team of scientists from Curtin University’s School of Earth and Planetary Sciences, the International Centre for Radio Astronomy (ICRAR), the Paris Observatory and more scoured the globe to find an answer.
Published today in Nature Astronomy, researchers analysed close to 8500 meteoroids and meteorite impacts, using data from ...
Sleep matters: Duration, timing, quality and more may affect cardiovascular disease risk
2025-04-14
Statement Highlights:
While the strongest evidence exists that getting sufficient sleep (duration of sleep) is important for overall health , other components of sleep health, such as consistent bedtime, uninterrupted sleep, daytime functioning and self-reported sleep satisfaction, also contribute to cardiometabolic health and related risk factors, including heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, inflammation, glucose intolerance, obesity and obstructive sleep apnea.
Differences in sleep health may contribute to increased risk factors and worse health outcomes, particularly for people in under-resourced communities and individuals ...
Light bulb moment for understanding DNA repair switches
2025-04-14
Researchers from the University of Birmingham have uncovered answers that provide the detail to explain two specific DNA repair processes that have long been in question.
The publication of two papers demonstrates how work led by laboratories from the Department of Cancer and Genomic Sciences, and School of Biosciences at the University of Birmingham has made strides in understanding how the repair process is correctly orchestrated.
The importance of understanding DNA repair
Our cells protect their DNA by constantly monitoring and repairing any damage. When DNA is damaged, internal signals activate within the cell to pinpoint the damage and recruit specialised proteins—DNA ...
New method for detecting nanoplastics in body fluids
2025-04-14
Microplastics and the much smaller nanoplastics enter the human body in various ways, for example through food or the air we breathe. A large proportion is excreted, but a certain amount remains in organs, blood and other body fluids. In the FFG bridge project Nano-VISION, which was launched two years ago together with the start-up BRAVE Analytics, a team led by Harald Fitzek from the Institute of Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) and an ophthalmologist from Graz addressed the question of whether nanoplastics also play a role in ophthalmology. The project partners have now been able to develop a method for detecting and quantifying nanoplastics ...
Do disasters delay early cancer diagnoses?
2025-04-14
Rates of colorectal cancer (CRC) diagnoses dropped during and shortly after Hurricanes Irma and Maria and the COVID-19 pandemic in Puerto Rico, according to a recent analysis. However, late-stage diagnoses eventually exceeded expectations, suggesting that limited access to cancer screening services due to these disasters likely hindered timely CRC diagnoses. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
During disasters, medical services may be delayed or inaccessible due to damaged infrastructure, overburdened health ...
Rise and shine: Natural light lessens morning fatigue
2025-04-14
Sleep is a necessary part of people’s daily routine, but modern lifestyles and technology have ushered in an era of decreased rest time and subsequent fatigue. Further, the bedroom environment, such as light, sound, and temperature, is important for a good night's sleep, though this is often neglected in residential architecture.
In search of a conclusive remedy, common sleep studies use artificial light that is easy to control. Osaka Metropolitan University researchers, however, believe natural light could be more effective for re-creating actual living environments.
To test this, Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology student Xiaorui Wang and Professor ...
Nature’s plan for delaying pest resistance deciphered
2025-04-14
Farmers in dozens of countries have embraced crops genetically engineered to produce proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) bacteria that kill some key pests yet are safe for people and wildlife. Although this biotech approach reduces reliance on insecticide sprays thereby providing economic and environmental benefits, resistance to Bt crops has evolved in at least 11 species of pests. Thus, effective ways to combat such pest resistance are urgently needed.
A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences identifies a natural strategy for thwarting pest resistance to Bt proteins. The researchers at the University of Arizona and ...
New guidance for managing obesity in children and adolescents
2025-04-14
A new guideline to help health care providers manage obesity in children and adolescents takes a patient-centred approach, emphasizing behavioural and psychological supports that focus on outcomes valued by patients and their families.
The guidelinehttps://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241456, based on the latest evidence, is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
It was developed by Obesity Canada through an extensive, 4-year-long collaboration involving adolescents and caregivers with lived obesity experience, methodologists, health care providers, and more than 50 multidisciplinary ...
High blood pressure? Eat more bananas
2025-04-14
New research from the University of Waterloo suggests increasing the ratio of dietary potassium to sodium intake may be more effective for lowering blood pressure than simply reducing sodium intake.
High blood pressure affects over 30 per cent of adults globally. It's the leading cause of coronary heart disease and stroke and may also lead to other afflictions like chronic kidney disease, heart failure, irregular heartbeats, and dementia.
"Usually, when we have high blood pressure, we are advised to eat less salt," said Anita Layton, professor of Applied Mathematics, ...
Weak evidence behind how we measure pain in babies
2025-04-14
A newly-published Cochrane review reveals significant gaps in the clinical rating scales used to assess pain in newborn babies, highlighting the urgent need for improved tools and global collaboration.
Despite the critical importance of accurately measuring pain in newborns, the review found that none of the available scales are backed by the high-quality evidence and methodological safeguards required to confirm their validity and reliability in clinical practice.
Neonatal pain assessment and management presents a challenge for clinical staff worldwide. Over 40 rating scales have been developed and adapted worldwide assessing ...
Novel breath test shows promise for diagnosing and monitoring bacterial infections
2025-04-13
This release has been removed upon request of the submitting institution. Please contact Luke Paskins, luke.paskins@beyondpr.com for more information. END ...
AI-guided lung ultrasound marks a major breakthrough in tuberculosis diagnosis
2025-04-13
(Monday, 14 April 2025, Vienna, Austria) A pioneering study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has demonstrated that an AI-powered lung ultrasound outperforms human experts by 9% in diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis (TB).1
The ULTR-AI suite analyses images from portable, smartphone-connected ultrasound devices, offering a sputum-free, rapid, and scalable alternative for TB detection. The results exceed the World Health Organization (WHO) benchmarks for pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis, marking a major opportunity for accessible and efficient TB triage.
Despite previous global declines, TB rates rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023.2 Early ...
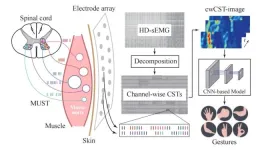
Towards hand gesture recognition using a channel-wise cumulative spike train image-driven model
2025-04-13
A research paper by scientists at Shanghai Jiao Tong University presented a novel channel-wise cumulative spike train image-driven model (cwCST-CNN) for hand gesture recognition.
The research paper, published on Mar. 21, 2025 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, leverage a custom convolutional neural network (CNN) to extract both local and global features for classifying hand gestures, by decomposing high-density surface EMG (HD-sEMG) signals into channel-wise cumulative spike trains (cw-CSTs) ...
Parasitic infection and treatment linked to cancer-related gene activity in the cervix
2025-04-12
Parasitic infection and treatment linked to cancer-related gene activity in the cervix
New research has revealed that Schistosoma haematobium (S. haematobium), a parasitic infection affecting millions globally, can trigger cancer-related gene activity in the cervical lining, with changes becoming even more pronounced after treatment.1 Presented today at ESCMID Global 2025, this pivotal study sheds new light on how this often-overlooked parasitic disease may contribute to cervical cancer risk at the molecular level.
Schistosomiasis is a widespread parasitic disease, particularly prevalent in regions with poor access to clean water and sanitation.2 ...
Over 3 million children died from AMR-related infections in 2022, major study shows
2025-04-12
A landmark study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has revealed that over 3 million children worldwide lost their lives in 2022 due to antimicrobial resistance (AMR)-related infections.1
The study underscores the urgent need for both regional and global strategies to control paediatric AMR, particularly in high-burden areas such as South-East Asia and Africa. AMR poses a critical threat to children, who are highly vulnerable to infections.2 Access to new antibiotic formulations is often much more limited for children because of product development delays.
The study data found ...
Study estimates proportion of adolescents living with overweight and obesity in England has increased by 50% between 2008 and 2023
2025-04-12
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2025, Malaga, Spain, 11-14 May) shows that the proportion of adolescents living with overweight or obesity in England has increased by 50% from 2008-2010 (22%) to 2021-2023 (33%). The research, presented in two studies, is by Dr Dinesh Giri, Consultant Paediatric Endocrinologist, Bristol Royal Hospital for Children and Honorary Senior Lecturer, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK, and Dr Senthil Senniappan, Consultant Paediatric Endocrinologist, Alder Hey Children’s Hospital, Liverpool, UK, and colleagues.
Previous ...
Welcome to the First International Conference on Cyborg and Bionic Systems
2025-04-12
The First International Conference on Cyborg and Bionic Systems (ICCBS 2025) will be held in Singapore, Republic of Singapore, from July 24 to July 26, 2025. This conference aims at providing a free, open, and diverse platform for experts, scholars, students and industry professionals from the fields of robotics, biomedical engineering, neural engineering, and related domains. The sponsor of the conference is Beijing Institute of Technology, and the organizer of the conference is the Journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems.
We look forward to welcoming experts, scholars and industry leaders from around ...
Breakthrough study identifies promising biomarker for early sepsis detection in neonates, children, and pregnant women
2025-04-11
Breakthrough study identifies promising biomarker for early sepsis detection in neonates, children, and pregnant women
A pioneering study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has uncovered the potential of interleukin-6 (IL-6) as a powerful diagnostic biomarker for the early detection of sepsis in high-risk patient groups, including neonates, children and pregnant women. This study is the first to evaluate IL-6’s diagnostic performance in a real-world cohort across all three populations.1
Sepsis, a life-threatening condition resulting from the immune system’s overreaction to infection, remains a leading global cause of mortality, accounting ...
3-year study of tirzepatide shows that most patients only gain 5% or less from their lowest or ‘nadir’ weight
2025-04-11
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2025, Malaga, Spain, 11-14 May) shows that around two thirds of participants of the SURMOUNT-1 trial had only regained 5% or less of their so-called nadir (or lowest weight) three years after beginning treatment with tirzepatide. The study is by Professor Louis Aronne, Comprehensive Weight Control Center, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA, and co-authors from Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN, USA, which funded the study.
Obesity management is a long-term journey during which fluctuations ...
Tirzepatide can produce clinically meaningful weight loss for at least 3 years in adults with overweight or obesity who don’t have diabetes
2025-04-11
Once-weekly treatment with tirzepatide can produce clinically meaningful and sustained weight loss for at least 3 years in adults with overweight or obesity who do not have diabetes, according to new research being presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Malaga, Spain (11-14 May). The findings also indicate that females and those without obesity-related complications may be more responsive to tirzepatide treatment.
The study, led by Dr Luca Busetto from the University of Padova in Italy and colleagues from Eli Lilly and Company that manufacture tirzepatide, is a continuation of the SURMOUNT-1 phase 3 trial of tirzepatide, a medication approved in ...
Common respiratory condition nearly triples the risk of death in adults, new study finds
2025-04-11
Common respiratory condition nearly triples the risk of death in adults, new study finds
A major study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has revealed that adults with respiratory syncytial virus-associated acute respiratory infection (RSV-ARI) face a 2.7-fold higher risk of death within one year compared to the general population.1
The findings underscore the significant, yet often under-recognised, long-term health and economic burden of RSV-ARI in adults, particularly among those with underlying conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma.
RSV-ARI refers ...
New research shows evidence of children’s gender biases reflected in their facial emotional expressions
2025-04-11
New research recently published in Archives of Sexual Behavior suggests children’s gender biases can be reflected in their facial emotional expressions.
Psychology professor Doug VanderLaan and his colleagues at the University of Toronto Mississauga, studied 296 children (148 boys and 148 girls) in Canada between the ages of four and nine years old while Wang Ivy Wong, Karen Kwan and their colleagues at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, and The Hong Kong Polytechnic University studied 309 children (155 boys and 154 girls) in Hong Kong. All children watched four short stories that included five illustrations with pre-recorded audio narratives. ...
Crustal brines at an oceanic transform fault
2025-04-11
Woods Hole, Mass. (April 11, 2025) - Being a geophysicist can sometimes feel like being a detective —uncovering clues, and then building a case based on the evidence.
In a new article published in Science Advances, a collaborative team led by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), presents a never-before-seen image of an oceanic transform fault from electromagnetic (EM) data collected at the Gofar fault in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The National Science Foundation funded work reveals ...
[1] ... [572]
[573]
[574]
[575]
[576]
[577]
[578]
[579]
580
[581]
[582]
[583]
[584]
[585]
[586]
[587]
[588]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.