Towards a fully automated approach for assessing English proficiency
2025-04-11
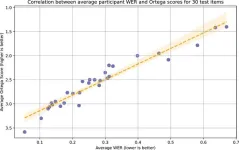
In today’s increasingly interconnected world, language learning has become essential for education, business, and cultural exchange. However, accurately measuring proficiency in language learners is a complex matter. One particularly valuable approach involves asking learners to listen to sentences and then repeat them back as accurately as possible. Known as elicited imitation (EI), this method reveals much more than mere memory and mimicking abilities. When sentences exceed our working memory capacity—typically beyond 8 to 10 syllables—successful repetition requires learners to quickly process and ...
Increase in alcohol deaths in England an ‘acute crisis’
2025-04-10
The persistent higher rate of alcohol deaths in England since the pandemic in 2020 is an “acute crisis” requiring urgent action from government, according to a new study led by researchers at UCL and the University of Sheffield.
For the study, published in Lancet Public Health, researchers analysed Office for National Statistics (ONS) figures of deaths caused solely by alcohol in England. They found that death rates were stable between 2009 and 2019, but increased by a fifth in 2020, rising by a further 13.5% between 2020 and 2022.
The team estimated that 3,911 more people had died solely because of alcohol in England ...
Government urged to tackle inequality in ‘low-carbon tech’ like solar panels and electric cars
2025-04-10
Decarbonisation in the automotive and housing sectors is paramount if the UK’s legally binding commitment to achieving net zero by 2050 is to succeed, say researchers at University of Sheffield
Exploring the presence of socioeconomic inequalities in the uptake of low-carbon technologies (LCTs), such as solar panels and electric vehicles, has important policy implications for the decarbonisation in the UK
The new report advocates for interventions at an individual, as well as community-level, to help those from more disadvantaged backgrounds adopt technologies that ...
Moffitt-led international study finds new drug delivery system effective against rare eye cancer
2025-04-10
TAMPA, Fla. (Apr. 10, 2025) — A multi-institutional study led by Moffitt Cancer Center found that percutaneous hepatic perfusion using a melphalan hepatic delivery system may help patients with a rare eye cancer that has spread to their liver. This disease, known as metastatic uveal melanoma, is traditionally very hard to treat and usually has poor outcomes.
The phase 3 FOCUS trial, published in the Annals of Surgical Oncology, compared two treatments for metastatic uveal melanoma. One group of patients received the melphalan hepatic delivery system treatment, while the other group received standard of care treatment. Patients treated with the melphalan hepatic delivery ...
Boston stroke neurologist elected new American Academy of Neurology president
2025-04-10
MINNEAPOLIS —The American Academy of Neurology (AAN), the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, has elected Natalia S. Rost, MD, MPH, FAAN, FAHA, as its 39th president. Rost is professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School in Boston, and the C. Miller Fisher Endowed Chair in Stroke Research and former chief of the stroke division at Massachusetts General Hospital. Rost succeeds Carlayne E. Jackson, MD, FAAN, who completed her two-year term as president during the recent AAN Annual Meeting.
“I applaud Dr. Jackson for her leadership, and I am thrilled to take the helm at the American Academy of Neurology ...
Center for Open Science launches collaborative health research replication initiative
2025-04-10
Charlottesville, VA — The Center for Open Science (COS) has announced the launch of the Replicability Project: Health Behavior (RPHB), a collaborative initiative that aims to strengthen the evidence base and advance scientific integrity in health-related research. The project will examine the replicability of a diverse sample of quantitative health studies published over the past decade (2015–2024).
Assessing the credibility of research is essential to advancing scientific integrity and maintaining public trust in science. The RPHB initiative aims to perform up to 60+ replications of empirical health behavior studies, providing crucial ...
Crystal L. Mackall, MD, FAACR, recognized with the 2025 AACR-Cancer Research Institute Lloyd J. Old Award in Cancer Immunology
2025-04-10
CHICAGO – The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)-Cancer Research Institute (CRI) Lloyd J. Old Award in Cancer Immunology will be presented to Crystal L. Mackall, MD, Fellow of the AACR Academy, during the AACR Annual Meeting 2025, to be held April 25-30 at the McCormick Place Convention Center in Chicago, Illinois.
Mackall is the Ernest and Amelia Gallo Family Professor and Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine at Stanford University, the founding director of the Stanford Center for Cancer Cell Therapy, and director of the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at Stanford. She is being honored for her illustrious contributions to cancer immunotherapy, including ...
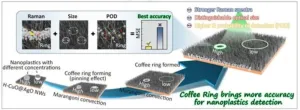
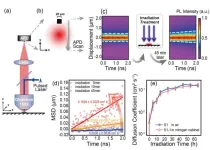
A novel strategy for detecting trace-level nanoplastics in aquatic environments: Multi-feature machine learning-enhanced SERS quantification leveraging the coffee ring effect
2025-04-10
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240260 discusses a novel strategy for detecting trace-level nanoplastics in aquatic environments.
Plastic materials have revolutionized human lifestyles through their versatile applications, yet their environmental legacy now presents critical challenges to global ecosystems and public health. Current models estimate annual plastic influx into aquatic systems at 4.8-12.7 million metric tonnes, with projections suggesting cumulative marine plastic accumulation ...
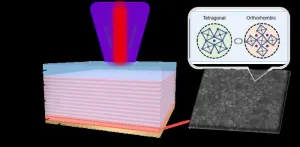
Blending the old and the new: Phase-change perovskite enable traditional VCSEL to achieve low-threshold, tunable single-mode lasers
2025-04-10
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240220, discusses how phase-change perovskite enables traditional VCSEL to achieve low-threshold, tunable single-mode lasers.
As an important light source, lasers are widely used in many fields such as communications, medical treatment, display technology and scientific research. However, with the continuous advancement of technology, people have put forward higher requirements on the performance of lasers, especially in terms of integration and tunability. Traditional lasers typically rely on fixed gain media and external microcavity structures (such as Fabry-Perot cavities, ...
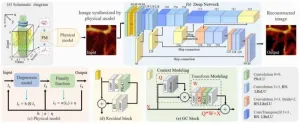
Enhanced photoacoustic microscopy with physics-embedded degeneration learning
2025-04-10
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240189, discusses enhanced photoacoustic microscopy with physics-embedded degeneration learning.
In recent years, photoacoustic imaging (PAI), as an emerging imaging technology, has gradually attracted widespread attention across various fields, particularly in interdisciplinary areas such as medicine, physics, and chemistry. In brief, PAI combines the unique advantages of both optics and acoustics. The fundamental principle of PAI is as follows: when laser light ...
Light boosts exciton transport in organic molecular crystal
2025-04-10
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; 10.29026/oea.2025.240207, discusses how light boosts exciton transport in organic molecular crystal.
Organic semiconductors, composed of organic molecules or polymers, offer advantages such as low cost, flexibility, lightweight design, and tunable structural-functional properties. They have significant applications in OLED displays (e.g., smartphones, TVs), organic photovoltaic cells (flexible solar panels), and flexible sensors. In organic semiconductors, excitons—carriers of excited-state ...
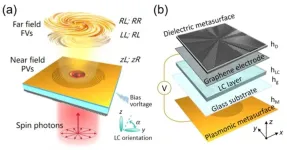
On-chip multi-channel near-far field terahertz vortices with parity breaking and active modulation
2025-04-10
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240250, discusses on-chip multi-channel near-far field terahertz vortices with parity breaking and active modulation.
Vortex beams with helical phase wavefronts can carry orbital angular momentum (OAM) and have promising applications in high-capacity communication, information processing and high-resolution imaging. With the further development of terahertz (THz) technology in the fields of communication, radar and substance detection, ...
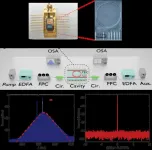
The generation of avoided-mode-crossing soliton microcombs
2025-04-10
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240257 , discusses generation of avoided-mode-crossing soliton microcombs.
Optical frequency combs refer to spectra composed of a series of frequency components that are uniformly spaced, resembling the teeth of a comb, thus the term "optical frequency comb." In recent years, optical frequency combs generated in microresonators (known as microcombs) have attracted significant attention due to their high repetition rates, broad bandwidths, ...
Unlocking the vibrant photonic realm: A new horizon for structural colors
2025-04-10
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Sciences; DOI 10.29026/oes.2025.240030, discusses unlocking the vibrant photonic realm.
Nature not only provides humans with abundant material resources but also offers rich colors, satisfying both material and spiritual needs. The vibrant and diverse colors displayed by peacock feathers, opals, and beetles are all a result of the exquisite structural colors found in nature. The micro- and nanostructures on their surfaces interact with light, producing phenomena such as diffraction, scattering, ...
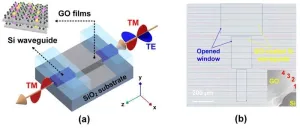
Integrated photonic polarizers with 2D reduced graphene oxide
2025-04-10
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Sciences; DOI 10.29026/oes.2025.240032 , discusses integrated photonic polarizers with 2D reduced graphene oxide.
In modern optical systems, controlling light polarization is of fundamental importance and underpins a variety of advanced optical technologies. Optical polarizers, which selectively transmit light with a specific polarization orientation while blocking light of the orthogonal polarization, are essential components underpinning modern optical systems for a diverse range of applications. The applications are divided into ...
Shouldering the burden of how to treat shoulder pain
2025-04-10
Shoulders are, in many ways, a marvel. One shoulder has four separate joints, packed with muscles, that allow us to move our arm in eight different major ways, giving us the most degrees of freedom of any joint in the body. We can swim, toss, hug, and even punch because of the movement our shoulders enable.
But the same complexity that allows us such motion also presents opportunities for pain when something goes wrong. Another complication: shoulders change as we age, and new types of injuries come with it. Clinical practitioners ...
Stevens researchers put glycemic response modeling on a data diet
2025-04-10
Hoboken, N.J., April 10, 2025 — If you eat a snack — a meatball, say, or a marshmallow — how will it affect your blood sugar? It’s a surprisingly tricky question: the body’s glycemic response to different foods varies based on individual genetics, microbiomes, hormonal fluctuations, and more. Because of that, providing personalized nutritional advice — which can help manage diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases, among other conditions — requires costly and intrusive testing, making it hard to deliver effective care at scale.
In a paper in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, ...
Genotype-to-phenotype map of human pelvis illuminates evolutionary tradeoffs between walking and childbirth
2025-04-10
A combined study on the morphology of the human pelvis – leveraging genetics and deep learning on data from more than 31,000 individuals – reveals genetic links between pelvic structure and function, locomotion, and childbirth outcomes, researchers report. The findings offer fresh insights into how our species evolved to balance the competing demands of bipedalism and childbirth. The transition to bipedalism in hominins led to significant changes in pelvic morphology, including a shorter and wider pelvis, which facilitated an upright posture and efficient locomotion. However, ...
Pleistocene-age Denisovan male identified in Taiwan
2025-04-10
A fossil Pleistocene-age hominin jawbone discovered in Taiwan has now been identified as belonging to a Denisovan, according to a new paleoproteomic analysis of the remains. The findings provide direct molecular evidence that Denisovans occupied diverse climates, from the cold Siberian mountains to the warm, humid subtropical latitudes of Taiwan, and offer new morphological insights into this enigmatic hominin lineage. Recent research has revealed a surprising variety of ancient human relatives that lived in eastern Asia during the Pleistocene before modern humans arrived. One of the most important discoveries is the Denisovans, a distinct group identified through DNA ...
KATRIN experiment sets most precise upper limit on neutrino mass: 0.45 eV
2025-04-10
Researchers from the KATRIN (Karlsruhe Tritium Neutrino) experiment report the most precise measurement of the upper mass limit of the neutrino to date, establishing it as 0.45 electron volts (eV) – less than one-millionth the mass of an electron. The findings tighten the constraints on one of the universe’s most elusive fundamental particles and push the boundaries of physics beyond the Standard Model. Neutrinos – electrically neutral elementary particles – are the most abundant particles in the universe and ...
How the cerebellum controls tongue movements to grab food
2025-04-10
By studying the skilled movements of marmoset tongues, researchers have discovered that Purkinje cells (P-cells) in a brain region called the cerebellum signal to stop protrusion as the tongue approaches its target, according to a study published April 10th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Reza Shadmehr from Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, U.S., and colleagues.
We use our tongue to shape the air and generate sounds to communicate, and we use our tongue to evaluate food morsels and transport them through the oral cavity when eating. These skillful acts involve coordination of more ...
It’s not you—it’s cancer
2025-04-10
Cancer ravages both body and mind. If you’ve ever lost loved ones to the disease, you might recognize the physical and emotional changes cancer patients often endure during their final months. They seem drained of strength and spirit. Even people who’ve maintained a positive outlook throughout their lives can enter a state of despair. New research published in Science suggests apathy and lack of motivation are symptoms of a condition called cancer cachexia. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory ...
Drug pollution alters migration behavior in salmon
2025-04-10
In the largest study of its kind to date, a team of international researchers has investigated how pharmaceutical pollution affects the behaviour and migration of Atlantic salmon.
The study, led by the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, revealed that commonly detected environmental levels of clobazam – a medication often prescribed for sleep disorders – increased the river-to-sea migration success of juvenile salmon in the wild.
The researchers also discovered that clobazam shortened the time it took for juvenile salmon to navigate through two hydropower dams along their migration route – obstacles that typically ...
Scientists decode citrus greening resistance and develop AI-assisted treatment
2025-04-10
In a groundbreaking study published in Science, a research team led by Prof. YE Jian from the Institute of Microbiology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has identified the first mechanism of citrus resistance to citrus greening disease, or huanglongbing (HLB).
Utilizing artificial intelligence (AI), the team has also developed antimicrobial peptides that offer a promising therapeutic approach to combat the disease. This discovery addresses a long-standing challenge in the agricultural community—the absence of naturally occurring HLB-resistant genes in citrus.
Citrus ...
Venom characteristics of a deadly snake can be predicted from local climate
2025-04-10
Local climate can be used to predict the venom characteristics of a deadly snake that is widespread in India, helping clinicians to provide targeted therapies for snake bite victims, according to a study publishing April 10 in the open-access journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases by Kartik Sunagar and colleagues at the Indian Institute of Science.
Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) is found across the Indian subcontinent and is responsible for over 40% of snake ...
[1] ... [579]
[580]
[581]
[582]
[583]
[584]
[585]
[586]
587
[588]
[589]
[590]
[591]
[592]
[593]
[594]
[595]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.