Warwick astronomers discover doomed pair of spiralling stars on our cosmic doorstep
2025-04-04
University of Warwick astronomers have discovered an extremely rare, high mass, compact binary star system only ~150 light years away. These two stars are on a collision course to explode as a type 1a supernova, appearing 10 times brighter than the moon in the night sky.
Type 1a supernovae are a special class of cosmic explosion, famously used as ‘standard candles’ to measure distances between Earth and their host galaxies. They occur when a white dwarf (the dense remnant core of a star) accumulates too much mass, is unable to withstand its own ...
Soil conditions significantly increase rainfall in world’s megastorm hotspots
2025-04-04
Storm forecasting is traditionally based on studying atmospheric conditions but ground-breaking research that also looks at land surface conditions is set to transform early warning systems in tropical regions. This will enable communities to better adapt to the destructive impacts of climate change.
The new study led by the UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (UKCEH) has shown that a large contrast in soil moisture levels over a range of hundreds of kilometres results in atmospheric changes that increase rainfall area and amount in several megastorm hotspots globally. This increase ranges from 10 to 30% depending on the region and size ...
NK cells complexed with bispecific antibody yield high response rates in patients with lymphoma
2025-04-04
A novel cell therapy approach using cord blood-derived natural killer (NK) cells pre-complexed with AFM13, or acimtamig, a CD30/CD16A bispecific antibody, was safe and generated strong response rates for patients with refractory CD30-positive lymphomas, according to a new study from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Results from the Phase I trial, published today in Nature Medicine, demonstrated an overall response rate of 92.9% and a complete response of 66.7% in 42 heavily pretreated patients. These findings ...
Planetary health diet and mediterranean diet associated with similar survival and sustainability benefits
2025-04-04
Milan, Italy – 4 April 2025. Two plant-based diets were associated with similar survival benefits and low environmental impact, according to research presented today at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2025,1 a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).
Diet contributes significantly to cardiovascular disease mortality, with estimates indicating that across the European region, one in every five premature deaths could be prevented by an optimised diet.2
“In 2019, the Planetary Health Diet (PHD) was developed to optimise global dietary quality while keeping the environmental impacts of food production within sustainable planetary ...
Singapore launches national standard to validate antimicrobial disinfectant products
2025-04-04
SS 705 provides a first-of-its-kind Singapore-developed assessment to test the effectiveness of antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral potency, as well as durability of surface disinfectants and coatings.
Enables manufacturers to verify claims, regulators to set baselines and consumers to make safer, more informed choices.
Singapore, 4 April 2025—As public awareness of hygiene and infection control grows in a post-pandemic world, Singapore has launched a strategic national standard to strengthen public health and industry accountability in the rapidly expanding disinfectant market.
Jointly ...
Molecular stool test could improve detection of tuberculosis in adults with HIV
2025-04-04
The Xpert MTB/Ultra molecular diagnostic test for stool samples, until now recommended only for children, could be established as an additional test for diagnosing tuberculosis in adults living with HIV. This is the main conclusion of the Stool4TB Alliance study, led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by the ”la Caixa” Foundation, in collaboration with the Manhiça Health Research Centre (CISM), the Research Center Borstel, the Makerere University, the Baylor College of Medicine Children’s Foundation – Eswatini, ...
Suspected fibrocartilaginous embolus in Asian small-clawed otter (Aonyx cinereus)
2025-04-04
An 11-year-old neutered male Asian small-clawed otter fell down the stairs while sleeping, after which it developed left-sided paralysis. Initial treatment involved once daily administration of prednisolone at 0.5 mg/kg.
Despite slight clinical sign improvements by day 10, paralysis persisted. MRI (T2WI) identified a well-defined, hyper-intense lesion on the left side within the spinal cord at the C2-3 intervertebral level. Based on CT and MRI findings, fibrocartilaginous embolus (FCE) was suspected.
Prednisolone was then tapered and by day 23 of illness, the otter was able to walk ...
Enhancing heat transfer using the turbulent flow of viscoelastic fluids
2025-04-04
Fluids play a crucial role in industrial processes like cooling, heating, and mixing. Traditionally, most industries would utilize Newtonian fluids—which have a constant viscosity—for such processes. However, many are now adopting viscoelastic fluids, which can behave as both liquids and elastic materials. These fluids can suppress turbulence in simple flows like straight pipes or channels, leading to reduced wall friction. This “drag reduction effect” has attracted significant interest due to its potential to enhance energy efficiency.
To advance the industrial applications ...
Exercise as an anti-ageing intervention to avoid detrimental impact of mental fatigue
2025-04-04
Retired people who habitually exercise are more able to fight the impacts of mental fatigue, new research suggests.
In a paper published in the Journal of Aging and Physical Activity, a team of researchers from the University of Birmingham and the University of Extremadura in Spain worked with groups of adults to find out whether age would increase, and regular exercise would decrease the impact of mental fatigue on a series of cognitive and physical performance tests.
In the first study, sedentary men between 65 and 79 performed worse in cognitive and physical tests compared to 52-64 year olds, with these ...
UMass Amherst Nursing Professor Emerita honored as ‘Living Legend’
2025-04-03
Many years ago, Cynthia Jacelon got an entry-level job in a challenging healthcare niche. It became the inspiration for a long, joyful and groundbreaking career in every dimension of nursing – for which she is now being honored.
“I am one of the few people who actually went to nursing school to work with older adults,” explains Jacelon, professor emerita at the Elaine Marieb College of Nursing and senior advisor at the Elaine Marieb Center for Nursing ...
New guidelines aim to improve cystic fibrosis screening
2025-04-03
All states should adopt updated screening protocols so more newborns with cystic fibrosis can be diagnosed in the first weeks of life, when interventions can have the greatest benefit, according to the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation guidelines published April 2 in the International Journal of Neonatal Screening.
Current newborn screening protocols vary across states. Some states use outdated protocols that often miss cases of the inherited disease, especially in newborns with Black, Hispanic and Asian, as well as American Indian and multiracial ancestry, said ...
Picky eaters by day, buffet by night: Butterfly, moth diets sync to plant aromas
2025-04-03
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The scent of blooming flowers and fresh plant life is not just a perk of springtime; it is a key driver in the survival and evolution of butterflies and moths. New research led by scientists at Penn State reveals how the daily cycles of plant aromas are linked to the dietary habits and evolution of the winged insects collectively known as Lepidoptera.
In a recent study published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, an international team of researchers tested a new hypothesis for why some Lepidoptera have very specific diets, feeding on only a few types ...
Pennington Biomedical’s Dr. Leanne Redman honored with the E. V. McCollum Award from the American Society for Nutrition
2025-04-03
The American Society for Nutrition, or ASN, and the ASN Foundation announced the distinguished recipients of the 2025 National Scientific Achievement Awards today. Recognizing outstanding contributions and pioneering advancements in the field of nutrition, these awards serve as a testament to excellence and innovation. Among the honorees is Pennington Biomedical Research Center’s Dr. Leanne Redman, who received the E. V. McCollum Award – given to a clinical investigator who is perceived as a major creative force, actively generating new concepts in nutrition and personally seeing to the execution of studies testing the validity of these concepts.
Dr. Redman is associate ...
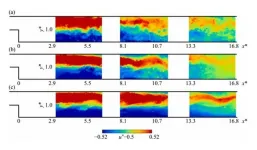
CCNY physicists uncover electronic interactions mediated via spin waves
2025-04-03
Groundbreaking research by physicists at The City College of New York is being credited for a novel discovery regarding the interaction of electronic excitations via spin waves. The finding by the Laboratory for Nano and Micro Photonics (LaNMP) team headed by physicist Vinod Menon could open the door to future technologies and advanced applications such as optical modulators, all-optical logic gates, and quantum transducers. The work is reported in the journal Nature Materials.
The researchers showed the emergence of interaction between electronic excitations (excitons – electron hole pairs) mediated via spin waves in atomically thin (2D) magnets. They demonstrated ...
Researchers’ 3D-printing formula may transform future of foam
2025-04-03
From seat cushions to mattresses to insulation, foam is everywhere — even if we don’t always see it.
Now, researchers at The University of Texas at Dallas have fused chemistry with technology to create a 3D-printed foam that is more durable and more recyclable than the polymer foam found in many everyday products.
The research, which appears in the March 1 print edition of RSC Applied Polymers, a journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry, focused on creating a sturdy but lightweight foam that could be 3D-printed, a method that is still largely unexplored in commercial manufacturing, said the study’s co-lead author, UT Dallas doctoral student Rebecca Johnson ...
Nurture more important than nature for robotic hand
2025-04-03
How does a robotic arm or a prosthetic hand learn a complex task like grasping and rotating a ball? The challenge for the human, prosthetic or robotic hand has always been to correctly learn to control the fingers to exert forces on an object. The sensitive skin and nerve endings that cover our hands have been attributed with helping us learn and adapt our manipulation, so roboticists have insisted on incorporating sensors on robotic hands. But–given that you can still learn to handle objects with gloves on– there must be something else at play.
This mystery is what inspired researchers in the ValeroLab in the Viterbi School of Engineering ...
Drug-delivering aptamers target leukemia stem cells for one-two knockout punch
2025-04-03
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Drug-carrying DNA aptamers can deliver a one-two punch to leukemia by precisely targeting the elusive cancer stem cells that seed cancer relapses, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign report.
The aptamers — short single-strand snippets of DNA that can target molecules like larger antibodies do — not only deliver cancer-fighting drugs, but also are themselves toxic to the cancer stem cells, the researchers said.
Led by Xing Wang, a U. of I. professor of bioengineering and of chemistry, the researchers documented their findings in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
“This ...
New study finds that over 95% of sponsored influencer posts on Twitter were not disclosed
2025-04-03
New INFORMS journal Marketing Science Article Key Takeaways:
Over 95% of sponsored influencer posts on Twitter were not disclosed.
Influencer sponsorship arrangements with younger brands are less likely to be disclosed.
A large number of consumers can’t detect the sponsorship arrangement without disclosure.
The consumer-protection regulatory environment around undisclosed sponsorships has lagged behind.
BALTIMORE, MD, April 3, 2025 – New research in the peer-reviewed journal Marketing Science has found that 95% of influencer posts on Twitter (now X), which are sponsored, are not disclosed.
The ...
New sea grant report helps great lakes fish farmers navigate aquaculture regulations
2025-04-03
DULUTH, Minn.–Fish farmers across the Great Lakes states can face a confusing web of permits, policies and regulations that can hinder the growth of their operations. A new Sea Grant publication, Aquaculture Regulations in the Great Lakes, offers much-needed clarity.
The report breaks down complex legal frameworks and provides practical insights to help aquaculture producers understand and navigate state and regional requirements with greater confidence. It was developed by the National Sea Grant Law Center (NSGLC) ...
Strain “trick” improves perovskite solar cells’ efficiency
2025-04-03
Solar energy is one of the most promising solutions for reducing our dependence on fossil fuels. But making solar panels more efficient is a constant challenge. Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have been a game-changer, offering rapid improvements in efficiency and potential for low-cost manufacturing. However, they still suffer from energy losses and operational stability issues.
The challenge with wide-bandgap perovskites
Perovskite solar cells, particularly those used in tandem configurations, rely on wide-bandgap (WBG) materials—semiconductors that absorb higher-energy ("bluer") ...
How GPS helps older drivers stay on the roads
2025-04-03
How GPS helps older drivers stay on the roads
Peer reviewed – observational study - humans
Sat Nav systems help keep older drivers on the roads for longer, according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published today reveals that over 65s with a poorer sense of direction rely more on help from GPS navigation systems such as Sat Nav or smartphone maps.
Those using GPS tended to drive more frequently - suggesting that the technology helps older people maintain driving independence.
Senior author Prof Michael Hornberger, from UEA’s Norwich Medical School, said: “Driving is usually the preferred mode of transport among ...
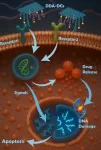
Estrogen and progesterone stimulate the body to make opioids
2025-04-03
Scientists have discovered a new mechanism that acts via an immune cell and points toward a different way of treating chronic pain.
Female hormones can suppress pain by making immune cells near the spinal cord produce opioids, a new study from researchers at UC San Francisco has found. This stops pain signals before they get to the brain.
The discovery could help with developing new treatments for chronic pain. It may also explain why some painkillers work better for women than men and why postmenopausal ...
Dancing with the cells – how acoustically levitating a diamond led to a breakthrough in biotech automation
2025-04-03
Engineers at a University of Bristol spin-out company have created a new technology that can move cells without touching them, enabling critical tasks that currently require large pieces of lab equipment to be carried out on a benchtop device.
The invention could accelerate the discovery of new medicines and unlock personalised medicine screening in clinics.
The groundbreaking concept was unveiled for the first time today in an article in Science published by Dr Luke Cox, where he describes his journey from University of Bristol ...
Machine learning helps construct an evolutionary timeline of bacteria
2025-04-03
University of Queensland scientists have helped to construct a detailed timeline for bacterial evolution, suggesting some bacteria used oxygen long before evolving the ability to produce it through photosynthesis.
The multinational collaboration – led by researchers from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology, the University of Bristol, Queensland University of Technology and UQ – focused on how microorganisms responded to the Great Oxygenation Event (GOE) about 2.33 billion years ago, which changed ...
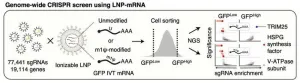
Cellular regulator of mRNA vaccine revealed... offering new therapeutic options
2025-04-03
A team of researchers led by Dr. KIM V. Narry, director of the Center for RNA Research at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), has uncovered a key cellular mechanism that affects the function of mRNA vaccines and therapeutics. Their study, recently published in Science, provides the first comprehensive understanding of how mRNA vaccines are delivered, processed, and degraded within cells—a breakthrough that could pave the way for more effective vaccines and RNA-based treatments.
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is the genetic blueprint that tells cells how to produce proteins. It plays a vital role in mRNA vaccines, such as those used for COVID-19, and is also a promising ...
[1] ... [581]
[582]
[583]
[584]
[585]
[586]
[587]
[588]
589
[590]
[591]
[592]
[593]
[594]
[595]
[596]
[597]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.