Health care practitioner bias and access to inpatient rehabilitation services among survivors of violence
2025-04-08
About The Study: In this mixed-methods qualitative study of hospital patients discharged to rehabilitation centers, significant disparities in denials for admission were observed among survivors of violence, who were disproportionally Black or Hispanic. Stigmatizing language found in medical records suggested that bias within the referral process may have contributed to these disparities. These findings underscore the need for reformed clinical documentation practices and enhanced oversight of ...
Mediterranean diet, physical activity, and bone health in older adults
2025-04-08
About The Study: In the PREDIMED-Plus trial, an energy-reduced Mediterranean diet and physical activity lifestyle intervention mitigated weight loss– and age-related bone mineral density decline among older women with metabolic syndrome compared with conventional ad libitum Mediterranean diet recommendations. Weight-loss lifestyle interventions with longer follow-up are warranted in the future to confirm these results in relation to bone health.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding authors, email Jesús F. García-Gavilán, Ph.D. (jesusfrancisco.garcia@urv.cat), and Jordi Salas-Salvadó, ...
PCORI commits to new patient-centered CER to empower health care decisions
2025-04-08
April 8, 2025
WASHINGTON, D.C. — Every day, millions of Americans make health care decisions without enough information to fully understand the trade-offs between approaches to care and make informed choices for themselves or their families. To help address these information gaps, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) has announced funding for new patient-centered comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER) studies across a range of conditions. These studies will help provide patients and caregivers with the evidence needed to make more informed health and health care decisions and more effectively manage their health.
Research ...
Researchers watch a single catalytic grain do work in real time
2025-04-08
PULLMAN, Wash. – A new way to watch catalytic reactions happen at the molecular level in real time could lead to better fundamental understanding and planning of the important reactions used in countless manufacturing processes every day.
A team of researchers from Washington State University and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) used a new probing technique to look at the surface of iron as it was exposed to oxygen to find out what makes one catalyst work better than another. The work is reported in the journal, Angewandte Chemie. It could eventually help engineers tune reactions better and develop new catalysts ...
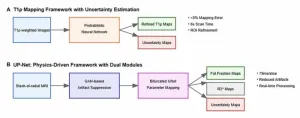
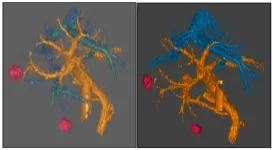
AI that measures its own uncertainty could improve liver cancer detection
2025-04-08
“These advancements, by providing more reliable and efficient diagnostic tools, may significantly impact clinical practice by addressing the ever-growing clinical demand and work pressure, while maintaining interpretability and clinical relevance.”
BUFFALO, NY – April 8, 2025 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget, Volume 16, on April 4, 2025, titled “Deep learning-based uncertainty quantification for quality assurance in hepatobiliary imaging-based techniques.”
Dr. ...
City of Hope study demonstrates proof of concept for targeted new approach to treat pancreatic cancer
2025-04-08
LOS ANGELES — Researchers at City of Hope®, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment organizations in the U.S. with its National Medical Center named top 5 in the nation for cancer by U.S. News & World Report, have identified a new molecular target for treating pancreatic cancer, reports a Gastroenterology study published today.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the deadliest human cancers worldwide because it evades most treatments. With few therapeutic options, 90% of these patients don’t ...
Flex appeal: ‘Trade-off’ between armor and efficiency in sea turtle shells
2025-04-08
When we picture sea turtles in the wild, it’s easy to envision them as armored warriors – their hard, resilient shells serving as near-impenetrable shields against oceanic threats like sharks. These sleek, streamlined shells aren’t just defensive – they’re engineered for speed, efficiency and survival. Designed to minimize drag, they allow sea turtles to glide effortlessly through the water, dive to astonishing depths, and handle the immense pressure shifts as they surface.
A sea turtle’s ...
Spray drying tech used in instant coffee applied to high-capacity battery production
2025-04-08
The Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI) and the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS) have jointly developed the 'spray drying technology-based high-performance dry electrode manufacturing technology' for the realization of high-capacity secondary batteries.
Secondary battery electrodes are made by mixing 'active materials' that store electrical energy, 'conductive additives' that help the flow of electricity, and 'binders' which act as a kind of adhesive. There are two methods for mixing these materials: the 'wet ...
Understanding consumer dynamics in community-supported agriculture in Japan
2025-04-08
Conventional food production and distribution systems degrade the environment due to several aspects, like overuse of fertilizers and high greenhouse gas emissions. This necessitates a shift towards low environmental impact, sustainable food systems like Community-Supported Agriculture (CSA). In CSA, consumers pay producers in advance for their harvest. In this way, farmers get financial stability, and consumers get a chance to engage in farming activities, which ultimately strengthens local food systems.
Despite its benefits, there are few studies on what makes consumers participate in CSA, particularly outside Western countries. Specifically, in Japan, where CSA ...
Cannabidiol therapy could reduce symptoms in autistic children and teenagers
2025-04-08
EMBARGOED UNTIL TUESDAY 8TH APRIL 13:25 CEST
CANNABIDIOL THERAPY COULD REDUCE SYMPTOMS IN AUTISTIC CHILDREN AND TEENAGERS
Tuesday 8th April, 13:25 CEST - New research presented at the 2025 European Congress of Psychiatry reveals that the use of cannabidiol (CBD) cannabis extract can lead to meaningful benefits and improve the behaviour of children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). ASD affects approximately 1 in 100 children around the world and symptoms can include difficulty interpreting language, ...
Do “completely dark” dark matter halos exist?
2025-04-08
Every galaxy is thought to form at the center of a dark matter halo – a region of gravitationally bound matter that extends far beyond the visible boundaries of a galaxy. Stars are formed when gravity within dark matter halos draws in gas, but astrophysicists don’t yet know whether star-free dark matter halos exist.
Now Ethan Nadler, a computational astrophysicist at UC San Diego, has calculated the mass below which halos fail to form stars. This work was done using analytic predictions from galaxy formation theory and cosmological simulations.
"Historically, our understanding of dark matter has been ...
In Guatemala, painted altar found at Tikal adds new context to mysterious Maya history
2025-04-08
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Just steps from the center of Tikal, a 2,400-year-old Maya city in the heart of modern-day Guatemala, a global team of researchers including scholars from Brown University have unearthed a buried altar that could unlock the secrets of a mysterious time of upheaval in the ancient world.
The altar, built around the late 300s A.D., is decorated with four painted panels of red, black and yellow depicting a person wearing a feathered headdress and flanked by shields ...
3 schools win NFL PLAY 60 grants to boost student fitness
2025-04-08
DALLAS, April 8, 2025 — For students to get their health into the endzone, a mix of various cardio and strength exercises that work different parts of the body is ideal for whole body health, according to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. That is why the American Heart Association and the National Football League (NFL), in collaboration with the 32 teams, held the NFL PLAY 60 Exercise Blitz to get students moving leading up to Super Bowl LIX in New Orleans. Three schools, named the national winners of the Exercise Blitz, received $1,000 NFL PLAY 60 grants for improvements to the schools’ physical ...
Urinals without splashback
2025-04-08
A urinal designed to avoid urine splashback on the user and the floor will improve sanitation, bathroom cleanliness, and user experience.
Urinal designs have not materially changed in over a century. The style of urinal that was elevated to the status of artistic landmark by Marcel Duchamp in his 1917 dada art piece “La Fontaine” would not look out of place in today’s public restrooms. Use of a typical public urinal often results in splatter of urine outside the confines of the device—onto the floor and, most unpleasantly, onto the user, a situation that creates costly messes to clean and risks transmitting disease. Zhao Pan, Kaveeshan ...
Even under stress, male-female pairs had each other’s backs
2025-04-08
When faced with a potential threat, mice often freeze in place. Moreover, when two animals are together, they typically freeze at the same time, matching each other’s periods of immobility.
In a new study, researchers found that coordination during fear looks different in males and females — and changes when stress is involved.
Male-female mouse pairs consistently stayed in sync during stressful situations, even when the animals were strangers. Same-sex pairs were more likely to fall out of step.
The findings, published in Biological Psychiatry Global Open Science, suggest that opposite-sex pairs may rely on a more flexible or complex coordination ...
Predictable visual stimuli as an early indicator for autism spectrum disorder in children
2025-04-08
Children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) often experience social communication impairments and engage in restricted and repetitive behaviors (RRBs). Early identification of these symptoms is critical for timely intervention, but detecting RRBs, in particular, remains a challenge. Previous studies using eye-tracking methods have revealed that children with ASD tend to favor non-social stimuli over social ones, a preference that aligns with ASD symptoms. However, the developmental timeline of this preference—especially regarding repetitive versus random movements—remains poorly understood. Research has shown that children with ASD may spend ...
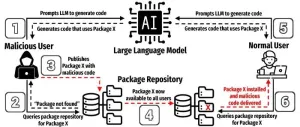
AI threats in software development revealed in new study from The University of Texas at San Antonio
2025-04-08
UTSA researchers recently completed one of the most comprehensive studies to date on the risks of using AI models to develop software. In a new paper, they demonstrate how a specific type of error could pose a serious threat to programmers that use AI to help write code.
Joe Spracklen, a UTSA doctoral student in computer science, led the study on how large language models (LLMs) frequently generate insecure code. His team’s paper has been accepted for publication at the USENIX Security Symposium 2025, a premier cybersecurity ...
Funding to support mental health at work is failing to deliver results
2025-04-08
EMBARGOED UNTIL TUESDAY 8TH APRIL AT 10:30 CEST
FUNDING TO SUPPORT MENTAL HEALTH AT WORK IS FAILING TO DELIVER RESULTS
Tuesday 8th April 2025 – 10:30 CEST - New research presented at the 2025 European Congress of Psychiatry reveals that in the last 25 years, although there has never been this level of funding, guidelines and regulation aimed towards mental health at work, employees are now reporting greater workplace demands and increasingly less control over work deadlines. Many also report that they fear their job will make them ill. These stressors have a stronger negative impact ...
The Lancet: Nearly 500,000 children could die from AIDS-related causes by 2030 without stable PEPFAR programmes, expert policy analysis estimates
2025-04-08
Peer-reviewed/ Review, Analysis and Opinion / People
The Lancet: Nearly 500,000 children could die from AIDS-related causes by 2030 without stable PEPFAR programmes, expert policy analysis estimates
Experts assessed the potential impacts on HIV/AIDS treatment and prevention efforts in sub-Saharan Africa if the US President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) is suspended or only receives limited, short-term funding, estimating that 1 million additional children could become infected with HIV and nearly 500,000 children could ...
Eclipse echoes: groundbreaking study reveals surprising avian vocal patterns during solar eclipse
2025-04-08
A new study published today in Scientific Reports reveals how birds responded to the April 8, 2024, total solar eclipse across North America. The study finds bird vocalizations significantly declined only where more than 99% solar obscuration occurred. Researchers from Loggerhead Instruments, Inc. and the K. Lisa Yang Center for Conservation Bioacoustics at the Cornell Lab of Ornithology analyzed data from 344 community-based acoustic monitoring devices, called Haikuboxes, using a novel neural network approach. Unlike previous studies, ...
Mirvie announces results from largest molecular study in pregnancy and clinical validation of simple blood test to predict risk for preeclampsia months before symptoms
2025-04-08
South San Francisco, CA (April 8, 2025) - Today, Mirvie announced results of a breakthrough study published in Nature Communications, revealing new advances in the biological understanding of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP), including preeclampsia - a leading cause of maternal morbidity and mortality as well as preterm birth. Researchers used data from more than 9,000 pregnancies within the multi-center Mirvie-sponsored Miracle of Life prospective study to discover and validate RNA signatures capable of distinguishing between severe and mild hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, including preeclampsia, months before ...
Eating only during the daytime could protect people from heart risks of shift work
2025-04-08
A study led by researchers at Mass General Brigham suggests that, when it comes to cardiovascular health, food timing could be a bigger risk factor than sleep timing
Numerous studies have shown that working the night shift is associated with serious health risks, including to the heart. However, a new study from Mass General Brigham suggests that eating only during the daytime could help people avoid the health risks associated with shift work. Results are published in Nature Communications.
“Our prior research has shown that circadian misalignment – the mistiming of our behavioral cycle relative to our internal body clock – increases cardiovascular risk factors,” ...
Discovery of mitochondrial protein by researchers at Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University opens path to therapeutic advances for heart and Alzheimer’s disease
2025-04-08
(Philadelphia, PA) – Calcium transport into and out of mitochondria – the powerhouses of cells – is central to cellular energy production and cell death. To maintain the balance of calcium within these powerhouses, cells rely on a protein known as the mitochondrial sodium-calcium exchanger, or NCLX. Now, in new research, scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University have discovered a novel regulator of NCLX activity, a protein called TMEM65, which helps move ...
Recognizing the bridge builders between neuroscience and psychiatry
2025-04-08
Mental health is in crisis worldwide. While the neurosciences are advancing rapidly, psychiatry still struggles to diagnose and effectively treat many disorders. The Synapsy Center for Neuroscience and Mental Health Research at the University of Geneva, Switzerland, is launching a new international prize to reward those who bring these two worlds closer together.
A new research model is needed
Depression, schizophrenia, anxiety or bipolar disorders: psychiatric illnesses affect hundreds of millions of people worldwide and are among the leading causes of disability, suffering and mortality. Yet clinical advances remain limited. Many diagnoses ...
Lactic acid bacteria can improve plant-based dairy alternatives
2025-04-08
A new study maps how specific lactic acid bacteria can enhance both the flavour and nutritional quality of plant-based dairy alternatives. The findings may have wide-reaching perspectives for the further development of sustainable foods.
Plant-based dairy alternatives – such as soy, oat, and almond drinks – are produced without animal ingredients for consumers seeking plant-based substitutes for milk and yoghurt. However, many of these products have the similar shortcomings: flavours that do not always appeal ...
[1] ... [586]
[587]
[588]
[589]
[590]
[591]
[592]
[593]
594
[595]
[596]
[597]
[598]
[599]
[600]
[601]
[602]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.